
Anjali Mishra Content Writer-SME
Content Writer-SME
Real image and virtual image are two different types of images with different properties. The primary difference between real image and virtual image can be underlined by how these images are generated and which of the two images can be obtained on the screen. A real image is formed by the convergence of light rays while a virtual image is an image that is created by the divergence of light rays.
In other words, real images are formed by a converging lens i.e. concave lens. While the virtual image is created by diverging lens i.e. convex lens. In this article we will learn some major differences between real and virtual image with the help of examples and ray diagrams.
Real Image
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A real image is an image that is formed by the convergence of light rays after getting reflected or refracted through a mirror or a lens.
- For seeing a real image, a screen needs to be placed, so that image can be formed on it.
- To obtain the real image the light source and the screen must be located in the same plane.
- The size of the real image formed is totally dependent on the distance it is placed from the mirror or lens.
- In a real image, light rays actually converge and the proof of this is that the image can be presented on screen.
- After converging at a fixed point, light rays diverge in different directions from that point.
- The difference between a real image and a virtual image is that rays diverge to form real image while it converges to form virtual images.
Example of Real Image FormationA real image is formed when a candle is placed in front of a converging lens. This can be explained as: “When the rays of light travel from the object i.e. candle to the lens and after reaching the lens, they start reflecting. All the light rays will converge at a specific point, after convergence all the light rays will diffract and move in different directions.” |
Ray Diagram of Real Image
The formation of real image is completely different from virtual image which can be understood well with the help of the ray diagram shown below:

Formation of Real Image
Read More:
Virtual Image
[Click Here for Previous year's Questions]
A virtual image is formed by the divergence of light rays after reflecting or refracting from a mirror or lens.
- A virtual image is an imaginary or perceived image, which does not actually exist in real life.
- When light rays strike the mirror, light rays diverge and it is assumed that they are converging somewhere behind the mirror.
- In this case, image can never be presented on screen.
- Thus, the virtual image formed behind the mirror or lens is always virtual and erect..
Example of Virtual Image FormationA virtual image is formed when a candle is placed before a diverging lens which can be explained as: When the rays of light from the object i.e. the candle reach the mirror or lens, they scatter in all directions and a virtual image is formed, which gives the impression of being present somewhere on the other side of the mirror or lens. |
Ray Diagram of Virtual Image
Along with conceptual understanding about image formation, the difference between real and virtual image can also be underlined with the help of ray diagram.
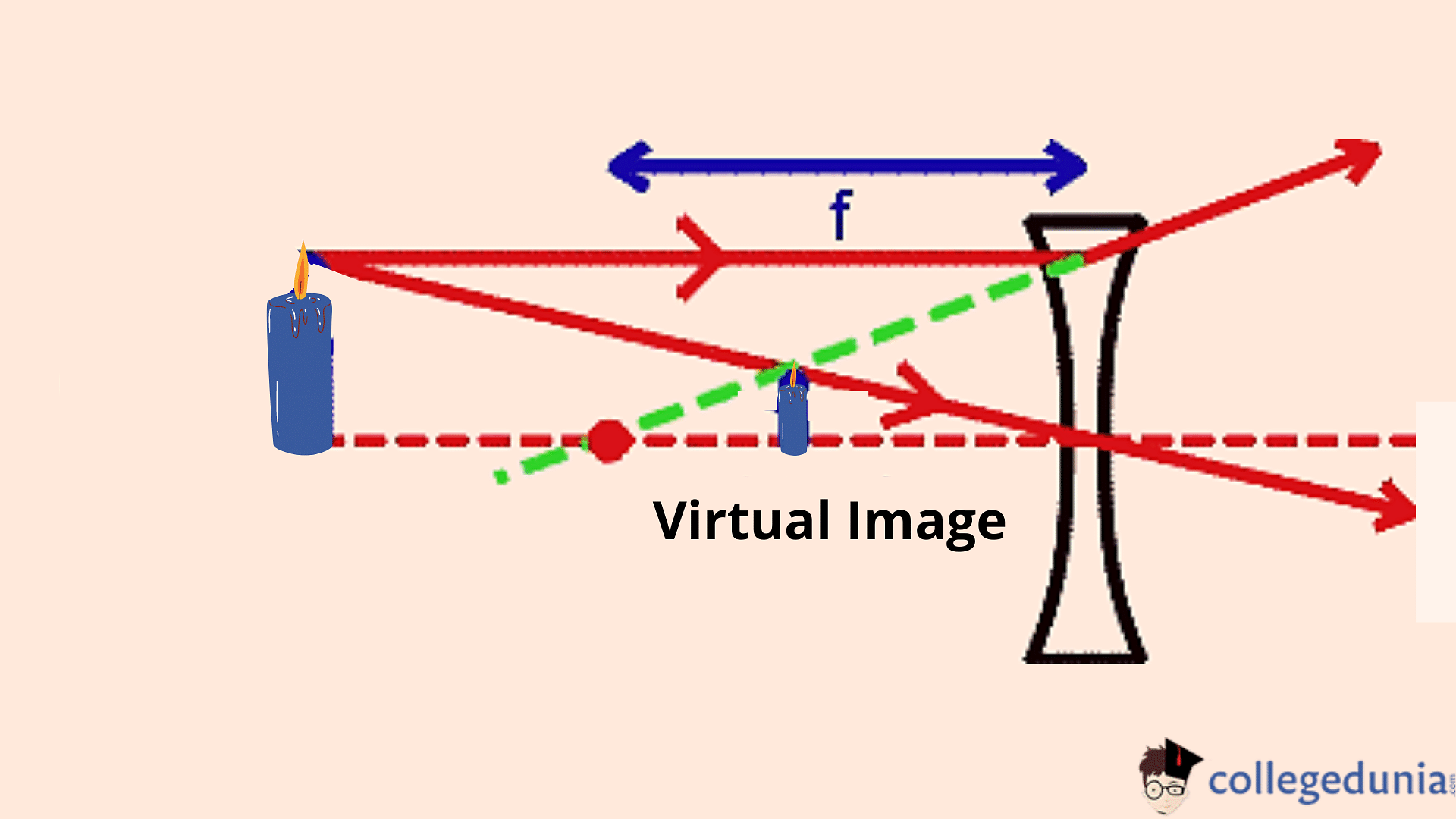
Difference between Real and Virtual Image
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The difference between real image and virtual image is as tabulated below –
| Properties | Real Image | Virtual Image |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A real image is an image that is created by the convergence of light rays, after reflecting/refracting from a mirror or lens. | A virtual image is an image that is created by the divergence of light rays, after reflecting/refracting from a lens or mirror. |
| Size of Image | The size of the image formed depends upon the distance at which the object is placed from the lens or mirror. | The size of the image formed depends upon the distance at which the object is placed from the lens or mirror. |
| Type of image | The real image formed is always inverted. | The virtual image is upright and erect. |
| Lens used | Converging Lens | Diverging Lens |
| Mirror used | Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
| Light Rays | The light rays actually converge or meet at a fixed point. | The light rays don’t actually meet anywhere, but it is perceived that they meet somewhere behind the mirror. |
| Image Reception | The real image can be presented on the screen. Moreover, this is the only way by which we can see real images. | The virtual image can not be presented on a screen under any circumstances, as there is no actual convergence of light rays happening. |
| Example | The projector lens fitted in the projector converges the image on a screen | The convex mirror used in the side mirror of vehicles shows the driver the road behind him. |
Check Out:
Things to Remember
- A real image is formed due to the convergence of light rays while the virtual image is formed due to the divergence of light rays.
- A real image can be presented on screen while the virtual image can not be presented on screen.
- A real image formed is inverted while a virtual image formed is erect.
- A real image is formed by only a concave mirror whereas a virtual image can be formed by concave, convex and plane mirror.
- The size of a real image and a virtual image depends upon the distance of the object from the mirror or lens.
- A common example of a real image is a projection lens in a projector. An example of a virtual image is a side mirror in vehicles.
Previous Year's questions
- The angle of minimum deviation for a prism is 40∘ and the angle of the prism is 60∘. The angle of incidence...
- The communication using optical fibers is based on the principle of….
- The critical angle for total internal reflection in diamond is 24.5. The refractive index of the diamond is…..
- The instrument used by doctors for endoscopy works on the principle of…[BCECE 2007]
- The refractive index of glass is 1.520 for red light and 1.525 for blue light. Let D1, and D2 be angles of minimum deviation…
- A prism is made up of material of refractive index √33. The angle of prism is…
- Two plane wavefronts of light, one incident on a thin convex lens and another on the refracting face…
- The bottom of a container is of a 4.0cm thick glass slab. The container contains two immiscible liquids A(μ=1.4)…
- When a point object is seen by an observer through a glass slab, the image is:…...
- Which of the following is not due to total internal reflection?...[NEET 2011]
- The angle of incidence for a ray of light at a refracting surface of a prism is 45∘...[NEET 2016]
- An electromagnetic radiation of frequency n, wavelength λ, travelling with velocity v in air...[NEET 1997]
- A small object is placed 50cm to the left of a thin convex lens of focal length 30cm...[UPSEE 2016]
- A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water (refractive index 4/3)...[BITSAT 1981]
- Glass has refractive index μ with respect to air and the critical angle for a ray of light going from glass to air is θ...[MHT CET 2019]
Sample Questions
Ques 1. What are real and virtual images? (3 marks)
Ans. Real Image is formed when a ray of light after reflection/refraction meets at a point to form an image. These images are inverted in nature and are obtained on a screen.
Virtual Images are formed when a ray of light, when extended appears to meet at a point to form an image. These images are erect and cannot be obtained on a screen.
Ques 2. Why can we not see virtual images on the screen? (2 marks)
Ans. A virtual image is formed due to the divergence of light rays and the image is perceived to be forming behind the mirror, but there is no actual convergence of light rays. As the actual convergence of light is a must for presenting an image on-screen, virtual images can not be presented on screen.
Ques 3. How is the real image formed by the projector not inverted? (2 marks)
Ans. The reason why the image formed by the projector is not inverted is that in a projector two lenses are used, and because of two lenses image is inverted two times and hence the final image formed on-screen is erect.
Ques 4. Give some examples of real images. (2 marks)
Ans. A very famous example of real image formation is the projector. The projectors used in cinema halls and conferences have a converging lens in them. So when light is passed through them, lenses converge the light on the screen and lead to real image formation.
Ques 5. Write 3 differences between real and virtual images. (3 marks)
Ans. The differences between real and virtual images are:
| Real Image | Virtual Image |
|---|---|
| The real image can be presented on the screen. Moreover, this is the only way by which we can see real images. | The virtual image can not be presented on a screen under any circumstances, as there is no actual convergence of light rays happening. |
| The real image formed is upright and erect as the actual object. | The virtual image created is an inverted form of the actual object. |
| Eg- Image formed by a projector | Eg- Image formed by the side mirror of a car |
Ques 6. Why are real images always inverted? (1 mark)
Ans. A real image is formed when the rays of light converge. A real image is formed below the principal axis, so they are inverted whereas a virtual image is always formed above the principal axis so these are erect.
Ques 7. Are real images always smaller than objects? (1 mark)
Ans. No, real images can be either small or large than the object. However, real images are always inverted.
Ques 8. Why a movie projector does not form inverted real images? (1 mark)
Ans. A movie projector uses two mirrors. The first mirror is used to concentrate the light source and the second mirror is used to focus the images on the screen. As the images invert twice, the final images are erect.
Read More:






Comments