
Content Writer
Collenchyma is a sub-part of Simple Permanent tissue. Collenchyma is living cells having small intercellular spaces. Plant tissue can be defined as a group of cells having a common origin and usually performing a common function in a plant body. There are 2 types of plant tissue i.e., Meristematic tissue and Permanent tissue. Permanent tissues are further sub-classified into Simple permanent and Complex permanent tissue. The Collenchyma is usually found in marginal regions of leaves and stems. Its primary function is to offer flexibility and support to plants.
Read more: Plant cell
| Table of Content |
KeyTerms: Parenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Collenchyma, cork cambium, phellogen, cellulose, pectin.
Simple Permanent tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
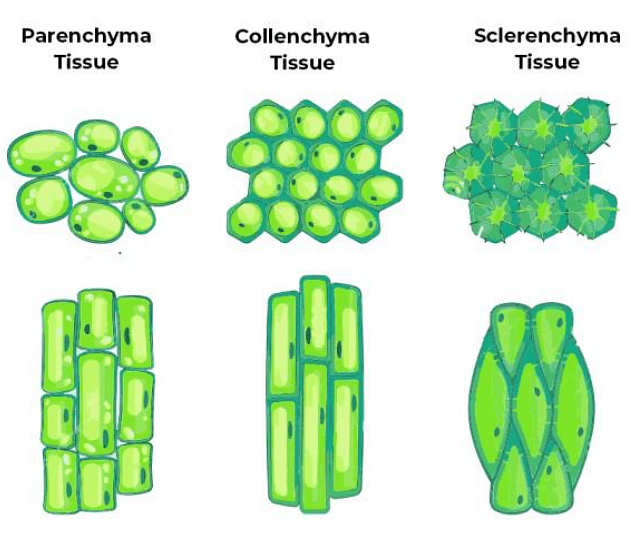
Simple Permanent tissue can be defined as tissues that perform the same function and have similar shapes. There are 3 types:
- Parenchyma: These tissues make up a large part of ground tissues in plants. They are living tissues with prominent nuclei and protoplasts. The shape of cells is usually oval, polygonal, or elongated. They are made up of cellulose and hemicellulose and perform a secretory function.
- 2. Collenchyma: these are also living cells as they can regenerate. The cell wall is made up of cellulose and pectin and provides mechanical support to the growing part of the plant.
- Sclerenchyma: These are dead cells without protoplasts and are usually long and narrow in appearance. The Sclerenchyma provides structural support to the plant body and also forms a protective covering around seeds and nuts.
Simple permanent tissue
What is Collenchyma Tissue?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
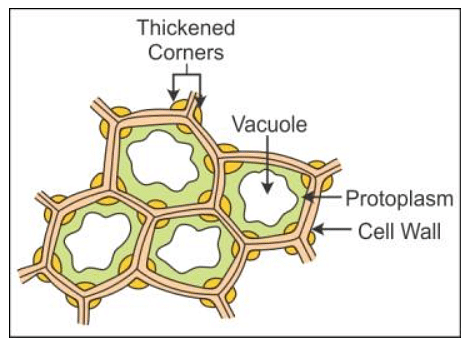
Collenchyma consists of non-uniformly thickened elongated plant cell walls.
- The cell of the collenchyma appears elongated and spindle-shaped.
- After absorbing water, collenchyma can expand radially as well as tangentially because of the weakly lignified cell wall.
- They play an important role in the plant's body as they provide structural support to the growing leaves and stems.
- The cell wall of the collenchyma is made up of cellulose and pectin.
- The thickness of the collenchyma is linked to reducing the mechanical stress on the plants.
- It is found in between the cortex of the stem and the endoderm of its vascular bundles.
Collenchyma tissue
Characteristics of Collenchyma Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Below are the listed characteristics of collenchyma:
- Collenchymas are made of living cells.
- Shapes of the cells are elongated, oval, spherical, or polygonal.
- The cell wall of collenchyma is made up of Cellulose and pectin.
- The cells are arranged compactly and intercellular spaces are very small.
- Collenchyma contains the primary cell wall which is unevenly thickened.
- They contain chloroplasts to store foods.
- When the plant goes through secondary growth then, collenchymatous tissues get crushed.
- They are mostly found under the epidermis of dicot plants. For example- in the midrib & petiole of leaves and young stem.
- Collenchyma provides mechanical support to the part of the plant where they are found.
Read more:
| Relevant Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chromoplasts | Plant Cell Model | Vascular Cambium |
| Plant Growth & Development | Primary wall | Seed Germination |
Types of Collenchyma Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Collenchyma tissue had been classified into 4 types based on the thickening of the cell wall. The four types of collenchyma are:
1. Lacunar Collenchyma
As the name "lacuna" means "space", these types of collenchyma tissue have intercellular spaces. In the lacunar collenchyma, thickening is more at the places adjacent to the spaces present. E.g. petioles of Salvia, stems of Malva, etc.

Lacunar Collenchyma
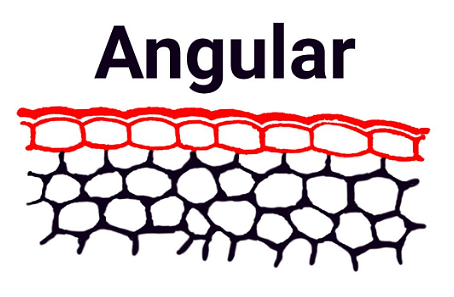
2. Angular Collenchyma
This is the most commonly found collenchyma tissue in the plant. Here, the thickenings of walls are present only at the corners. In the Angular Collenchyma, intercellular spaces are absent and instead, they have a circular lumen. E.g. Cucurbita.
Angular Collenchyma
3. Annular collenchyma
In the annular collenchymatous cells, the cell walls are uniformly thickened.

Annular Collenchyma
4. Lamellar Collenchyma
The lamellar collenchymas are also called plate collenchyma due to their specific appearance. Their walls are tangentially thickened and are arranged into an ordered row pattern. E.g. stems of Clerodendron.

Lamellar Collenchyma
Functions of Collenchyma Tissue
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The functions performed by Collenchyma can be listed below:
- The primary function of collenchymatous cells is to provide mechanical support to the growing or developing parts of the plants.
- It further protects the leaves of the plants from tearing.
- Collenchyma also grows with growing parts of the plants.
- It gives flexibility to the growing part of the plants.
- Sometimes, collenchyma also contains chloroplasts and hence performs the function of photosynthesis and stores food.
- Collenchyma undergoes dedifferentiation to form phellogen or cork cambium and regain Meristematic activity.
Things to remember
- Collenchyma consists of non-uniformly thickened cell walls.
- The cells of Collenchyma are arranged compactly.
- The intercellular spaces in Collenchyma are very small.
- Collenchymas are made of living cells.
- Collenchyma tissue had been classified into 4 types.
- Lacunar Collenchyma tissue has intercellular spaces.
- The thickenings of walls are present only at the corners in Angular Collenchyma.
- The cell walls are uniformly thickened in Annular Collenchyma.
- Lamellar Collenchyma is thickened tangentially.
Sample Questions
Ques. Lists the functions performed by Collenchyma. (3 marks)
Ans. The primary function of collenchymatous cells is to provide mechanical support to the growing or developing parts of the plants and it also protects the leaves of the plants from tearing. Collenchymatous cells also contain chloroplasts and hence perform photosynthesis and store food. Collenchyma also provides flexibility to the growing parts of the plants like petiole, roots, and shoots.
Ques. What is Plant tissue and mention its types. (3 marks)
Ans. Plant tissue can be defined as a group of cells having a common origin and usually performing a common function in a plant body. There are 2 types of plant tissue i.e, Meristematic tissue and Permanent tissue.
The Meristematic tissue is further classified into 3 types i.e., Apical Meristem, Lateral Meristem, and Intercalary Meristem while the Permanent tissues are further sub-classified into Simple permanent and Complex permanent tissue.
There are 3 types of simple permanent tissue i.e., Parenchyma, Sclerenchyma, and Collenchyma while Complex Permanent tissue is of 2 types i.e., Xylem which helps in the conduction of water, and Phloem which helps in the transportation of minerals.
Ques. What is Sclerenchyma? (3 marks)
Ans. Sclerenchyma cells are dead cells and have extremely thick secondary cell walls. The cell wall of Sclerenchyma is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. The sclerenchymatous cells provide strength and support to the part of the plant. The Sclerenchyma also provides structural support to the plant body and also forms a protective covering around seeds and nuts.
Ques. What do you know about Collenchyma? (3 marks)
Ans. Collenchyma is long and living cells. The cell wall of the collenchyma has uneven thickness. It consists of cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose. The role of collenchyma is to provide mechanical strength, support, and structure as well as flexibility to the growing leaf veins stems of young plants and petioles that in turn allow easy bending to stand against wind and thus prevent breaking of these young structures of plants.
Ques. Do Collenchyma cells consist of chloroplasts? (3 marks)
Ans. A collenchyma cell usually doesn't have chloroplasts, but some collenchyma cells have chloroplasts which allow sunlight to pass and reach deep-seated photosynthetic tissues and perform the function of storage of food.
Ques. Explain the similarity between collenchyma and parenchyma. (3 marks)
Ans. Collenchyma and Parenchyma are very difficult to differentiate from each other due to their tiny structure. Both collenchyma and parenchyma are present in the stems, petioles, and leaves of the plant. Both have cell walls and have a common element i.e., cellulose. Both provide mechanical strength to the growing plant parts. The parenchyma and collenchyma are thin-walled and have columnar protoplasts.
Ques. Define Parenchyma and list its functioning. (5 marks)
Ans. It is a type of simple permanent tissue and it makes up a majority of the ground tissue. Parenchyma tissue is non-vascular and is composed of simple, living, and undifferentiated cells which perform various functions.
Parenchyma performs a variety of functions such as:
- They have large intercellular spaces which help in the storage of food.
- Parenchyma cells are responsible for the transport of nutrients and other minerals.
- They also perform functions such as photosynthesis.
- Aerenchyma cells are the large spaces present in parenchyma that perform the function of gaseous exchange.
- Parenchyma cells are totipotent in nature.
Ques. Differentiate between Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma. (5 marks)
Ans.
| Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
|---|---|
| Collenchyma cells are living cells with a thick cell wall. | Sclerenchyma cells are dead cells having extremely thick secondary cell wall. |
| The cell wall of collenchyma is made up of cellulose and pectin. | The cell wall of Sclerenchyma is made up of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin. |
| Collenchyma has simple and straight pits. | Sclerenchyma has simple and oblique pits. |
| It provides mechanical support to growing parts of plants like roots and shoots. | It provides strength to the elements in the plants that have ceased elongation. |
Ques. Distinguish between Parenchyma and Collenchyma (5 marks)
Ans.
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma |
|---|---|
| The parenchymatous cells have origination in ground and protoderm meristems. | The collenchymatous cells originate from pro- cambium. |
| They are found in every delicate part of the plant. | They are found specifically in growing part of the plants like roots, shoots, petioles. |
| Parenchyma cells are living and unspecialized. | Collenchyma cells are living but are highly specialized. |
| Cell wall is made up of only cellulose. | Cell wall is made up of cellulose and pectin. |
| They perform functions like food storage, gaseous exchange and photosynthesis. | They usually provide mechanical support to the growing part of the plants like roots and shoots. |
Ques. Write difference between Meristematic and Permanent tissue. (5 marks)
Ans.
| Meristematic tissue | Permanent tissue |
|---|---|
| Cells can divide throughout their life. | Cells lose the ability to divide and perform specific functions. |
| Located in specific regions of plants i.e., apical, lateral and intercalary. | Distributed throughout the body of plant. |
| Cells are very active in nature and have dense cytoplasm. | Cells shape and size vary and cell wall is thick. |
| Cell wall is made up of cellulose. | Cell wall is made up of cellulose/ suberin/lignin. |
| They lack vacuoles. | They are vacuolated. |
Check out:





Comments