
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Haploids and diploids are the two most common types of ploidies. The female parent contributes one chromosome, while the male parent contributes the other. Each pair's two chromosomes include genetic elements that correspond to the same innate traits. Every chromosomal pair in the same cell is unique from the other chromosome pairs. The number of chromosomal sets present in a biological cell is referred to as haploid or diploid. Haploid cells only contain one set of chromosomes, whereas diploid cells have two sets. As a result, their distinctions are highlighted even further.
| Table of Contents |
Key Takeaways: Chromosomes, Mitosis, Autosomal, Reproductive System, Genetics, Haploid, Diploid.
Diploid Cells
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Diploid cell is one that contains two sets of chromosomes. Humans have twenty-three (23) pairs of chromosomes, bringing the total number of chromosomes to forty-six (46) pairs. The first twenty-two pairs are autosomal, meaning they pass along non-sexual traits, while the last pair is known as the sex chromosome. When two haploid cells fuse, a diploid cell is created. Diploid is the most common type of mammal. This means that each chromosome in a mammalian cell has two identical copies. Mitosis is used to generate these cells.
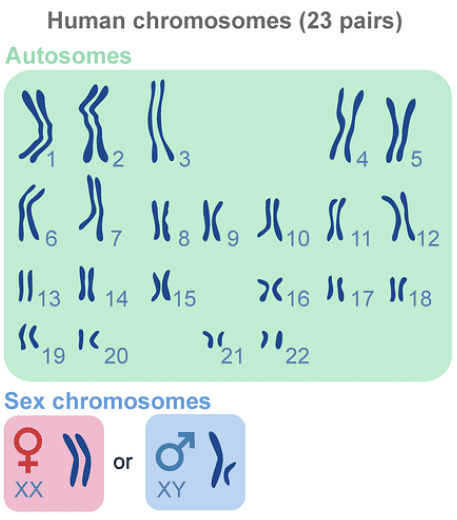
23 pairs of chromosomes
Diploid Cells make up all somatic cells in humans. It's worth noting that all cells in the body, with the exception of those in the reproductive system, are classified as somatic cells. The father passes down one set of chromosomes, while the mother passes down the other set. Also, some creatures have tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) or hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) somatic cells.
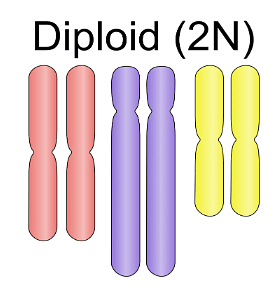
Diploid Cells
Also Read:
Haploid Cells
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Haploid cell, on the other hand, is defined as a cell with only one set of chromosomes. Haploid cells can be found in a variety of algae, as well as a few male bees, wasps, and ants. Monoploid cells relate to the number of unique chromosomes in a single biological cell, whereas haploid cells refer to the number of unique chromosomes in a single biological cell.
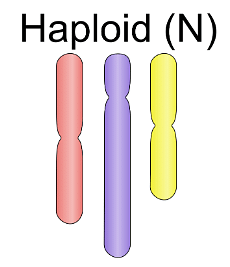
Haploid Cells
Furthermore, mitotic cell division produces diploid cells, while meiotic cell division produces haploid cells. Meiosis is a kind of cell division in which diploid cells divide to produce haploid germ cells or spores, and then the diploid germ cell divides twice again to produce four haploid cells. Meiosis is a process in which parent cells divide their chromosomal sets into two. It is only applicable to gametes or sex cells. This is why a diploid person goes through meiosis, which results in haploid offspring.
Read More: Difference between Cytogenesis and Molecular Genesis
Difference between Haploid cells and Diploid cells
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The Difference between haploid and diploid cells are listed below:
| Diploid Cell | Haploid Cell |
|---|---|
| When eukaryotes produce non-sex cells or somatic cells, this chromosomal set is produced. | When a sex cell or gamete is generated in eukaryotes, this chromosomal set is produced. |
| Mitosis cell division results in the formation of cells. | After Meiotic cell division, cells are created. |
| Because it contains two sets of homologous copies of chromosomes, the number of chromosomes is twice that of haploids. | Because it only has one set of chromosomes, it has half the number of diploids. |
| Fertilised eggs are used to create diploids. | Unfertilized eggs are used to create haploids. |
| These cells perform a critical part in an organism's growth, functionality, and development. | These cells are important for genetic diversity since they produce their own signature and are used in sexual reproduction. |
| Mammals, fish, plants | Ants, bees, wasps |
| Blood cells, skin cells, muscle cells (Somatic cells) | Male or Female Germ cells (Gametes) |
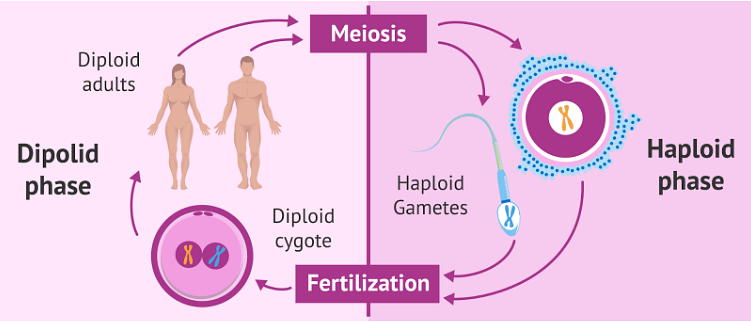
Difference between Haploid and Diploid cells
Read More:
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- A haploid cell contains only one set of chromosomes, whereas a diploid cell contains two sets.
- Humans have diploid somatic cells and haploid gametes.
- Mitotic cell division produces diploid cells; meiotic cell division produces haploid cells.
- In mitosis, a diploid cell divides twice to produce four identical daughter cells, which are referred to as haploids.
- Humans and most animal cells are considered diploid organisms, whereas algae and fungi are generally haploid organisms throughout their life cycle. Male bees, wasps, and ants are haploid as well.
- A diploid cell has 46 chromosomes in total, whereas haploid cells have 23 homologous chromosome pairs.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the definition of haploid? (2 Marks)
Ans. A cell with a single set of chromosomes is referred to as a haploid. The number of chromosomes in egg or sperm cells sometimes referred to as gametes, is also referred to as haploid. Half of the chromosomes seen in normal diploid cells, often known as somatic cells, are found in gametes.
Ques. Is a zygote haploid or diploid? (2 Marks)
Ans. The zygote has genes from both parents, making it diploid (carrying two sets of chromosomes). Except for bacteria, all species' sexual reproduction involves the combining of haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote.
Ques. What is a good example of a diploid? (2 Marks)
Ans. A cell or organism with two sets of chromosomes is referred to as a diploid. A somatic cell is an example of a cell in a diploid state. Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes, however, human haploid gametes (egg and sperm cells) have just 23.
Ques. What is the significance of haploid cells? (3 Marks)
Ans. Haploid cells are important in sexual reproduction and the creation of genetic variation. One set of chromosomes exists in haploid cells (23 Chromosomes). The most prevalent sort of Haploid Cells is Gametes or Sex Cells. Meiosis produces haploid cells, which are genetically varied as well. A Diploid Cell is formed when the Haploid Cells of the female and male mate during conception. Genetic recombination occurs as a result of gamete fusion, which leads to key differences in the evolutionary process.
Ques. In the case of diploid and haploid cells, how many chromosomes are there in a human? (3 Marks)
Ans. Haploid cells have half as many chromosomes as diploid cells. A diploid cell has 46 chromosomes, whereas a haploid cell has 23. Haploid cells include things like sperm and ova. They are Haploid because when they fuse (fertilise), the zygote has twice as many Haploid Chromosomes as the parent. Finally, human diploid cells have 46 chromosomes, while haploid cells have 23.
Ques. Mention a few organisms with both diploid and haploid cells as examples. (3 Marks)
Ans. Haploid cells have only one set of chromosomes in an organism. Haploid organisms are always those that reproduce asexually. Sexually reproducing organisms are always Diploid, and their cells have two sets of chromosomes (one from each of the parents). Eggs and sperm cells are haplotypes in humans. Frogs, fishes, humans, and the majority of plants are all diploid organisms. Bees, male ants, and wasps are only a few examples of haploid creatures.
Ques. What is the significance of diploid cells? (3 Marks)
Ans. Diploid cells play a vital role in the formation and growth of many species. Diploid cells play a crucial role in the reproductive process. Humans have two sets of chromosomes as adults. The merger of two haploid cells results in a diploid cell (gametes or Sex Cells). Mitochondria can also be seen in diploid cells. Mitochondria stores DNA, which is crucial because it contains the instructions that your cells need to make proteins that affect the body's function in a variety of ways.
Ques. Write a note on Chromosomes. (5 Marks)
Also Read:





Comments