
Content Curator
Epithelial tissue is one of the four types of human cell tissues. It is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM). The cells in this tissue are packed compactly within a thin extracellular matrix. The type of cells and number of layers varies in different parts of the body.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Cell epithelium, Epithelium, Squamous Epithelium, Stratified Squamous Epithelium, Epithelial tissue function, Types of Epithelial tissue
What is Epithelial Tissue?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Epithelial which is also known as Epithelium consists of Two words- ‘EPI’ which means Upon and ‘Thelio’ which means growth. Epithelial tissue is a tissue that grows upon another tissue.
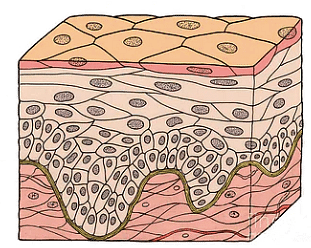
Epithelial Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue covers either external or internal surface.
- These Cells are capable of division and regeneration throughout life.
- Epithelial tissue is non-vascularised.
- Epithelial tissue was introduced by Rush.
- Two types of Epithelial tissue are- Simple and Compound tissues.
- Epithelial tissue forms the outer covering of the skin and lines the respiratory, digestive, reproductive and excretory tracts.
- Perform Functions like absorption, Protection, Secretion and Sensation.
- Epithelial tissue is non-vascularised.
Also Read:
| Related Topics To Structural Organisation in Animals | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plasmodium Life Cycle | Lizard and Moth Life Cycle | Silkworm Life Cycle |
| Types of Reproduction | Biogeochemical Cycles | Anatomy of the Earthworm |
| Agriculture Soil | Ant Life Cycle | Components of Ecosystem |
Anatomy of Epithelial Tissue
[Click Here for Previous Year's Questions]
The epithelial cells are the building block of epithelial tissues. They are surrounded by cellular membranes. These cells consist of a free surface or a basal surface. One surface of the tissue is exposed to either the body fluid or the external environment.
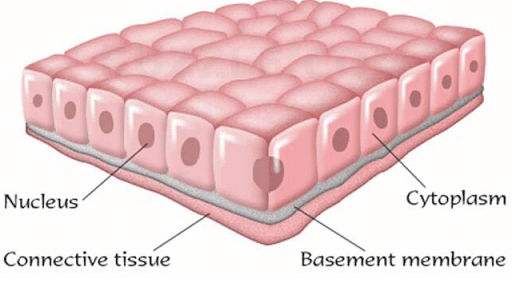
Structure of Epithelial Tissue
- Epithelial cells are compact and have no Intercellular matrix.
- One surface is attached to the basement membrane, which consists of polysaccharides and fibers called the basement membrane.
- The basement membrane consists of 2 layers- Basal Lamina and Fibrous lamina.
- Basal Lamina is made of glycoprotein, secreted by epithelial cells.
- Fibrous Lamina is made of reticular fibers and Collagen.
- Special Junctions are present between the cells of Epithelium which provide adhesion to individual cells.
- Three main type of junctions are-
- Tight junctions: Plasma membranes of adjacent cells fuse together to form tight junctions with the help of enzyme known as occludin.
- Adhering junction- The membranes adhere to each other in certain places only by actin filaments with the help of cadherin enzyme. They keep the neighboring tissues well cemented together.
- Gap junction- Gap junctions physically connect the adjacent cells with the help of connexins to form the pore between the Cytoplasm of two adjacent cells.
Functions of Epithelial Tissues
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The functions of Epithelial Tissues are:
1. Protection
The Epithelial Tissues main function is protection of body cells against desiccation, invasion by pathogens and toxins.
2. Transportation
Epithelial Tissues regulate the exchange of materials between body and external environment as well as the internal exchange between body parts of the body.The Respiratory system, Digestive and Urinary System, it allows the exchange of molecules between the underlying cells, capillaries, ducts and the body cavity.
3. Secretion
Exocrine and endocrine glands are made up of epithelial tissues. The glandular epithelium secretes hormones and enzymes.
4. Absorption
The epithelial lining of the digestive tract absorbs nutrients and water. Microvilli and Cilia on the surface of cells increase the surface area.
Read More:
Types of Epithelial Tissues
[Click Here for Previous Year's Questions]
There are two types of Epithelial tissues:- Simple Epithelium and Compound Epithelium. Which are further subdivided. Refer the diagram for subdivision:

Types of Epithelial Tissues
1. Simple Epithelium Tissues
They have a single layer of cells which function as lining for ductus, cavities and tubes. They are further divided on the basis of shapes and structural modifications of cells.
- Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue
- Unilayered
- A rounded/flattened nucleus is present.
- Cells are scale-like in shape.
- Also known as Pavement Epithelium.
- Location- Bowman’s Capsule, Blood vessel, Heart, Lining of Coelom, Alveoli
- Function- Filtration and diffusion

Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- The margin of squamous cells are irregular and consist of a single layer of flattened cells.
- Cells have a cube-like structure.
- Location- Inner surface of cornea and lens of eye, kidney tubules, pancreatic ducts, salivary and the surface of ovary.
- Function- Absorption and Secretion

Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Columnar Epithelium cells have a tall structure like a pillar and have elongated nuclei.
- Location- Lines stomach, Intestines and digestive glands.
- Function- Absorption and Secretion

Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Pseudostratified Epithelium
- Pseudostratified Epithelium are simple columnar epithelial cells whose nuclei appear at different heights, giving the impression that the epithelium is stratified when the cells are viewed in cross section.
- They are of Two types- Long Cells and Short Cells
- The long cells extend upto free surface and the nuclei have an oval shape.
- The short cells have rounded nuclei and don't reach the outer surface.
- Location- Bronchi, Eustachian Tube, Olfactory, Trachea
- Function- Movement and secretion of mucus.

Pseudostratified Epithelium
2. Compound Epithelium Tissue
The Compound Epithelium Tissue is composed of multi-layered cells and have limited role in Secretion and Absorption. They provide protection against chemical and mechanical stress. They cover the moist surface of buccal cavity, Pharynx, Dry surface of skin, Pancreatic Ducts and inner lining of ducts. They are of two types-
- Transitional Epithelium- Also known as Plastic Epithelium and are stretchable in nature.
- Stratified Epithelium- Non stretchable in nature.
Things To Remember
- Epithelial tissue appears as large sheets of cells covering all surfaces of the body exposed to the external environment and lining internal body cavities.
- Epithelial tissues are derived from all three major embryonic layers in our body.
- Epithelial tissues provide the body’s first line of protection from physical, biological, and chemical damage.
- Act as a gatekeeper of the body.
- Three types of Cell Junction- Tight junction, Anchoring and Gap junctions.
- The function of Epithelial Tissue is Absorption,Transportation and Secretion
- Two types of Epithelial Tissues: Simple epithelium and Compound epithelium.
- Simple Epithelium Have further subdivisions- simple squamous epithelium, simple cuboidal epithelium, simple columnar epithelium, Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Compound Epithelium is subdivided into two divisions-Transitional and Stratified Epithelium.
Previous Year's Questions
- Which of the following is correctly stated as it happens in the common cockroach ?
- Haversian canals occur in...[NEET 1989]
- Histamine secreting cells are found in…...[NEET 1989]
- Which of the following features is not present in Periplaneta americana ?..[NEET 2016]
- Consider the following four statements (A−D)(A−D) related to the common frog Rana tigrina, and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T)(T) and which ones are false (F)(F) . Statements : (A) On dry land it would die due to lack of O2O2 if its mouth is forcibly kept closed for a few days (B) it has four-chambered heart (C) On dry land it turns uricotelic from ureotelic (D) Its life-history is carried out in pond water….[Neet 2011]
- Protein present in cartilage is….[Neet 1997]
- If the head of cockroach is removed, It may live for few days because:...[Neet 2020]
- An epithelial tissue which has thin flat cells, arranged edge to edge so as to appear like closely packed tiles, is found to be present at….[Neet 1994]
- Areolar connective tissue joins-...[Neet 2006]
- Basement membrane is made up of...[Neet 1997]
- Which type of tissue correctly matches with its locations ?...[Neet 2016]
- Which one of the following is one of the paths followed by air or O2 during respiration in the adult male Periplaneta americana as it enters the animal body?….[Neet 2013]
- Which one of the following is correct pairing of a body part with the kind of muscle tissue present in it?..[Neet 2009]
Sample Questions
Ques 1. What are epithelial tissues ? (2 marks)
Ans. Epithelial tissue is one of the four important forms of body tissue found in our organs and covers internal and external surfaces for our body. It has numerous one of a kind structures and functions depending on which body part. The overall function of Epithelial tissue is Protection, secretion, absorption etc.
Ques 2. What is simple epithelium? (2 marks)
Ans. Simple Epithelium Cells can be columnar, cuboidal and squamous and consist of one layer of epithelial cells lying on a basement membrane.
Ques 3. What are the Types of epithelial cells based on their arrangement? (3 marks)
Ans. Epithelial tissue vary on how the cells are arranged. The descriptors for the way the cells are arranged, include:
- Simple: A simple epithelium means only one layer of cells is present.
- Stratified: A stratified epithelium made of more than one layer of cells.
- Pseudostratified: A pseudostratified epithelium made of closely packed cells that appear to be arranged in layers because they’re different sizes, but there’s just one layer of cells.
Ques 4. Name the Types of epithelial cells in your body? (5 marks)
Ans. The shapes and types of layers of epithelial cells can be of several types. There are several types of epithelial tissue, including:
- Simple squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium normally strains blood vessels and body cavities and regulates the passage of materials into the underlying tissue.
- Simple cuboidal epithelium: This kind of epithelium is usually discovered in glandular (secreting) tissue and kidney tubules.
- Simple columnar epithelium: This sort of epithelium is regularly specialized for absorption and commonly has apical cilia or microvilli. These cells line your stomach and intestines.
- Stratified squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium generally has defensive functions, which includes safety against microorganisms from invading underlying tissue and/or safety towards water loss. The outer layer of your skin (the dermis) is made from stratified squamous epithelial cells.
- Stratified cuboidal epithelium: This form of epithelium is not as not unusual and is determined inside the excretory ducts of your salivary and sweat glands.
- Stratified columnar epithelium: This form of epithelium isn't as commonplace and is visible in the mucous membrane (conjunctiva) lining your eyelids, where it’s both protecting and mucus-secreting.
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: This type of epithelium strains your upper respiratory tract and normally has a whole lot of cilia.
Ques 5. What does the epithelium do/Functions of Epithelial tissues? (5 marks)
Ans. Epithelial tissue has numerous critical features which are important to life.They can have one or a mixture of the subsequent several functions:
- Protection: Epithelial tissue protects several components of your body. For instance, your pores and skin is made from epithelial tissue and protects the tissues deeper to your body, which includes blood vessels, muscle and internal organs. The cilia at the epithelial cells that line your intestines defend the relaxation of your body from intestinal microorganisms.
- Secretion: Epithelial tissue in your glands (glandular epithelium) can secrete (release) enzymes, hormones and fluids.
- Absorption: The epithelial lining of your internal organs, such as your liver and lungs, can permit the absorption of certain materials. For instance, the inner epithelial lining of your intestines absorbs vitamins from the meals you devour.
- Excretion: Excretion is the removal of waste out of your body. The epithelial tissue for your kidneys excrete waste, and the epithelial tissue in your sweat glands excrete sweat.
- Filtration: The epithelium of your breathing tract filters out dust and particles and cleans the air that you breathe in. Epithelial tissue for your kidneys filters your blood.
- Diffusion: In biology, diffusion is the passive motion of molecules or debris from regions of better concentrations to areas of lower attention. Simple squamous epithelial cells form a membrane that allows selective diffusion of substances to bypass via. Diffusion helps with filtration, absorption and secretion capabilities.
- Sensory reception: Sensory nerve endings which are embedded in epithelial tissue permit your body to get hold of out of doors sensory stimuli. As an instance, the stereocilia at the floor of the epithelial tissue in your ear are crucial for listening to and balance. In addition, your flavor buds are embedded inside the stratified squamous epithelium of your tongue.
Ques 6.Where Is Epithelial Tissue Found? (3 marks)
Ans. These tissues cover the whole surface of the body. From top respiration tract lining tract lining, blood vessel lining, digestive tract, air sac lining of lungs , the tubular lining of kidneys, glandular ducts, , the liner of mammary glands, salivary glands lining, sweat gland, urinary bladder, urethra, ureter lining, lining of respiratory passage and ducts of many glands, the liner of the mouth and vagina to the lining of an outer or apical layer of the cell, those tissues are determined nearly anywhere.
Ques 7.What Are The General Characteristics Of Epithelial Tissue? (2 marks)
Ans. All the epithelial tissues have these characteristics-
- Attachment
- Regeneration
- Polarity
- Cellularity
- Vascularity
Ques 8. What Cells Are In Epithelial Tissue? (2 marks)
Ans. Epithelial tissue have three types of cells-
- Squamous
- Cuboidal
- Columnar
Do Check Out:





Comments