
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
The refractive index is a common occurrence that occurs on around us often.
When a light ray travels from one medium to another, it alters its direction. It occurs because of differences in the speed of light in each medium.
Note:
The refractive index of water, for example, is 1.33, so the speed of light in water is 1.33 times slower than in a vacuum.
In a vacuum, speed of the light is 3x108 meters/second, and in air speed of light is 2.98x108 meters/second.
Read Also:
Light-Reflection and Refraction Important Question| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Light, Ray, Index of water, Air, speed, vaccum, Index of refraction, Refraction
Definition of Refractive Index
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The speed of light in a vacuum divided by the speed of light in a specific medium.
The bending of a light ray as it passes through one medium and into another is measured by the Refractive Index.
It is also referred to as the index of refraction.
If
i = a ray’s angle of incidence in vacuum
(an angle formed by the incoming ray with the perpendicular of a medium’s surface called the normal)
r = a ray’s angle of refraction
(an angle formed by the ray in the medium and surface)
The refractive index n is the ratio of the sine of the incidence angle to the sine of the refraction angle.
i.e., n = sin i / sin r.
Read More: Difference Between Mirror and Lens
Again,
The refractive index ‘n’ is calculated by dividing the velocity of light ‘c’ of a specific wavelength in an empty space by its velocity ‘v’ in a substance.
c = the velocity/speed of light of a specific wavelength in air,
v = the velocity of light in any medium
i.e. n = c/v
Thus, Refractive Index measures how far light rays bend as they pass through one medium and into another.
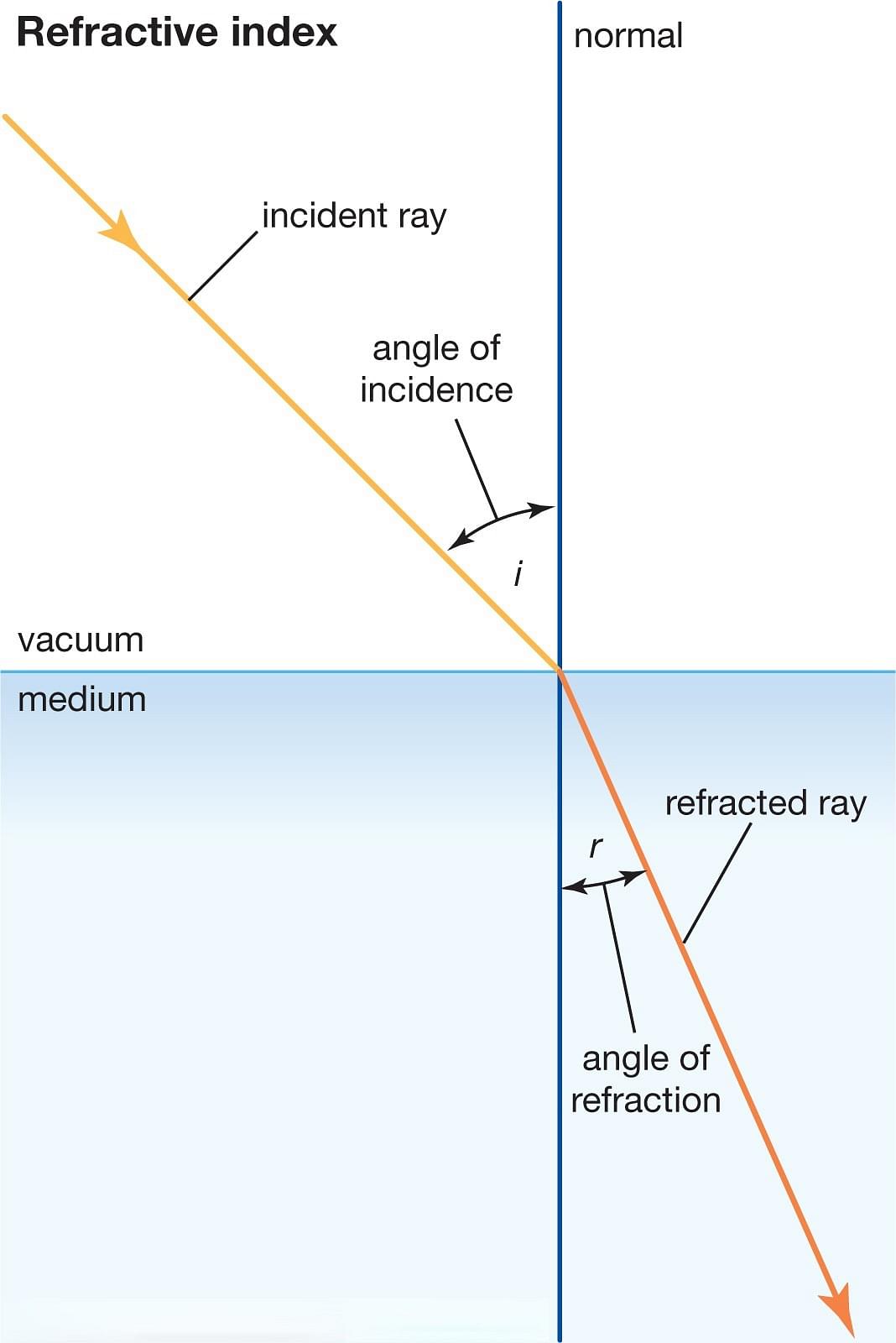
Refractive Index
Check Important Notes for Reflection of Light
The Refraction Phenomenon is divided into two parts:
- In the medium, the light travels at a certain speed.
- Refraction Angles
Factors influence the refractive index:
- the medium’s character
- physical circumstances
- the wavelength of light colour
Refractive Index Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The refractive index of a medium can be calculated using the following formula:
n = c/v
where,
n = refractive index of the medium
c = velocity of light in vacuum
v = velocity of light in the medium
Also Check:
About Absolute Refractive Index (ARI)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The refractive index is calculated using two distinct mediums. When one of the two mediums is regarded as a vacuum, the refractive index of the second medium is known as Absolute Refractive Index in relation to the first medium. The absolute Refractive Index is denoted by the sign n2.
As a result,
n2 equals the speed of light in vacuum divided by the speed of light in the second medium.
When compared to the speed of light in air, light travels faster in a vacuum. Assume that the speed of light in the air is “c,” while the speed of light in the specified medium is “v.” The refractive index of a material is then determined as follows:
nm = Light Speed in Air/ Light Speed in Given Medium
c/v = nm
The refractive index of water, for example, is 1.33, so the speed of light in water is 1.33 times slower than in a vacuum.

Absolute Refractive Index
Read Also: Law of Reflection
Application of Refractive Index in daily life:
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- The refractive index describes the behaviour of light in various materials.
- The index is used to determine a material’s focusing power, such as lenses.
- It can also be used to determine how many particles are dissolved in a solution.
Also Read:
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- A light ray travels from one medium to another, it alters its direction because of the differences in the speed of light in every medium.
- Definition: Refractive Index is the ratio ofspeed of light in a vacuum divided by the speed of light in a specific medium.
- The refractive index n is the ratio of the sine of the incidence angle to the sine of the refraction angle.
i.e., n = sin i / sin r.
- The refractive index ‘n’ is calculated by i.e.
n = c/v
c = the velocity/speed of light of a specific wavelength in air,
v = the velocity of light in any medium
- The refractive index of the second medium is known as Absolute Refractive Index in relation to the first medium, “n2".
- Application of Refractive Index in daily life such as to determine a material’s focusing power, to determine how many particles are dissolved in a solution.
Sample questions
Ques. Explain with the help of a diagram, why a pencil partly immersed in water appears to be bent at the water surface. [2 marks]
Ans. Light from various locations on the pencil refracts and appears to come from a point above the original position when immersed in water.

Ques. Why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium into another? [1 marks]
Ans. Due to change in velocity in the medium and to reduce the time taken to travel the same.
Ques. A ray of light enters a rectangular glass slab of refractive index 1.5. It is found that the ray emerges from the opposite face of the slab without being displaced. If its speed in air is 3 x 108 ms-1 then what is its speed in glass? [1 marks]
Ans.

Ques. The speed of light in a transparent medium is 0.6 times that of its speed in vacuum. What is the refractive index of the medium? [1 marks]
Ans.

Ques. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and the speed of light in air is 3 x 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in water. [2 marks]
Ans.

Ques. The refractive index of glass is 1.50 and the speed of light in air is 3 x 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in glass. [2 marks]
Ans.


Ques.
(a) “The refractive index of diamond is 2.42”. What is the meaning of this statement?
(b) Name a liquid whose mass density is less than that of water but it is optically denser than water. [3 marks]
Ans.
- This suggests that the ratio of light speed in air to light speed in diamond is 2.42.
- Kerosene
Ques. State the law of refraction of light that defines the refractive index of a medium with respect to the other. Express it mathematically. How is refractive index of any medium ‘A’ with respect to a medium ‘B’ related to the speed of propagation of light in two media A and B? State the name of this constant when one medium is vacuum or air.
The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to vacuum are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 m/s, find the speed of light in (i) vacuum, (ii) water. [5 marks]
Ans. Snell’s law: The ratio of sine of angle of incidence (i.e. sin i) to the sine of angle of refraction (i.e. sin r) is always constant for the light of given colour and for the given pair of media.


Ques. The refractive indices of four media A, B, C and D are given in the following table:

If light, travels from one medium to another, in which case the change in speed will be (i) minimum, (ii) maximum? [1 marks]
Ans.
- bare minimum change is seen as light moves between 1.50 and 1.52, i.e. B and C.
- the greatest change is seen when light moves between 1.33 and 2.40, i.e. A and D.
Ques. “The refractive index of diamond is 2.42”. What is the meaning of this statement in relation to speed of light? [1 marks]
Ans. Since, \(v= \frac{c}{n}\), n = 2.42 means that the speed of light in diamond is \(\frac {1}{2.42}\) times the speed of light in free space.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Read More:





Comments