
Content Curator
The difference between Cardiac Muscle and Skeletal Muscle is more than the similarity it prevails. Coming to the similarity, they have only a single similarity which is that they both fall under the striated muscles. One major difference between the two is that skeletal muscles are controlled by the nervous system while the cardiac muscles are controlled involuntarily. Muscles of all types in the body help in maintaining body posture.
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways: Cardiac muscle, Skeletal muscle, Energy, Nervous system, Food
Cardiac Muscles
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
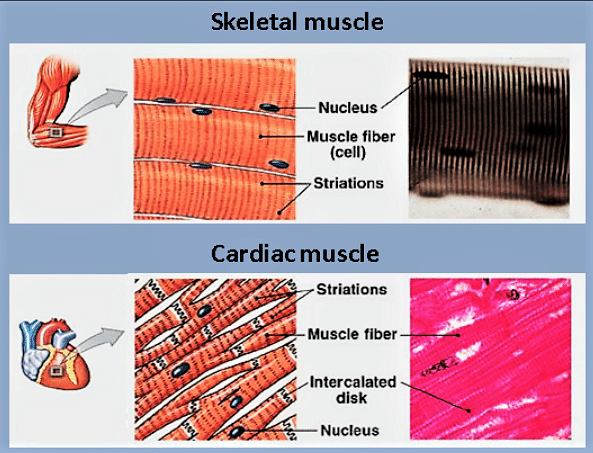
Cardiac muscles tend to execute the muscular involuntary movement and are located in the heart. They are self-simulating and have an average speed of energy requirement and contraction. They have intercalated discs and the T-tube which attaches the myocyte and the syncytium. They help the heart to pump blood all over the body.
Skeletal Muscles
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Skeletal Muscles tend to accomplish voluntary muscular movements and are affiliated with all the bones of the body. They are not self-simulating and have a high speed of energy requirement and contraction. Skeletal muscles give myoblasts which help in creating the fibers in the muscles. They help with the body processes like writing, walking, and running.
Difference between Cardiac and Skeletal Muscles
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
| Parameter of Differentiation | Cardiac Muscles | Skeletal Muscles |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Only in Heart. Specifically present in the myocardium of the heart. | Affiliated to all the bones of the body using tendons |
| Length | Shorter than skeletal muscles | Longer than cardiac muscles |
| Cell Type | Uni-nucleated | Multinucleated |
| Shape | Semi-Spindle | Cylindrical |
| Contracts | Without the neural stimulation | With the neural stimulation |
| Endomysium | Dense | Less dense |
| Controlled By | Autonomic nervous system | Somatic nervous system |
| Gap Junctions | Present | Absent |
| Speed of Contraction | High | Low |
| Function | Pumping Blood, involuntarily muscular movement | Body Movements, voluntarily muscular movement |
| Contraction Type | Rhythmic | Non-rhythmic |
| Muscle Fatigue | Do not Fatigue | Easily Fatigue |
| Energy Requirement | Intermediate | Low |
| Self-stimulation | Yes | No |
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- The cardiac muscles are controlled involuntarily while the somatic nervous system is required to control the skeletal muscles.
- The shape of cardiac muscle is semi-spindle while the skeletal muscle is of cylindrical type.
- The cardiac muscles are loosely bounded while the skeletal muscles are tightly bounded.
- The skeletal muscles are longer than the cardiac muscles.
- While the cardiac muscles are uninucleate, the skeletal muscles are multinucleated.
- The cardiac muscles are dense in the case of endomysium as compared to the skeletal muscles.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. Mention the types of muscles in the human body. (3 marks)
- Cardiac Muscles
- Skeletal Muscles
- Smooth Muscles
Ques. Write down the similarities between the cardiac muscle and the skeletal muscles. (5 marks)
- They aid in the formation of the muscular tissues present in the animal body.
- They both come under the striated muscles.
- They both are regulated and controlled by the nervous system of the body.
- These muscles are used in the internal and external movements exhibited by the body.
- In both cases, the muscle strength increases on stretching.
Ques. Briefly explain the cardiac muscles. (2 marks)
Ques. Briefly explain the skeletal muscles. (2 marks)
Ques. Differentiate between the cardiac muscles and skeletal muscles based on the length, cell type, and shape. (3 marks)
Cell Type- While the cardiac muscles are uninucleate which means they have only one nucleus, the skeletal cells are multinucleated which means they have more than one nucleus.
Shape- Cardiac muscles have a semi-spindle kind of shape while the skeletal muscles have a cylindrical shape.
Ques. Briefly explain the smooth muscles. (2 marks)
Ques. Mention the function, contraction type, muscle fatigue, and energy requirement in cardiac and skeletal muscles. (4 marks)
Contraction Type- Cardiac muscles have rhythmic contraction whereas the skeletal muscles have non-rhythmic contractions.
Muscle Fatigue- The cardiac muscles do not fatigue whereas the skeletal muscles get fatigued.
Energy Requirement- Cardiac muscles possess intermediate energy requirements. Skeletal muscles require low energy.
Read Also:





Comments