Question:
A parallel plate capacitor with plate area A and plate separation d is filed with a dielectric material of dielectric constant K = 4. The thickness of the dielectric material is x, where \(x < d\).

Let C1 and C2 be the capacitance of the system for \(x=\frac{1}{3d}\) and \(x=\frac{2d}{3}\), respectively. If \(C_1 = 2μF\), the value of C2 is __________μF.
A parallel plate capacitor with plate area A and plate separation d is filed with a dielectric material of dielectric constant K = 4. The thickness of the dielectric material is x, where \(x < d\).

Let C1 and C2 be the capacitance of the system for \(x=\frac{1}{3d}\) and \(x=\frac{2d}{3}\), respectively. If \(C_1 = 2μF\), the value of C2 is __________μF.

Let C1 and C2 be the capacitance of the system for \(x=\frac{1}{3d}\) and \(x=\frac{2d}{3}\), respectively. If \(C_1 = 2μF\), the value of C2 is __________μF.
Updated On: Nov 13, 2024
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Correct Answer: 3
Solution and Explanation
The value of \(C_2\) is 3 μF.
Was this answer helpful?
0
1
Top Questions on electrostatic potential and capacitance
An electric charge \(10^{-6} \, \mu C\) is placed at the origin (0, 0) of an X-Y coordinate system. Two points P and Q are situated at \((\sqrt{3}, \sqrt{3}) \, \text{mm}\) and \((\sqrt{6}, 0) \, \text{mm}\) respectively. The potential difference between the points P and Q will be:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
- An infinitely long thin wire, having a uniform charge density per unit length of \(5 nC/m,\) is passing through a spherical shell of radius \(1 m\), as shown in the figure. A \(10 nC\) charge is distributed uniformly over the spherical shell. If the configuration of the charges remains static, the magnitude of the potential difference between points P and R, in Volt, is ______. [Given: In SI units \(\frac{1}{ 4πϵ0} = 9 × 10^9 , ln \ 2 = 0.7\). Ignore the area pierced by the wire.]
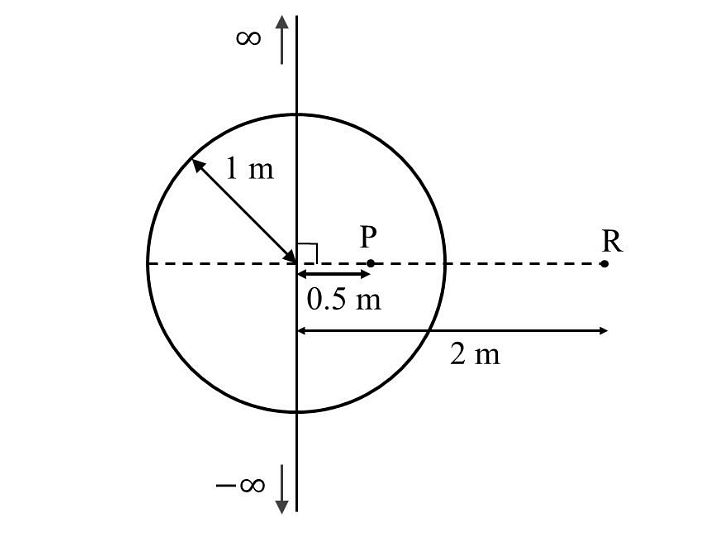
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
- An electric dipole is placed as shown in the figure.
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
- A capacitor of capacitance $900\, \mu F$ is charged by a $100\, V$ battery The capacitor is disconnected from the battery and connected to another uncharged identical capacitor such that one plate of uncharged capacitor connected to positive plate and another plate of uncharged capacitor connected to negative plate of the charged capacitor The loss of energy in this process is measured as $x \times 10^{-2} J$ The value of $x$ is ______
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
- A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plate has a capacitance of $15\, pF$ The separation between the plate becomes twice and the space between them is filled with a medium of dielectric constant $3.5$. Then the capacitance becomes $\frac{x}{4} pF$ The value of $x$ is _______
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- electrostatic potential and capacitance
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Let \( A = \{1, 2, 3, 4\} \) and \( R = \{(1, 2), (2, 3), (1, 4)\} \) be a relation on \( A \).Let \( S \) be the equivalence relation on \( A \) such that \( R \subseteq S \) and the number of elements in \( S \) is \( n \). Then, the minimum value of \( n \) is _____
- JEE Main - 2024
- Relations and functions
- Let the foci and length of the latus rectum of an ellipse \[ \frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1, \quad a > b \quad \text{be } (\pm 5, 0) \text{ and } \sqrt{50}, \] respectively. Then, the square of the eccentricity of the hyperbola \[ \frac{x^2}{b^2} - \frac{y^2}{a^2 b^2} = 1 \] equals _____
- JEE Main - 2024
- Coordinate Geometry
- If \( \alpha \) denotes the number of solutions of \( |1 - i|^x = 2^x \) and \( \beta = \frac{|z|}{\arg(z)} \), where \[ z = \frac{\pi}{4} (1 + i)^4 \left( \frac{1 - \sqrt{\pi} i}{\sqrt{\pi} + i} + \frac{\sqrt{\pi} - i}{1 + \sqrt{\pi} i} \right), \quad i = \sqrt{-1}, \] then the distance of the point \( (\alpha, \beta) \) from the line \( 4x - 3y = 7 \) is _____
- JEE Main - 2024
- complex numbers
- In the expansion of \[ (1 + x)(1 - x^2) \left( 1 + \frac{3}{x} + \frac{3}{x^2} + \frac{1}{x^3} \right)^5, \quad x \neq 0, \]the sum of the coefficients of \( x^3 \) and \( x^{-13} \) is equal to ____
- JEE Main - 2024
- Binomial theorem
Let \( \vec{a} = 3\hat{i} + \hat{j} - 2\hat{k} \), \( \vec{b} = 4\hat{i} + \hat{j} + 7\hat{k} \), and \( \vec{c} = \hat{i} - 3\hat{j} + 4\hat{k} \) be three vectors.
If a vector \( \vec{p} \) satisfies \( \vec{p} \times \vec{b} = \vec{c} \times \vec{b} \) and \( \vec{p} \cdot \vec{a} = 0 \), then \( \vec{p} \cdot (\hat{i} - \hat{j} - \hat{k}) \) is equal to- JEE Main - 2024
- Vector Algebra
View More Questions



