
Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
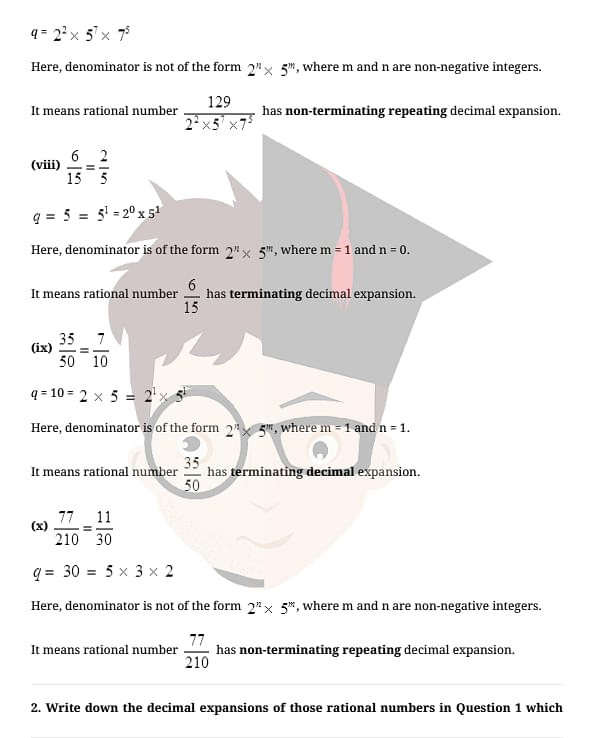
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers Exercise 1.4 deals with the concepts of rational numbers and their decimal expansions. The exercise has 3 short questions of the exercise discussing when the decimal expansion of a rational number is terminating and when it is non-terminating.
Download PDF: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.4
Check out the solutions of Class 10 Maths NCERT solutions chapter 1 Real Numbers Exercise 1.4





Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Real Numbers
Check out other exercise solutions of Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Also Read:
| Class 10 Chapter 1 Real Numbers Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| What are Real Numbers? | Euclid’s division Lemma | Root 2 is an irrational number |
| Real Numbers Important Questions | MCQs for Real Numbers | Real Numbers Formula |
Also Read:
| CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Study Guides | ||
|---|---|---|
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths | Trigonometry | Math Study Notes |
| Math Formula | Mensuration | Arithmetic |
| Calculus | Math MCQs | Difference between in Maths |







Comments