
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Nuclear membrane also known as Nuclear envelope is a double membrane layer that isolates the nucleus' contents from the remainder of the cell. Both animal and plant cells contain it. The nuclear envelope protects the genetic material of the cell from chemical reactions occurring outside of the nucleus.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Cell, Animal Cell, Plant cell, nucleus, cytoplasm, nucleoplas, DNA, Genes
Read More: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
What is a Nuclear Membrane?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
All eukaryotic cells, such as those found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, have a nucleus, which serves as a command centre and stores DNA.
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is a double-layered membrane that surrounds and protects each nucleus. It is responsible for separating the nucleoplasm (the fluid within the nucleus) from the cytoplasm.
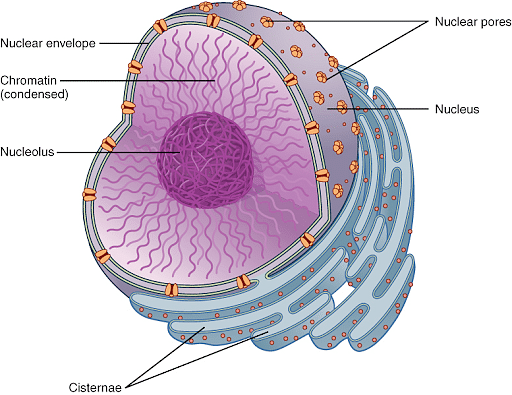
Nuclear Membrane
In both plant and animal cells, the nuclear membrane is present. Cells perform a wide range of tasks, including protein synthesis, chemical conversion to energy, and waste disposal.
This barrier protects the cells' genetic material from the outside of the nucleus, where chemical processes occur. It also contains a number of proteins that are essential for the arrangement of DNA and the regulation of genes.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant DNA Technology | Translation | Allele |
| DNA Cloning | Structure of DNA | Structure of RNA |
| Nuclues Vs Nucleoid | Chromosome Vs Chromatid | DNA Fingerprinting |
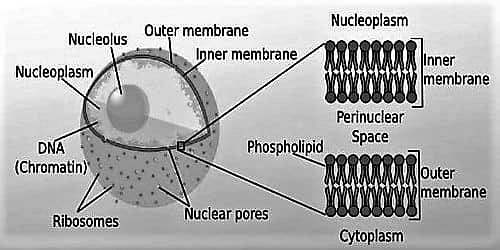
Structure of Nuclear Membrane
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
There are two membranes that make up a nuclear membrane: an inner and an outer membrane. Both membranes are made up of phospholipids arranged in a bilayer. A total of four phospholipid series make up the nuclear membrane.
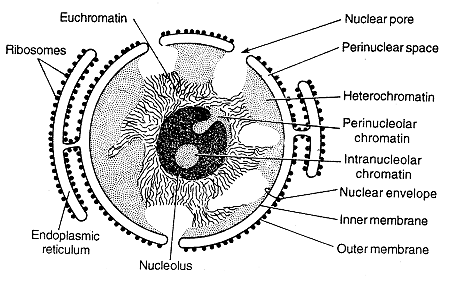
Structure of Nuclear Membrane
The outer and inner membranes are separated by the perinuclear gap. The rough endoplasmic reticulum controls the outer membrane. It is a type of organelle that aids in the movement of proteins.
The outer membrane and the rough endoplasmic reticulum, which are the real sites of protein creation, are both coated in ribosomes.
Nuclear lamina connects the nucleoplasm to the inner nuclear membrane. The nuclear lamina also secures and connects to chromatin, which is loosely organised in protein structure and DNA. The nuclear membrane is supported and strengthened by a protein layer.
Parts of Nuclear Membrane
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The nuclear membrane encloses the nucleus of the cell and is made up of the following components:
Outer Membrane
It is made up of two layers of lipid molecules. The lipids that make up the outer layer have ribosomes on the surface that connect to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Inner Membrane
It contains proteins that help to reorganise the nucleus and keep the genetic material chained together. The nuclear lamina joins the inner and outer membranes with a layer of proteins and fibres. It provides structural support for the nucleus, assists in DNA repair, and regulates cell cycle functions like cell division and DNA replication.
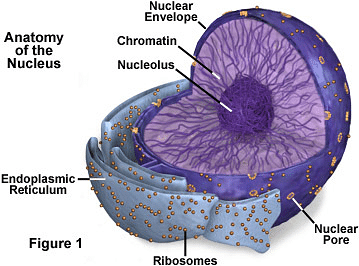
Inner Membrane
Nuclear Pores
They flow through the nuclear membrane's inner and outer membranes and are made up of huge, complicated proteins that allow a few molecules to pass through the nuclear envelope. Each nuclear pore is made up of 30 different proteins that work together to transport materials. They also connect the inner and outer membranes.
Nucleolus
These are little spherical structures that are located in the nucleus and are frequently found closer to the nuclear membrane than in a centralised location. The Nucleolus Organising Region (NOR) of chromosomes, which is known to store the genes required for full ribosome synthesis, is what distinguishes them from other nuclear materials. Ribosomal RNA subunits are encoded by them.
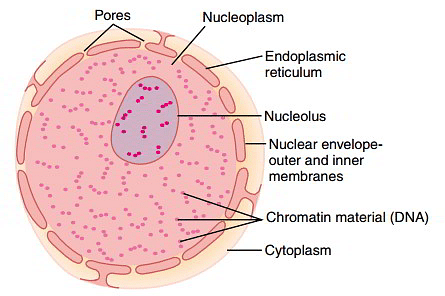
Nucleolus
Nucleoplasm
It is a form of protoplasm that is comparable to the cytoplasm and can be found all the way from the cell body to the outside of the nucleus. The nuclear hyaloplasm is a more soluble and viscous liquid element of the nucleoplasm.
Nucleoplasm
Because the nucleus performs unique duties, a separate sort of protoplasm is necessary. Water, dissolved ions, and a mixture of other components make up the nucleoplasm. This element is contained within the nuclear envelope, which contains nucleotides and critical replication enzymes.
Read More: Mitosis and Meiosis
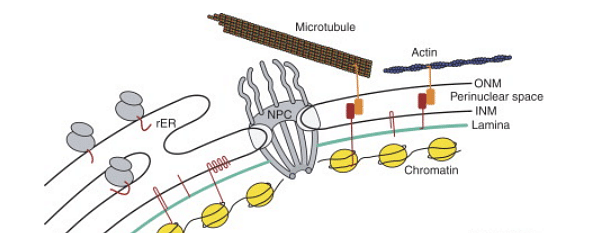
Functions of Nuclear Membrane
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The nuclear membrane serves the following critical functions:
- Nuclear pores are microscopic openings in the nuclear envelope. The pores allow the content of the nucleus to flow in and out. It also serves as a link between the exterior and interior membranes.
- During the interphase phase of cell division, the surface area of the nuclear envelope expands and doubles the nuclear pores.
Functions of Nuclear Membrane
- The nucleus is protected by a double membrane with many pores that assist and govern the crossing of macromolecules like proteins and RNA while allowing free passage of water, ions, ATP, and tiny molecules. The cell's information flow is controlled by the membrane, which is carried out by macromolecules.
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- The Nuclear Envelope, also known as the Nuclear Membrane, is a lipid-based structure that contains the hereditary material of Eukaryotic cells.
- The nucleus is surrounded by a porous framework. It is in charge of the piece of hereditary data that allows proteins and nucleic acids to enter while preserving the nucleus inside the DNA.
- The nucleus of a cell contains chromosomal material or DNA, which is referred to as chromatin. It also has a nucleolus consisting of RNA (ribonucleic acid corrosive) and proteins that help to build Ribosomes.
- Two lipid bilayer membranes surround the nucleus, which contains the genetic material, forming the nuclear membrane.
- Perinuclear space is the space between the inner and outer membranes.
- The nuclear membrane is broken during mitosis to allow the mitotic spindle fibres to adhere to the chromosomes.
- Plant nuclear membranes lack many of the proteins found in animal cell nuclear membranes. However, they do have several pore membrane proteins that are only found in plants.
- Animal cells include centrosomes, which assist and organise DNA as the cell prepares to divide.
- Plants, on the other hand, lack these structures and appear to rely solely on the nuclear membrane for cell division and organisation.
Previous Year Questions
- If you are provided with root tips of onion in your class and are asked to count the chromosomes, which of the following stages can be most conveniently looked into ?..[NEET 2004]
- Which one of the following precedes reformation of nuclear envelope during M-phase of cell cycle ?..[NEET 2004]
- Colchicine is employed to diploidize a haploid cell as it...[NEET 1996]
- The exchange of genetic material between chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes during first meiotic division is called...[NEET 1996]
- A somatic cell that has just completed the S phase of its cell cycle, as compared to gamete ofthe same species, has….[NEET 2015]
- A stage of mitosis is shown in the diagram. Which stage is it and what are its characteristics?...[NEET 2013]
- Identify the correct statement with regard to G1 phase (Gap 1)ofinterphase...[NEET 2020]
- If APC is defective in a human cell, which of the following is expected to occur ?…..[NEET 2017]
- Arrange the following events of meiosis in a proper sequence and select the correct option. I. Terminalisation II. Crossing over III. Synapsis IV. Disjunction of genome....[NEET 2015]
- Cells in G0 phase...[NEET 2019]
- Crossing over takes place between which chromatids and in which stage of the cell cycle ?...[NEET 2019]
- The microtubules from opposite poles of spindle get attached to the kinetochores of sister chromatids in...[AMUEEE 2009]
- Cell cycle includes the sequence...[AMUEEE 2014]
- Chiasmata formation takes place during…..[AMUEEE 2010]
- DNA replication takes place during...[JKCET 2015]
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the nuclear membrane's primary function? (2 marks)
Ans. The nuclear membrane encloses and protects the DNA within the nucleus from cytoplasmic chemicals. It also controls the flow of chemicals into and out of the nucleus.
Ques. What is the distinction between the cell and nuclear membranes? (2 marks)
Ans. The lipid bilayer that surrounds the entire cell is known as the cell membrane. The nucleus, on the other hand, is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. The cell membrane is made up of a continuous sheet of material. The nuclear membrane, on the other hand, is made up of a sequence of vesicles that come together to enclose the nucleus rather than a continuous sheet.
Ques. What if the nucleus didn't have a membrane? (2 marks)
Ans. The nuclear membrane keeps the nucleus in normal form and prevents cytoplasm from leaking into the nucleus. If the nuclear membrane were not present, cytoplasmic chemicals would enter the nucleus and damage a portion of the DNA. This would damage the cell's ability to operate and eventually result in cell death.
Ques. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell? (2 marks)
Ans. A prokaryotic cell is generally smaller in size (1-10 pm), the nuclear region is poorly defined, the cell organelles are not membrane-bound and has a single chromosome.
A eukaryotic cell is generally larger in size (5-100 pm), the nuclear region is well defined with a nuclear membrane. Membrane-bound cell organelles are present and has more than one chromosome.
Ques. Give the function of the nuclear membrane. (2 marks)
Ans. The nuclear membrane present as outer covering in the nucleus allows the transfer of material inside and out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Ques. What is a nucleoid? (2 marks)
Ans. The nuclear region in some cells are poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane, it contains only nucleic acid. This undefined nuclear region with nucleic acid in it is called a nucleoid.
Ques. What is the function of the nucleus in a cell? (2 marks)
Ans. The nucleus plays a very important role in the reproduction of cells. It also helps the single cell to divide and form two new daughter cells.
It plays an important role in determining how the cell will develop and what form it will exhibit at maturity, by directing the chemical activities of the cell.
Ques. Explain the following terms: (3 marks)
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Nucleus.
Ans. (a) Plasma membrane: It is a thin membrane that controls the passage of materials in and out of the cell. It is also called a selectively permeable membrane. It makes the outer boundary of the cell and is made up of lipo-protein,
(b) Cytoplasm: It is a transparent jelly-like thick substance present in the cell. It makes the ground of the cell in which all the cell organelles are suspended.
(c) Nucleus: It is a double-layered membrane structure that contains chromosomes required for the inheritance of characteristics from one generation to the other.
Ques. Write short notes on the following (2 marks)
(1) Cytoplasm
(2) Nucleus of a cell
Ans.
- The cytoplasm is the fluid present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Organelles of cells are present in the cytoplasm. These are mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc. The cytoplasm is made up of basic elements like C, H, O, and N. They are found in the form of carbohydrates, proteins and water.
- Nucleus of a cell is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. The nucleus also contains nucleolus and chromosomes. The nucleus helps in inheritance and acts as the control centre of the activities of the cell.
Ques. Name the different parts of the nucleus and give the function of each part. (2 marks)
Ans.
- Nuclear membrane- It separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. It allows the exchange of substances between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm.
- Nucleoplasm- Chromosomes and nucleoli are present in the nucleoplasm.
- Chromosomes - They play an important role in the inheritance of characters from one generation to another.
Ques. What is membrane biogenesis? (2 marks)
Ans. The endoplasmic reticulum helps in the manufacture of proteins and fat molecules or lipids which are important for cell function. These proteins and lipids help in the building of the cell membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis.
Ques. What is the difference in chromatin, chromosomes and gene? (2 marks)
Ans. (1) Chromatin: It is a fine network of thread-like structures made up of DNA or RNA. It gets condense to form chromosomes.
(2) Chromosome: The chromosomes are made from chromatin material and are located in the cell.
(3) Genes are found in chromosomes.
Also Check:





Comments