
Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
A membrane-enclosed sac is termed a Food Vacuole. Food Vacuole is present in unicellular protozoans such as plasmodium, amoeba, etc. In biology, a vacuole is termed as a space in a cell that is fully empty of cytoplasm. It is a lined membrane filled with fluid. Vacuoles are usually cytoplasmic organs. They perform functions such as ingestion, storage, digestion, expulsion, and excretion of excess water. In-plant cells large central vacuoles are found. It enables them to attain a large size without accumulating bulk, which makes metabolism difficult. In this article, we will learn in-depth about Food Vacuole.
Read More: Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
Definition And Meaning Of Food Vacuoles
Food Vacuoles are an organelle that is membrane-bound and present in all fungal cells and plants and some proteins, bacterial cells, and animals. Food Vacuole is present in unicellular protozoans such as plasmodium, amoeba, etc. The vacuole is bound by a single membrane.
Vacuoles are those non-cytoplasmic areas that are found inside the cytoplasm and separated by the specific membranes from the latter. These are believed to be formed because of the pinching and expansion of the ER. A membrane-enclosed sac is termed a Food Vacuole. It has one important function which is a Digestive Function. space in a cell that is fully empty of cytoplasm. It is a lined membrane and it’s filled with fluid.
Large vacuoles are even found in 3 genera of filamentous bacteria of sulfur, the Beggiatoa, Thioploca, and Thiomargarita. Several vacuoles in a single cell may be found. Every vacuole is segregated from the cytoplasm with a single unit membrane which is called the Tonoplast.
Food vacuoles contain sap, water, excretory products, and other materials which are not useful for the cell.

Structure Of Food Vacuole
- Food Vacuoles have no specific or basic size or shape. Food Vacuole’s structure varies according to the need and requirements of the cells.
- In the actively dividing and immature plant cells these vacuoles are quite small. They arise priorly in young dividing cells, generally by progressive fusion of vesicles which are derived from Golgi apparatus.
- The vacuole is surrounded by a cell membrane which is called a vacuolar or tonoplast membrane which is filled with the sap of the cell.
- Every vacuole is segregated from the cytoplasm with a single unit membrane which is called the Tonoplast. Tonoplast is a cytoplasmic membrane. It separates the vacuolar contents of the cytoplasm from the cells.
- These vacuoles are functionally and structurally linked to lysosomes in animal cells and they may contain a range of hydrolytic enzymes.
- The plant vacuoles' pH may be as high as 10 because of large quantities of alkaline particles and substances or low to 3 because of accumulation of acids.
Read More: Human Digestive System
Types Of Vacuoles
- Sap Vacuoles
These are those types of vacuoles that have several transport systems to pass the different substances. Numerous small sap vacuoles are there in animal and young plant cells. In some mature plants, small vacuoles fuse to form a single large central vacuole. It occupies around 90% of the cell. The central vacuole spreads the cytoplasm of a thin peripheral layer. It facilitates rapid exchange and the surrounding environment.
- Contractile Vacuoles
These are those kinds of vacuoles that occur in some algae and protist cells which are found mostly in freshwater. These are those types of contractile vacuoles which have a highly collapsible and expandable membrane. These are also connected to a few canals which are for feeding. These canals have water with or without waste products from the cytoplasm surrounding them. It pours the same into the vacuole of the contractile.
- Food Vacuoles
These kinds of vacuoles are present in protozoan protists cells, in several lower animals, and phagocytes of higher animals. These are formed by the fusion of a lysosome and a phagosome. It has digestive enzymes with which the nutrients are digested. Then these digested materials pass out into the cytoplasm’s surroundings.
- Air Vacuoles (Gas Vacuoles, Pseudo-Vacuoles)
These kinds of vacuoles are found only in Prokaryotes. This vacuole is not just a single entity, and it is as such surrounded by a common membrane. It has numerous numbers of sub-microscopic vesicles. In this, every vesicle is the one that is surrounded by a membrane of protein and encloses metabolic gases. It does not only store gases but also provides mechanical strength, buoyancy, and protection from harmful radiations.
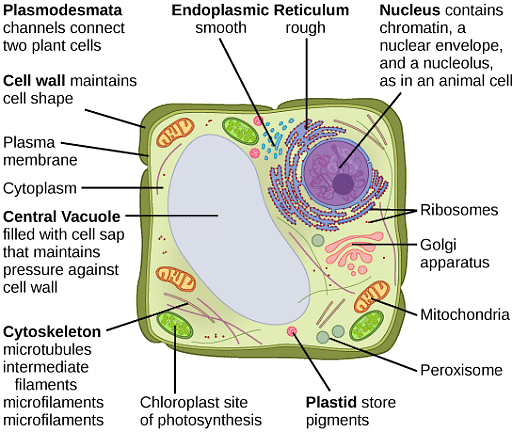
Function And Structure Of Vacuoles
Functions Of Food Vacuoles
Vacuoles have numerous functions. Some of them are-
- They can store various types of molecules. It even acts as a storage organelle for both waste products and nutrients.
- Some products which are stored by vacuoles have a metabolic function.
- They can sequester substances that are harmful to cells of plants, only if they are present in the cytoplasm in bulk.
- They have a vital homeostatic function in cells of plants and these are subjected to various variations in the environment.
- These vacuoles maintain turgor pressure at constant levels due to the large changes in tonicity of fluids in the immediate nature by interchanging somatic pressure of vacuole and cytoplasm. A part of which is resynthesis of polymers and controlled breakdown such as polyphosphate in the vacuole, by altering.
- Due to the increase in size, they allow the organs or germinating plants to grow quickly and mostly water.
- Stored proteins in seeds are needed for germination and these are kept in ‘Protein Bodies’, and these are modifying vacuoles.
Read Also:
Things To Remember Based on Food Vacuole
- A membrane-enclosed sac is termed a Food Vacuole. It has one important function which is a Digestive Function.
- Food Vacuole is present in unicellular protozoans such as plasmodium, amoeba, etc.
- In biology, a vacuole is termed as a space in a cell that is fully empty of cytoplasm.
- It is a lined membrane filled with fluid.
- Vacuoles are usually cytoplasmic organs, especially found in Protozoa.
- There are 4 types of food vacuoles.
- Sap Vacuole
- Contractile Vacuole
- Air Vacuole
- Food Vacuole
- It even acts as a storage organelle for both waste products and nutrients.
- Food Vacuole’s structure varies according to the need and requirements of the cells.
Important Questions Based on Food Vacuole
Ques: What is the part of the cells which stores vital substances? (1 mark)
Ans: The vacuole is that part of the cell which stores vital substances.
Ques: Which part of the cells stores nutrients? (1 marks)
Ans: The vacuole is the part of the cell that stores nutrients.
Ques: Which is the type of vacuole that stores nutrients? (1 mark)
Ans: Sap Vacuole is the type of vacuole that stores nutrients in it.
Ques: Vacuoles are the ones that are formed by the fusion of? (1 mark)
Ans: Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of Vesicles.
Ques: Which is the process which does not occur in cell vacuoles? (1 mark)
Ans: DNA does not occur in the cell vacuoles.
Ques: What is the function of food vacuoles in fungal cells? (2 marks)
Ans: The function of food vacuoles in the fungal cell, they are involved in numerous processes including cell pH of homeostasis and with the ion’s concentration, storing amino acids, osmoregulation, and polyphosphate and processes of degradation.
Ques: What is the basic meaning of Food Vacuoles? (2 marks)
Ans: Food Vacuoles are an organelle that is membrane-bound and present in all fungal cells and plants and some proteins, bacterial cells, and animals. Food Vacuole is present in unicellular protozoans such as plasmodium, amoeba, etc. The vacuole is bound by a single membrane.
Ques: What are the four types of Food Vacuole? (2 marks)
Ans: The four types of vacuoles are-
- Sap Vacuole
- Contractile Vacuole
- Air Vacuole
- Food Vacuole
Ques: What are the basic functions of a food vacuole? (4 marks)
Ans: Vacuoles have numerous functions. Some of them are-
- They can store various types of molecules. It even acts as a storage organelle for both waste products and nutrients.
- Some products which are stored by vacuoles have a metabolic function.
- They can sequester substances that are harmful to cells of plants, only if they are present in the cytoplasm in bulk.
- They have a vital homeostatic function in cells of plants and these are subjected to various variations in the environment.
Read Also:






Comments