
Sarah Izhar Content Writer
Content Writer
Fragmentation is a type of asexual reproduction that involves the development of new organisms from small fragments. This process occurs when a parent organism divides itself into multiple fragments.
- Organisms that reproduce by fragmentation includes plants, fungi, sea stars, sponges, annelids, and cyanobacteria.
- Each fragment that develops into a new individual are identical to the original organism.
In this article, we will learn more about what is fragmentation, and fragementation in plants and animals.
What is Fragmentation?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In biology, fragmentation is one of the most common methods of reproduction where an organism’s body splits into multiple pieces or fragments giving rise to new organisms. This type of reproduction primarily occurs in multicellular organisms like plants, animals, fungi, and some unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria or blue-green algae.
- The new organisms produced do not show genetic variation as they are identical to one another.
- A common example of fragmentation is Spirogyra. Other examples of organisms where fragmentation occurs are molds, yeasts, and fungi.
Process of Fragmentation
The process of fragmentation includes three steps which are as follows:
- Breaking or splitting of the parent body into two or more pieces or fragments.
- Growth and regeneration of the fragments takes place.
- Maturation of fragments into new organisms.
Fragmentation in Plants
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Fragmentation in plants is a common mode of vegetative reproduction through which plants divide and give rise to new ones. The detachment of rooted shoots from the main axis marks the beginning of this process.
- This process is observed in non-vascular plants like mosses and liverworts in which fragmentation is mediated by wind, animals, or water.
- Only a few plants can form adventitious plantlets on their leaves, which then detach to form independently matured plants.
- These are called specialized or reproductive structures in plants.
- Other organisms that produce organs are turions and bulbils.
Artificial Fragmentation in Plants
Fragmentation is also used propagate plants artificially through grafting, cutting, layering, and division.
- Artificial fragmentation in plants is achieved by micropropagation of storage organs like corms, rhizomes tubers.
- It is a beneficial method as multiple new plants are formed from a single plant.

Fragmentation in Plants
Fragmentation in Animals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Fragmentation in animals is found in coral colonies, sea stars, and sponges. These organisms depend on fragmentation for reproduction. Fragmentation in spirogyra, hydra, and planaria also takes place.
- Paratomy and Architomy are the common methods used during fragmentation.
- Both terms represent the splitting that occurs as a result of certain developmental changes.
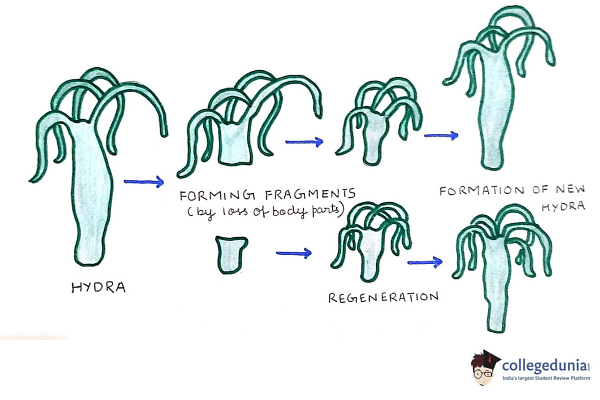
Fragmentation in Hydra
Paratomy
The splitting of an organism in a plane perpendicular to the anterio-posterior axis is called paratomy.
- Each fragment possesses its own tissues and organs.
- The process of paratomy begins just after the regeneration of anterior structures in posterior axis.
Architomy
In the case of architomy, the organism divides into various fragments and develops into a mature organism.
- In this method, the development of furrow occurs before splitting.
Things to Remember
- Fragmentation is an asexual mode of reproduction.
- Plants and a few animals reproduce themselves by fragmentation.
- A part of the body gets fragmented and develops into a whole new individual.
- The newly grown individuals are identical and are referred to as clones.
- This process of splitting can be done artificially to propagate plants.
- Artificial fragmentation can be done by cutting, grafting, layering, and division.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the foundation of biological classification based on? (1 mark)
a) Structure of cell wall
b) Structure of Nucleus
c) Asexual Reproduction
d) Nutrition
Ans. Nutrition (d)
Explanation: The classification of all organisms is based on the nutrition and mode of their nutrition. Therefore, d is the correct answer.
Ques. Asexual reproduction occurs in Spirogyra via fragmentation. (1 mark)
a) True
b) False
Ans. True (a)
Explanation: Spirogyra is an algae. Algae are one of the organisms that reproduce via asexual reproduction methods. Thus, the given statement is true.
Ques. Which of the following organisms reproduces through fragmentation? (1 mark)
a) Hydra and Amoeba
b) Rhizopus and Penicillium
c) Spirogyra
d) Paramecium and Plasmodium
Ans. Spirogyra (c)
Explanation: Fragmentation occurs in plants and some sea creatures. Spirogyra is an algae that can reproduce by fragmentation. Hydra reproduces by budding. Amoeba and plasmodium reproduce by fission. Therefore, C is the correct answer.
Ques. The organism that reproduces through fragmentation is known as? (1 mark)
a) Spirogyra
b) Sponges
c) Rhizopus
d) Both A & B
Ans. Both A & B (d)
Explanation: Reproduction by fragmentation can be seen in algae like spirogyra and other organisms like rhizopus. Therefore, d is the correct answer.
Ques. Which of these, when matured, breaks up into smaller pieces? (1 mark)
a) Rhodella
b) Spirogyra
c) Caulerpa
d) None of the above
Ans. Spirogyra (b)
Explanation: Spirogyra is an algae that reproduces by fragmentation. It involves breaking into parts and developing new individuals from a fragment. The rest of the two organisms do not undergo fragmentation. Therefore, b is the correct answer.
Ques. Rhizopus replicates asexually through fragmentation. (1 mark)
a) True
b) False
Ans. True (a)
Explanation: Rhizopus is an organism that shows asexual reproduction by fragmentation method. Thus, the given statement is true.
Ques. Which of the following represents the mode of reproduction in unicellular organisms? (1 mark)
a) Budding
b) Fragmentation
c) Multiple Fission
d) All of the above.
Ans. All of the above (d)
Explanation: Budding, Fission, and Fragmentation are all modes of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms like yeast, amoeba, etc. Thus, d is the correct answer.
Ques. Why is Fragmentation not possible in humans? (2 marks)
Ans. Fragmentation is not possible in all multicellular organisms because different multicellular organisms have different levels of complexity. Tissues are organized as specialized tissues. These must be placed in specific locations on the body. In case of regeneration, most lizards can lose their tails and then have them grow back. But if they lose their forelimb or hindlimb, it will not regrow.
Ques. How does fragmentation occur in spirogyra? (2 marks)
Ans. Spirogyra is a water algae which consists of filamentous thallus.
- These thallus are broken into fragments when the conditions are favorable.
- This division happens when the centre lamella between the cells undergo mitosis divison giving rise to new filaments which ultimately mature to form adults.
Ques. How does reproduction in planaria takes place? (2 marks)
Ans. Planaria are flat worms that can either reproduce sexually or asexually.
- These organisms reproduce sexually by laying eggs.
- While, fragmentation is a method via which planaria reproduce.
- They divide their bodies into fragments and give rise to another organism.






Comments