
Content Strategy Manager
Human body is composed of many connective tissues and cartilage is one of them. Cartilage is very strong connective tissue that protects joints and bones. It also reduces friction between two joints that occurs in excessively functioning joints. Although cartilage is one of the connective tissues, it is different then other tissues.
- Cartilage does not possess blood vessels.
- It is secreted by chondrocytes.
- Unlike other connective tissues, cartilages are suspended in the matrix.
- The term elastic in elastic cartilage refers to the property of elasticity.
- Elastic cartilage is much more flexible than any other tissues.
- Elastic cartilage and elastic connective tissue are two types of tissues found in the human body that have elastic properties.
Key terms: Connective tissue, Cartilages, Elastic tissues, Fibers, Elasticity in organs.
What is Elastic Cartilage?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Elastic cartilage is a type of tissue that provides support with flexibility. It is a structural tissue for body parts which are non-load-bearing. For example, it gives structural support and frames the ears, nose and epiglottis. These are the body parts that do not experience high mechanical loads.
- Elastic cartilage is yellow in appearance.
- It is more pliable than other tissues.
- It has elastin along with the collagen fibers.
There are two other forms of cartilage tissue- Hyaline cartilage and Fibrous cartilage.
What is Elastic Connective Tissue?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Connective Tissue in general, is a type of tissue that connects, supports, joints or separates other tissues and organs. Connective tissues are classified into 4 classes:
- Blood
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Connective tissue proper (Elastic Connective Tissue)
Among these three types of connective tissue, cartilage is more flexible and also has elastic type of tissue. However, elastic cartilage and elastic connective tissue differ from each other in some manner.
Elastic connective tissue is dense and provides tensile strength-resistance to stretching. Like elastic cartilage, it has both elastic and collagen fibers (Fibroblasts). An elastic property of flexibility of elastic tissue means that it ensures that structure can return to its original position after stretching it.
- Elastic connective tissue is found in dermis and pericardium that supports and encloses the heart.
- This fibrous tissue is found where the organ is going under mechanical stretch.
- The elastic connective tissue or connective tissue proper occurs as an elastic layer in the wall of the artery (elastica).
Read More:
| Chapter-Related articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Difference Between Sensory and Motor Neurons | Types of Reflexes | Spinal Cord Diagram |
| Nervous System Diseases | Difference Between Neurosis and Psychosis | Neuroscience |
Structure and Function of Elastic Cartilage
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Elastic cartilage is a type of cartilage that is found in several parts of the body, including the ears and nose. It is unique because it contains elastic fibers in addition to the collagen and proteoglycans that make up other types of cartilage.
Structure
The most flexible cartilage among all the 3 types that supports the part of the body which needs to bend and move is an elastic cartilage. As the name suggests, it is composed of elastic fibers and collagen with elastin protein.
Location of this cartilage is the external ear and larynx (voice box).
- It has a perichondrium-a layer of dense connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage.
- It appears yellow in color and is also referred to as yellow fibrocartilage.
- Found as suspended in the matrix.
The histology of elastic cartilage is represented in below diagram.
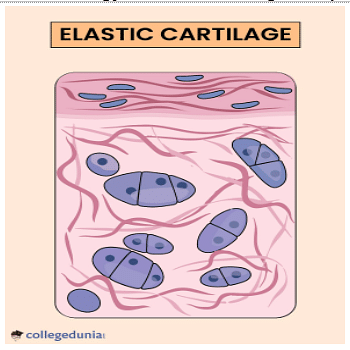
Elastic cartilage, suspended into matrix.
Functions
Prime function of elastic cartilage is to give flexibility and structural support to the organs.
The role elastic cartilage plays are as follows;
- To change the shape of cartilage in response to tension, bending or compression.
- It ensures that the organ returns to its original shape after stretching.
Structure and Function of Elastic Connective Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Structure
These tissues are formed via elastogenesis. This process involves proteins like fibulin-4, fibulin-5, microfibril associated proteins.

Schematic representation of elastic connective tissue. The circle represents the nucleus.
Functions
Elastic connective tissue is found in lungs and arteries, dermis layer of skin, ligaments and in tendons. The main role of tissue in these organs is to give strength and elasticity to the structure of the organ.
Difference Between Elastic Cartilage and Elastic Connective Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Though the function of both elastic cartilage and elastic connective tissues seems to be similar, they have some differences in terms of location, structure, type of fibers etc. Some major differences between elastic cartilage and elastic connective tissue are given in the table below.
| Elastic Cartilage | Elastic Connective Tissue |
|---|---|
| It is one of three types of cartilage. | It is one of the four type of connective tissues. |
| This cartilage type provides strength and rigidity to the structure. | This tissue gives tensile strength and elasticity to the structure. |
| They have chondrocytes present in it. | They have fibroblast cells in it. |
| It is found in the external ear, nose and epiglottis. | It is found in lungs, arteries, dermis and ligaments-tendons. |
| Chondroitin sulfate is present. | Chondroitin sulfate is absent. |
| Fibers present in elastic cartilage are type II collagen fibers. | It contains type I collagen fibers |
Classification of Connective Tissue and Cartilage
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Connective tissues and cartilage can be classified as following;
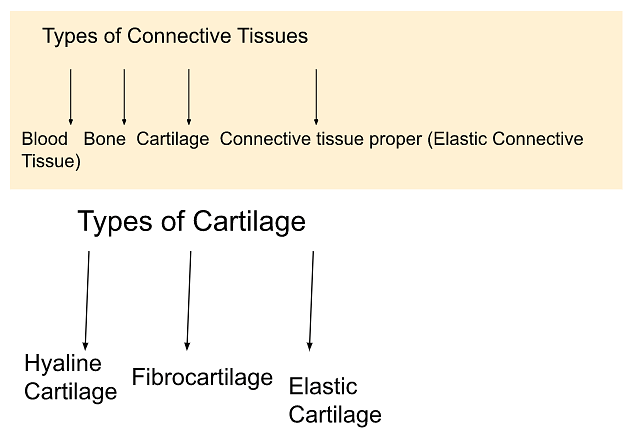
Classification of Connective Tissue and Cartilage
Read more:
Things to Remember
- Connective tissues have 4 different types such as blood, bone, cartilage and elastic connective tissue.
- Cartilage has 3 types such as Hyaline cartilage, Fibrocartilage, Elastic cartilage.
- Elastic cartilages provide strength after stretching. It is found in the ears and nose.
- Elastic connective tissue gives tensile strength and structure to the organ. It is found in lund, arteries, dermis and ligaments-tendons.
- Elastic cartilage has chondrocytes whereas elastic connective tissue has fibroblasts.
- Elastic cartilage is more strong and flexible than other connective tissues
Sample Questions
Ques. Define the four types of connective tissue and state how elastic connective tissue functions. (4 marks)
Ans. Connective tissues can be classified into 4 types;
- Blood
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Elastic connective tissue or connective tissue proper
Elastic connective tissue gives tensile strength and support to the organ like lung and arteries.
The main role is to provide structure to the organ. It also provides elasticity.
Ques. What are three different types of cartilages and what among them is more flexible? (2 marks)
Ans. Cartilage is one type of connective tissue that is further classified into 3 types of cartilage.
- Hyaline cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
- Elastic cartilage
Among these three types, the elastic cartilage is much more flexible than other types. The term elastin refers to the property of elasticity. Elastic cartilage has more fibers also.
Ques. Give the difference between elastic cartilage and elastic connective tissue. (5 marks)
Ans. Elastic connective tissue and elastic cartilage differ in terms of location, structure, composition, strongness etc. main differences are tabulated below.
| Elastic Cartilage | Elastic Connective Tissue |
|---|---|
| It is one of the 3 types of cartilage. | It is one among the 4 types of connective tissues. |
| Strength and rigidity is majorly provided by elastic cartilage. | Tensile strength and support is provided by elastic connective tissue. |
| It consists chondrocytes. | It consists fibroblasts. |
| Elastic cartilage is located at external ears, nose and epiglotis. | Elastic connective tissue is present in lungs, srtries, ligaments etc. |
| Chondroitin sulfate is present. | Chondroitin sulfate is absent. |
| It possess collagen type II fibers. | It possess collagen type I fibers. |
Ques. Which of the following is not a type of cartilage? (1 mark)
(a) Hyaline
(b) Chondroitin
(c) Microfibril
(d) Fibrocartilage
(e) b and c both
Ans. e. B and c both.
Explanation. Microfibril and chondroitin are types of protein, not the cartilages. Rest are the cartilage types. Hence, the answer is option e.
Ques. Give the definition of cartilage and connective tissue. (2 marks)
Ans. Connective tissue: Connective tissue is the tissue that connects, joins or separates the organs. It can be either blood, bone, cartilages or elastic connective tissue.
Cartilage: It is a one type of connective tissue with elastic fibers and more flexibility. It gives strength and ensures that the organ returns to its original shape after stretching.
Ques. Elastic cartilage appears in which color? (1 mark)
(a) Yellow
(b) Red
(c) White
(d) Coloreless
Ans. a. Yellow
Explanation: Elastic cartilage is also called yellow fibrocartilage. Which means it has a yellowish appearance.Therefore, the correct answer is a.
Ques. Why does the body need elasticity in organs? What organs are an example of having elasticity? (2 marks)
Ans. Human body has many organs which are made up of elastic tissues. It is required to provide elasticity because it ensures that the structure will gain its original shape after stretching it. Such flexibility and elasticity is provided by elastic tissue. When an organ faces some mechanical stretch, it has to be returned in its original form and shape to function.
Some of the organs need to be bent or stretched to function. For example, nose, ears, ligaments and tendons are type of of organ that consists elastic tissue.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Check:





Comments