
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Plants modify their stems in a variety of ways to suit their adaptation demands. Rhizomes, bulbs, corms, and tubers are underground stems that resemble the roots of plants, but nodes and internodes, leaves, and buds distinguish them. Stems have been adapted by nature to accomplish roles like food storage, plant support, protection, and vegetative growth. Geophytes are the plants that fall within this group. Following a period of vigorous growth, both corms and bulbs require a period of rest. Bulb examples include garlic, while corm examples include crocus, gladiolus, autumn crocus, and so on.
| Table of Content |
Key takeaways: Corm, Bulb, Roots, Bud, Stems, Food
What is Corm?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Several plants have a corm, which is a swelling subterranean plant stem modification. During one growing season, Corms are designed to store nutrients and food that the plant can use later. They aid in the production of various plant parts such as roots, leaves, and flowers in preparation for the plant's next growing season.
Cormlets or individual corms are used to reproduce corms. These cormlets can be split from the parent plant to create perfect replicas. The look of corms is flattened or somewhat spherical. Under the earth, roots can sprout from the corm base. The parent corm usually dies back, and the corm lets it become the plant's source the following year. The corm collects nutrients and has membranous to scaly leaves. It preserves them for the following season. For vegetative multiplication, the corm can be separated and moved to various sections of the garden. Classic corm examples include gladiolus, crocus, and crocosmia.
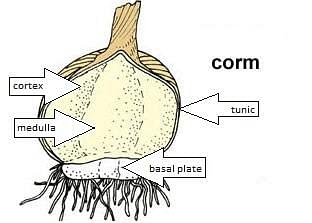
Corm
What is Bulb?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bulb is another stem alteration. This type of stem is found on most perennial monocotyledons, and it serves as a resting place for their seeds. A bulb is characterized by a huge, central bud that grows underground and is usually shaped like a globe. A bud grows from the bulb's center, producing leaves and flowers. It also has fleshy or membrane leaves that grow from a short stem. The bulb base sprouts a clump of adventitious roots. The bulb's branches emerge from the lateral buds. The leaves are where all the plant's food is stored. As the bulbs become older, they are replaced by new bulbs.
Apart from garlic, the onion is the best example of a bulb. Bulb plants include lilies, tulips, and hyacinths. Some bulbs, such as the lily, tulip, and iris, are grown for their decorative blossoms.

Bulb
Also Read: Nodes and Internode
Differnce between Corm and Bulb
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The difference between corm and bulb is listed below:
| Characteristics | Corm | Bulb |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | It may be spherical, elongated or compressed. | It may be spherical or pyriform. |
| Structure | It usually has a round and swollen stem base with scaly leaves. | It has short stems with a fleshy leaf base. |
| Type | It is underground stem modification. | It is a condensed shoot that grows underground. |
| Stem | It is enlarged and swollen. | It is of conical shape. |
| Buds | It is an external bud. | It is an internal bud. |
| Adventitious root | It is developed all over the stem. | It is developed on the ventral; side. |
| Food storage | It is in a stem. | It is in leaf base. |
| Tunic | It is absent. | It is present. |
| Nodes | Distinct circular nodes are present. | No clear cut nodes are present. |
| Cork | Corm is surrounded by cork. | Cork is absent. |
| Growth and propagation | It is usually on the sides or above the stem. | New bulbs are replaced by old ones. |
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Corm and bulb are underground stem adaptations that have been developed for food storage and to survive in harsh environments.
- Corms are swollen underground stems that serve as food storage for the plant while it is dormant.
- It has a spherical shape with a flattened base, and it grows vertically below ground.
- An underground stalk with fleshy and scale-like layers encircling a central bud is known as a bulb.
- A cluster of adventitious roots makes up the bulb's base. The bulbs' shoots emerge from the lateral buds, and their leaves have the ability to store food.
- An apical bud, located in the bulb's center, produces leaves and flowers.
Also Read:
Sample Question
Ques. What are geophytes? (2 marks)
Ques. What are sub-aerial and aerial stems? (2 marks)
Ques. What are bulbs? (4 marks)
Apart from garlic, the onion is the best example of a bulb. Bulb plants include lilies, tulips, and hyacinths. Some bulbs, such as the lily, tulip, and iris, are grown for their decorative blossoms.
Ques. What are corms? (4 marks)
Corms resemble bulbs in appearance, but they vary in that they lack the stratified scales found in bulbs. Cormlets or individual corms are used to reproduce corms. These cormlets can be split from the parent plant to create perfect replicas. The look of corms is flattened or somewhat spherical. Under the earth, roots can sprout from the corm base. The parent corm usually dies back, and the corm lets it become the plant's source the following year. The corm collects nutrients and has membranous to scaly leaves. It preserves them for the following season. For vegetative multiplication, the corm can be separated and moved to various sections of the garden. Classic corm examples include gladiolus, crocus, and crocosmia.
Ques. Write the difference between Corm and bulbs. (5 marks)
| Characteristics | Corm | Bulb |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | It may be spherical, elongated or compressed. | It may be spherical or pyriform. |
| Structure | It usually has round and swollen stem base with scaly leaves. | It has short stems with fleshy leaf base. |
| Type | It is underground stem modification. | It is a condensed shoot that grows underground. |
| Stem | It is enlarged and swollen. | It is of conical shape. |
| Buds | It is an external bud. | It is an internal bud. |
Ques. What are the functions of stem? (5 marks)
- It retains leaves, flowers, and fruits in place.
- The stem permits the leaves to be arranged in such a way that they get direct sunlight, allowing them to perform photosynthesis efficiently. Gas exchange is also possible due to the arrangement and positioning of the leaves.
- The vascular bundles of stems include xylem and phloem, which transport water and minerals throughout the plant.
- Stems produce flowers and fruits in such a way that pollination, fertilisation, and seed dispersal are made easier.
- Some stems are modified in order to store food and water. Succulents, for example.
Ques. How do corms grow and propagate? (5 marks)







Comments