Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Universal Set is a set that contains all related sets and subsets including itself. It is a set that includes the elements of all the related sets, without any repetition.
- Universal Set is denoted by the capital letter ‘U’.
- A set is defined as a well-organized collection of objects or items in Maths.
- The objects or items in a set are referred to as the ‘Elements’ of a set.
- The elements in a Universal Set are not repeated, and thus, are unique.
Example of Universal Set: Consider two sets A = {a, b, c} and B = {1, 2, 3, a, b}. Thus, the Universal Set will be U = {a, b, c, 1, 2, 3}.
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Sets
Key Terms: Universal Set, Sets, Union of Sets, Complement of Sets, Venn Diagram, Natural Numbers, Elements, Finite Set, Subsets
What is a Set?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Set is a well-defined collection of objects or elements. Sets are an integral part of the Set Theory proposed by Georg Cantor, a German mathematician.
- Sets are collections of elements like numbers, letters, etc.
- Elements of a set are the items or objects in a set.
- A set is denoted by a Capital Letter with its elements listed in Curly Brackets as A = {…..}.
- Sets are a crucial component of Mathematical Logic and organization.

Sets can be classified into various types as follows:
- Universal Set
- Empty Set
- Finite and Infinite Sets
- Equal Sets
- Subset
- Power Set
- Singleton Set
- Empty Set
- Disjoint Sets
Read More:
What is Universal Set?
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Universal Set is a set that consists of all the elements of all the related sets. There is no repetition of elements in a Universal Set.
- It is a collection of all elements or members of all the related sets, known as its subsets.
- Universal Set is denoted by the alphabet “U”.
- Consider a set of all Natural Numbers as a Universal Set N.
- Sets of even and odd numbers or prime numbers are subsets of Universal Set N.
Universal Set Definition
Universal Set is defined as a set that contains all the elements or objects of other sets, including its own elements. It is usually denoted by the letter U or E. It can be either a finite or infinite set.
Consider that a Universal Set U consists of Sets A, B, and C. These sets are referred to as Subsets of Universal Set U and are denoted as
- A ⊂ U (A subset of U)
- B ⊂ U (B subset of U)
- C ⊂ U (C subset of U)
Symbol of Universal Set
- Universal Set is denoted by the symbol U or E.
- It is composed of all the elements of its subsets, including its own elements.
Sets Detailed Video Explanation
Complement of Universal Set
There is a complement for every set in Set Theory. An Empty Set is considered to be a complement of a Universal Set.
- Universal set is a set of all elements of all its related subsets.
- Empty set has no elements of the subsets.
- Therefore, an empty set is the complement of a universal set.
- Empty set is also referred to as a Null set and is denoted by ‘{}’ or the symbol 'Φ'.
Universal Set Example
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Universal Set is defined as a larger set that contains elements of all the related sets, without any repetition of elements. Consider a Universal Set N which is a set of Natural Numbers. Now, consider the given sets:
- Set of Even Numbers, A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, …}
- Set of Odd Numbers, B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, …}
So, the Universal Set U consists of all natural numbers which include both even and odd numbers, such that, U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,….}. Thus, Set U is a universal set that has all the elements of Set A and Set B.
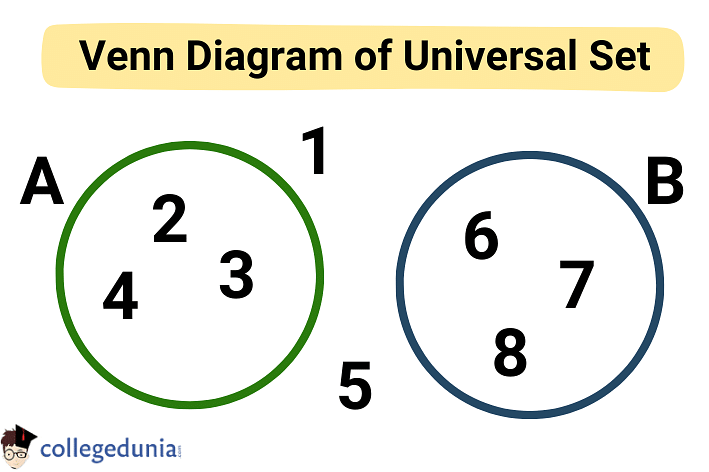
Venn Diagram of Universal Set
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Venn Diagram are used to show the relationship between sets in form of pictorial representation.
- They are basically the graphical representation of Sets.
- Universal Set is represented by a rectangle in Venn Diagrams.
- The subsets are represented by circles or ovals.
Consider a Universal Set U along with its two subsets A and B.
- Universal Set U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}.
- Set A = {2, 3, 4}
- Set B = {6, 7, 8}
Thus, the Venn Diagram of the Universal Set will be as follows:
Check More:
Universal Set and Union of Sets
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There is a persisting confusion between the Union of Sets and the Universal Set.
- Universal Set consists of all the elements or objects, including its own elements.
- Union of Sets is a set operation that results in a set that has all elements belonging to either of the given sets.
- Universal Set is denoted by ‘U’, while Union of Sets is denoted by ‘∪’.
Example: Consider a Universal Set U and two other sets A and B.
- U = {Dog, Cow, Lion}
- A = {1,6,9}
- B = {k,l,h,g}
Universal Set of the given sets will be
U = {1, 6, 9, k, l, h, g, Dog, Cow, Lion}
It includes all the elements of Sets A, B, and the universal set itself.
Union of Sets will be given as
A U B = {1, 6, 9, k, l, g, h}
Union of sets includes the elements of only Sets A and B.
Read More: Sets Important Questions
Difference Between Universal Set and Union of Sets
The difference between Universal Set and Union of Sets is as follows:
| Universal Set | Union of Set |
|---|---|
| Universal Set is a set of all the elements of all related sets, including its own elements. | Union of Sets is a set operation between two sets where the resultant set includes all the elements belonging to both the given sets. |
| It is denoted by the symbol U. | It is denoted by the symbol ∪. (A ∪ B; Read as A union B) |
Things to Remember
- Universal Set is a type of set that includes all the elements of other sets, including its own elements.
- It is a larger set that contains elements of all the related sets, without any repetition.
- Universal Sets are dented by ‘U’ or ‘E’ in Set Theory.
- An Empty Set is the complement of a Universal Set.
- Union of Sets is different from Universal Set as it includes all elements belonging to either set or both.
- Sets are defined as well-organized collections of elements in Maths.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Previous Years’ Questions
- Two sets A and B are as under: A = {(a,b)... (JEE Main - 2018)
- Let A, B, C be finite sets. Suppose that n(A) = 10, n(B) = 15… (BITSAT - 2017)
- If A and B are not disjoint sets, then n(A∪B)...
- If A and B are events such that P(A) = 0.42, P(B) = 0.48 and P(A and B)... (VITEEE - 2018)
- Two finite sets A and B have m and n elements respectively. If… (KEAM)
- The set of all real numbers x for which… (JEE Advanced - 2002)
- Two finite sets have m and n elements. The total number of subsets…
- Two finite sets have m and n elements. The total number…
- In a certain town 25% families own a cell phone, 15% families own… (KEAM)
- In a class of 140 students numbered 1 to 140, all even-numbered students… (JEE Main - 2019)
- If A and B are non-empty sets such that… (KEAM)
- A survey shows that 63% of Americans like cheese where as… (JKCET - 2013)
- If a class of 175 students the following data shows the number… (COMEDK UGET - 2015)
- If a set A has 4 elements, then the total number of proper subsets of set… (COMEDK UGET - 2015)
Sample Questions
Ques. Consider three sets X = {9,6,8}, Y = {1,2,3}, and Z = {10,12,36}. Find out the Universal Set of all three sets X, Y, and Z. (3 Marks)
Ans. Universal Set is defined as a set that includes all the elements of its subsets without any repetition.
Given three sets are:
- X = {9,6,8}
- Y = {1,2,3}
- Z = {10,12,36}
Thus, the universal set will be
U = {1, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 36}
Ques. What is a Universal Set? (3 Marks)
Ans. Universal Set is a set of all the elements or members of all the related subsets. It is usually denoted by the symbol E or U. It contains all the elements or objects of other sets, including its own elements without any repetition.
- For example, assume U = {List of Integers}.
- Here, a set of natural numbers, even numbers, and odd numbers are all subsets of this universal set of integers.
Ques. Three sets are given as A = {10,69,93}, B = {69,3,6}, and C = {10,12,34,93}. Find out the universal set of all three sets named A, B, and C. (3 Marks)
Ans. As we know that a Universal Set is a set that comprises all the elements of its subsets without any repetition.
The given sets are as follows:
- A = {10,69,93}
- B = {69,3,6}
- C = {10,12,34,93}
Therefore, the Universal Set will be
U = {3, 6, 10, 12, 34, 69, 93}
Ques. If X = {Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, Australia}, and Y= {Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian, Antarctic}, then Which of the following could be the Universal Set? (3 Marks)
(a) Oceans
(b) Countries
(c) World
(d) All of the above
Ans. (c) World
Explanation: The First Set is X = {Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, Australia}. This set is denoting the names of the various countries. The Second Set is Y = {Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian, Antarctic} which is denoting the names of the various oceans. Thus, a Universal Set of both these sets will be
U = {Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, Australia, Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, Indian, Antarctic}
This set together represents the world as the world constitutes both oceans and countries.
Ques. If U = {Whole Numbers less than 40} and P = {1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36}, then which of the following sets overlaps with P, and is also a part of U?
(a) Q = {Factor of 36}
(b) R = {Multiple of 4}
(c) Even Primes
(d) All of the above (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) Q = {Factor of 36}
Explanation: It is given that,
- U = {Whole Numbers less than 40}
- P = {1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36}
Factors of 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 36. Thus, it is overlapping Set P and is also a part of U.
Ques. Let U = {2, 4, 5, 14, 17, 28, 35, 52}. Give the following subsets of U:
(a) X = {x: x is divisible by 10}
(b) Y = {y:y is a multiple of 14} (3 Marks)
Ans. (a) X is a set such that the numbers of that set are divisible by 10. Since in the universal set, there is no number divisible by 10, X = {}.
(b) Y is a set such that the numbers of that set are multiples of 14. There are 2 numbers, 14 and 28 which satisfy that criterion. Hence, Y = {14, 28}.
Ques. How to solve Universal Sets? (3 Marks)
Ans. In order to understand how to solve universal sets, consider three sets A, B, and C.
- A = {2, 4, 6}
- B = {1, 3, 7, 9, 11}
- C = {4, 8, 11}
The universal set will consist of all the elements of the given sets. Therefore, the universal set U of A, B, and C is
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11}
All the elements of the three sets are present in the given universal set without any repetition.
Ques. What will be the Universal Set of all Right Triangles? (3 Marks)
Ans. Triangles are closed polygons with three sides and three angles. Triangles can be classified into various types based on their sides and angles. Therefore, the universal set of all right triangles is a Triangle only. It is a set containing all different types of triangles such as equilateral Triangles, isosceles triangles, scalene triangles, acute-angled triangles, right-angled triangles, and obtuse-angled triangles.
Ques. What are the various Set Operations? (2 Marks)
Ans. There are four different types of Set Operations in Set Theory:
- Union of Sets (∪)
- Intersection of Sets (∩)
- Difference of Sets (–)
- Complement of a Set (A' or Ac)
Ques. What is a Singleton Set? (2 Marks)
Ans. Singleton Set is a set in which only one element is present. For example,
Set A = { k | k is an integer between 3 and 5}
Thus, the set will be expressed as A = {2}.
Check-Out:





Comments