
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Concave lens is a diverging lens that has a surface that is curved inside. Concave lens diverges a beam of light into a smaller, upright and virtual image. Concave lenses have thick edges and thin centre. Uses of concave lenses are treatment of myopia or short sightedness. Concave Lens Formula is: \(\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}\). In this article, we'll take a closer look at the concave lens, image formation in concave lens and its properties.
Also Read: Convex Lens
| Table of Content |
What is a Concave Lens?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Concave lenses diverge a straight light beam from the source into a smaller, upright virtual image. They can form both real and virtual images. At least one surface of a concave lens is curved on the inside. It is shaped round at the center and bulges outwards through the edges. A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens. They are used to cure myopia or short-sightedness because they make faraway objects appear smaller.

Concave Lens
Read More:
Concave Lens Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Concave lens formula is used to determine the type of image created by the concave lens. It is also used to identify the position of the image. The formula for the concave lens is:
| \(\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u}\) f is the focal length, v is the distance of the image from the center, u is the distance of the object from the center |
The magnification of the image can be determined by the following equation:
| \(M = \frac{h_i}{h_0} = \frac{v}{u}\)
M is the magnification, hi is the image height, ho is the object height. |
Image Formation in Concave Lens
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Image Formation in Concave Lens cases:
Case 1: When Object is placed at infinity
In this case,
- The image will be formed at the focus F where the light rays converge after reflection.
- A virtual image is formed.
- The image is very small in size.
- The image is erect.

Image Formation in Concave lens When Object is placed at infinity
Case 2: When an object is placed at a defined distance (between infinity and optical center)
In this case,
- A virtual image will be formed between focus F and the optical centre. i.e at A’B’.
- A real image is formed beyond the mirror.
- The image is erect
- The image diminished.
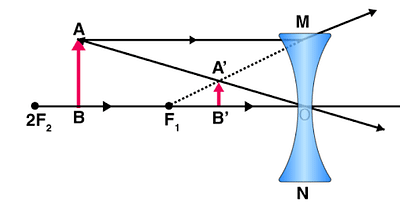
Image Formation in Concave lens When an object is placed at a defined distance
Uses of Concave Lens
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The following are some uses of concave lens:
- In Telescope: Concave lenses are used as a magnifier in telescopes and binoculars. The concave lenses form a magnified image of the object. The manufacturers of telescopes and binoculars use concave lenses before or in the eyepiece to help people focus more clearly.
- In Glasses: Myopia, often known as nearsightedness, is corrected with concave lenses. Myopia is a condition in which a person's eyeball is abnormally long, causing images of distant objects to fall short of the retina. As a result, concave lenses are utilized in spectacles to correct the shortage by spreading light rays out before they reach the eyeball. This allows the person to see items in the distance more clearly.
- In Peepholes: Peepholes, sometimes known as door viewers, are security devices that provide a 360-degree view of objects or areas outside of walls or doors. A concave lens is used to reduce the object's proportions and provide a wider view of the object or area.
Things to Remember
- A concave lens diverges a beam from the source and forms a diminished, upright virtual image.
- Concave lens is also called a diverging lens.
- Telescopes, peepholes, and eyeglasses use concave lenses.
- The edges of a concave lens are thicker and the centre is thinner.
- The magnification of the image can be calculated as M=hi/h0 = v/u
- The lens formula for a concave lens is 1/f=1/v +1/u
- A virtual image is formed at the focus when the object is placed at infinity.
- A virtual image is formed between the focus and the optical centre when the object is placed at a definite distance from the concave lens.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques: A concave lens has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the lens can a 5 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at 15 cm from the lens? Also, calculate the size of the image formed. (Delhi 2007, 3 Marks)
Ans:

Ques: Draw the ray diagram in each case to show the position and nature of the image formed when the object is placed:
(i) at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror
(ii) between the pole P and focus F of a concave mirror
(iii) in front of a convex mirror
(iv) at 2F of a convex lens
(v) in front of a concave lens (All India 2017, 5 Marks)
Ans: (i) Real, inverted and same size image is formed at the centre of curvature.

(ii) Virtual, enlarged and erect image is formed behind the mirror.

(iii) Virtual, erect and diminished image is formed behind the mirror.

(iv) Real, inverted and size to size, image is formed at 2F on the other side of the lens.

(v) Virtual, erect and diminished image is formed between O and F on the same side of the object.

Ques: (a) If the image formed by a lens is diminished in size and erect, for all positions of the object, what type of lens is it?
(b) Name the point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviated.
(c) An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed. (Delhi, 2011 5 Marks)
Ans: (a) Concave lens.
(b) The point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviated is the optical center.
(c) Given that: u = – 30 cm, f = 20 cm
(i) 
(ii) m= v/u = 60/-30 = -2
So, the image is inverted and double in size of the object.
Ques: (a) What is meant by ‘power of a lens’?
(b) State and define the S.I. unit of power of a lens.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in close contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of this combination. (All India 2011, 5 Marks)
P = 1/f
(b) The SI unit of power of a lens is ‘diopter’. A lens of focal length 100cm has a power of 1 dioptre, i.e. 1 dioptre = 1 m-1.
(c) Power of the combination-
P = P1 + P2
P = 100/25 + 100/ -10
P = 4-10 = -6D
Ques: (a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between infinity and the optical centre of a concave lens.
(b) A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. Calculate
(i) the distance of the object from the lens.
(ii) the magnification for the image formed.
(iii) the nature of the image formed. (All India 2011, 5 Marks)
Ans: (a) When the object is at any position between infinity and optical centre:

Position of Image: Between F and optical centre
Nature of Image: Virtual, erect and diminished
(b) f = -15cm, v = -10cm
(i) 
(ii) m = -10/-30 = ?
(iii) m is +ve, so the image is erect. v is -ve, so the image is virtual. As, m<1, image is diminished.
Ques: (a) Under what condition will a glass lens placed in a transparent liquid become invisible?
(b) Describe and illustrate with a diagram how we should arrange two converging lenses so that a parallel beam of light entering one lens emerges as a parallel beam after passing through the second lens.
(c) An object is placed at a distance of 3 cm from a concave lens of focal length 12 cm. Find the (i) position and (ii) nature of the image formed. (All India 2015, 5 Marks)
Ans: (a) The glass lens will become invisible when the refractive index of a glass lens becomes equal to the refractive index of transparent liquid.
(b) Parallel beam converges at focus of the first lens and emerges parallel at the focus of second lens.

Ques: (a) With the help of a ray diagram explain why a concave lens diverges the rays of a parallel beam of light.
(b) A 2.0 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 15 cm. At what distance from the lens, should the object be placed so that it forms an image 10 cm from the lens? Also find the nature and the size of the image formed. (Foreign 2015, 5 Marks)
>Ans: (a) When a parallel beam of light incident on a concave lens, the rays of light will refract towards the normal to the surface. This is because it moves from rarer to denser medium and travels in a straight line inside the lens until it reaches the back of the lens. At the back of the lens, each ray of light will again refract and bend away from the normal to the surface as it moves from denser to rarer medium.

Thus, because of the concave shape of both the faces, the double concave lens diverges the rays of the parallel beam of incident light.

Ques: At a distance of 30cm, a candle is placed in front of a concave mirror. On a screen 15cm away from the mirror, its true picture is obtained. What is the magnification of the image? (1 mark)
Ans: Magnification, m = -v/u = +15/-30 = - 0.5. The image is both real and inverted.
Ques: What types of mirrors are used in a car's headlights, and why? (1 mark)
Ans: A concave mirror is used in the headlight of a car to get a parallel beam of light.
Ques: A 2 cm height object is positioned 16 cm away from a concave mirror, which produces a true image of 3 centimeters high
(i) What is the mirror's focal length?
(ii) Determine the image's location. (3 Marks)
Ans: The object's size is O = 2 cm and u = -16 cm.
I = -3 cm is the image's size.
-v/u = I/O = m, or -v/-16 = -3/2, or v = 16 x (-3/2) = -24 cm,
or v = 16 x (-3/2) = -24 cm.
At a distance of 24 cm in front of the mirror, the picture is generated.
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
= 1/-24 + 1/-16
= - 1/24 - 1/16 = -5/48
f = -48/5 = -9.6 cm.
Ques: When a concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens, and convex lens are immersed in water, what happens to their focal length? Is it going to change? If so, please explain. (3 marks)
Ans: When spherical mirrors (both concave and convex) are immersed in water, the focal length of the mirrors does not change. This is due to the fact that the focal length of mirrors is independent of the external medium in which they are held.
Refraction occurs in the case of lenses. The refractive index of a lens falls when it is submerged in water. As a result, the focal length of the lens increases.
Ques: List four qualities of the picture generated by a concave mirror when an object is put between the mirror's focus and pole. (2 marks)
Ans: The four qualities of a concave mirror are:
- Behind the mirror, the picture is produced.
- It has been enlarged.
- It is only virtual.
- It is standing straight.
Also read:






Comments