
Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Light is the energy that enables us to see everything around us. Light is mainly emitted from a source like the Sun. At night time, in the absence of our natural source of light - the Sun, we use artificial sources of light to see objects. When light falls on an object, it gets reflected. This reflected ray of light makes it possible for us to see things. Light takes the quickest path between any two given points. Hence, light travels in a straight line. This property of light is known as rectilinear propagation of light. Light, Shadows and Reflections Class 6 notes are given in this article with sample questions.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Light, Transparent Object, Mirrors, Reflection, Shadows, Sources of Light, Pinhole Camera
Sources of Light
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Light is derived from the sources which are classified as natural and man-made sources of light.
- Natural Source of Light: The source of light already present in nature is known as a natural source of light. For example - Sun.
- Man Made Source of Light: The source of light prepared by humans artificially is known as man made or artificial source of light. For example, candles, bulbs, torches, etc.
On the basis of the tendency of the object to produce light, they can be classified as -
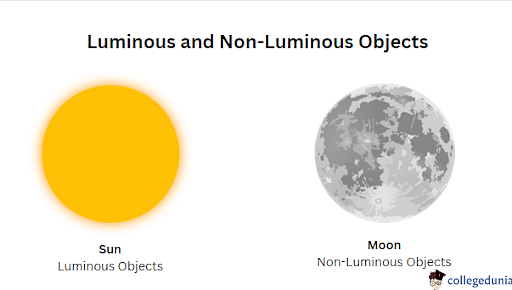
- Luminous objects: An object with a tendency to produce light and heat is known as a luminous object. Example: Sun, bulb, etc.
- Non - luminous object: An object which does not have a tendency to produce light or heat is known as a non-luminous object. These objects reflect the light that is emitted by non-luminous objects. Example: the moon.
Sources of Light
Transparent, Opaque, and Translucent Objects
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
On the basis of their interaction with light, objects are of different types -
- Transparent Object: An object through which light completely passes is known as a transparent object. They allow light to pass without scattering it.
- Translucent Object: An object which allows partial passage of light is known as a translucent object. The vision through a translucent object appears murky.
- Opaque Object: An object that completely blocks light and does not allow it to pass through is called an opaque object.
What Are Shadows?
The dark patch that is formed on the other side of an opaque object when a ray of light falls on it is known as a shadow. Shadows can be formed on a screen like walls of a room, ground, or the surfaces of buildings.
- For the formation of a shadow, three prerequisites are required - a source of light, an object, and a screen.
- The size of a shadow is dependent on the distance between the source of light and the object.
- The shadow will appear larger when the source of light will be closer to the object.
- The shadow will appear smaller when the source of light is farther away from the object.
In the evening, the size of the shadow is small while in the morning, it is bigger. This is because a smaller incidence angle leads to larger shadows while a bigger incidence angle leads to smaller shadows.
Characteristics of Shadows
Shadows are in an erected and real form.
- The color of the shadow is black.
- A shadow can be smaller, bigger, or even the same size as an object.

Shadows
Formation of the image by pinhole camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera consisting of a light-proof box, a small hole for the passage of rays of light, and a thin film for a screen. It is a box with a small pinhole in the front and a translucent screen in the back.
It works on the principle that light travels in a straight line. The light rays coming from outside enter through a small hole and form an inverted image on the screen.
Advantages of Pin Hole Camera
- The image formed by a pin hole camera is free from the defect of lenses as it does not require any lens to produce the image.
- The camera is able to take extremely sharp pictures of still objects.
- It is easy to construct and operate.
- It is cheaper.
Disadvantages of Pin Hole Camera
- The exposure time of pin hole camera is uncertain as it is too large. Therefore, the final image is either over-exposed or underexposed.
- The camera cannot take pictures of moving objects.
- If the pin hole of the camera becomes wider, then the final image appears to be blurred
Mirrors and Reflection
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A mirror is a surface consisting of a glass that reflects light which is incident on it to form clear and erect images.
Reflection of Light
Light incident on a surface gets reflected or bounces back. The phenomenon of light bouncing off surfaces is known as the reflection of light.
- Reflection occurs as the incident light is reflected when it falls on a clear surface.
- Due to the reflection of light, the image formed is always erect.
- When a ray of light falls on a shiny and glossy surface, it gets reflected.
- During reflection of light, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The image formed is the same size and color as the object.
- The right side of the object appears to be left in the image and vice versa.

Reflection of Light
Characteristics of images
Images are formed due to converging light rays that come after reflection from the object.
- Unlike shadows, images too have color.
- A real image is formed on a screen by the actual convergence of light
- A virtual image cannot be obtained on a screen and is formed as a result of the apparent convergence of diverging rays of light.
A plane mirror changes the direction of the light that falls on it. This helps us see images.
Things to Remember
- The energy derived from the lamp or sun which allows us to see things is known as light.
- Light always travels in a straight line.
- A shadow is a dark patch formed on the opposite side of the object when an opaque object is placed in the path of light.
- The bouncing back of the light when it falls on a surface is called the reflection of light.
- Images are coloured in nature, and the shadows are dark.
Sample Questions
Ques 1: Differentiate between an Image and a shadow. (5 marks)
Ans: The differences between an image and a shadow are as follows -
| Image | Shadow |
|---|---|
| When reflected rays intersect each other, an image is formed. | When the light does not reach behind the object, a shadow is formed. |
| Image is seen when reflected rays reach the eyes of the observer. | No light reaches the eyes of the observer |
| Information like color and structure can be known from the Image | No information is provided by shadow |
| Image can be inverted or even straight | It can not be inverted |
Ques 2: What is the difference between Umbra and Penumbra? (3 marks)
Ans: The differences between umbra and penumbra are as follows -
| Umbra | Penumbra |
|---|---|
| The darkest part of a shadow is known as Umbra | It is the less dark part of the shadow |
| Light does not reach this region | From some parts of the sources, light reaches this region |
| The central part of a shadow is Umbra | Penumbra is the counterpart of a shadow |
Ques 3: Explain Luminous and Non-Luminous objects. Give examples of both types. (2 marks)
Ans: Luminous and Non luminous objects are explained as follows -
- Luminous Object: An object which has its own light is known as a Luminous object. For example, Sun, torch, burning candle, bulb, firefly, etc.
- Non-Luminous Object: The object which does not produce its own light is called as Non-Luminous Object. For example, Moon, furniture, notebook, blackboard, etc.
Ques 4: What kind of image is formed by a plane mirror? (2 marks)
Ans: The images formed by a plane mirror are erect and laterally inverted but are of the same size as that of an object. The colour of the image formed is the same as that of the object placed in front of the plane mirror.
Ques 5: Define Incident and Reflected rays. (2 marks)
Ans: Incident ray: The light ray which falls on the surface of the mirror is known as the Incident ray.
Reflected ray: The light ray which returns back from the mirror is called a Reflected ray.
Ques 6: Define Shadow. How is it formed? What are the different conditions required for the formation of a shadow? (3 marks)
Ans: When a light ray falls on an opaque object, a dark patch is formed behind the surface of that object. This is formed as the light can not pass through the object or we can say that the light is blocked by the object.
Conditions required for the formation of a shadow is as follows:
- Presence of light source
- Presence of Opaque object in the way of light
- The opaque object blocks the light falling on its surface
Ques 7: Define eclipse and write in brief about its two types. (3 marks)
Ans: In the presence of a light source, a shadow is formed by celestial bodies on each other. This phenomenon is known as an eclipse. There are two types of eclipse:
- Solar Eclipse: This eclipse occurs when the moon comes between the sun and the earth. Thus, the shadow of the moon falls on the earth and is known as the Solar eclipse.
- Lunar Eclipse: In this, the earth comes between the moon and the sun. The shadow of the earth falls on the moon and is called a Lunar eclipse.
Ques 8: On the ability to pass light through itself, name the different types of objects with examples. (5 marks)
Ans: Objects are categorized into three groups on the ability to pass light through themselves and they are as follows:
- Transparent Objects: Light can easily pass through these objects. For example, Clear air, clean water, clean glass, etc.
- Translucent Objects: Light passes partially through these objects and the person can not clearly see through them. Example: Greased paper, butter paper, wax paper, etc.
- Opaque Objects: Light is blocked out and shadow is formed due to the presence of opaque objects when placed in the path of light rays. Example: Stone, blackboard, wall, etc.
Check out:






Comments