
Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Poles of Magnets refers to the ends of a magnet. Magnets comprise two poles known as the North Pole and the South Pole. Like poles of a magnet repel each other while the opposite poles attract each other. The forces of a magnet in a particular region refer to the magnetic field lines. The magnetic impact on moving electric currents, charges, and magnetic materials is described by a magnetic field. It is a vector quantity. In this article, we will study the magnetic poles, their orientation, the properties of magnetic field lines, and their direction.
Read More: Magnetism and Gauss’s Law
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Magnetism, Magnets, Magnetic effect, Magnetic poles, magnetic field lines, Repulsion, North Pole, South Pole
What is a Magnetic Pole?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The magnetically strong regions of magnets are referred to as "poles". When more than one magnet pole is present, they resist, pull, or attract each other. Like poles repel one another, but opposite poles always attract each other. Magnetism is the science of attraction and repulsion. There are two magnetic poles namely North Pole and the South Pole.
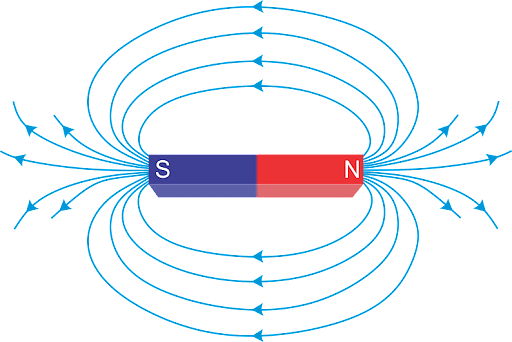
Magnetic Pole
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Spectrum | Faraday's Law | Magnetometer |
| Magnetisation and Magnetic Intensity | NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter | Magnetic Declination |
How to determine the Poles Orientation?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
When the poles of the magnet are not labeled as ‘N’ or ‘S’, we can use a few methods to determine its orientation. These are:
- One may simply identify which is the North and South Pole by placing the magnet near the compass.
- Dangling the magnet from a string is another technique to determine its orientation. When you dangle a magnet, it will naturally turn in a way that one pole points north and the other points south, which is why they are called the "North" and "South" poles.
Magnetic Field Lines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Magnetic field lines represent the effect of magnetic forces in a location. It's a diagram used to represent and comprehend magnetic field lines. They represent the direction of magnetic fields in monopoles at a regional level.
Because monopoles do not exist in nature, we use several ways to characterize field lines. One of these is the tight relationship between magnetic monopoles and electric charges. The field lines enter from the South Pole and exit from the North Pole of the magnet, according to a few norms that we have adopted.
Along the space at every point, field lines may theoretically be computed. However, it is difficult to depict it in the visual media. As a result, the density of field lines is used to represent the field strength.
Monopoles are theoretical objects that have either north or south poles. Magnetic charges, which are comparable to protons and electrons, provide another approach to examine these poles. They can be artificially manufactured since their existence is contested. It should be mentioned that monopoles diminish the electrostatic phenomena. The field lines meet at the south pole and split at the north pole.
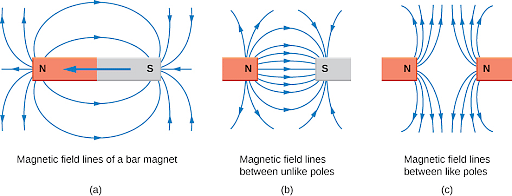
Magnetic Field Lines
Read More: Biot-Savart Law
Properties of Magnetic Field Lines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Magnetic Field Lines have the following properties:
- When outside the magnet, the magnetic field line runs from north to south.
- When within the magnet, the magnetic field line runs from the south pole to the north pole.
- Magnetic field lines look like concentric circles, with no two lines crossing.
- When magnetic field lines are close to one other, they get closer, but when they are distant from the magnet, they become further apart.
- The strength of the magnetic field is determined by the proximity of field lines.
Read More: Moving Charges and Magnetism
Direction of the Magnetic Field Lines
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are two poles in a bar magnet, one labeled as north and the other as south. The magnetic field lines form a loop and enter from the south and exit from the north. The field line of a monopole magnet emanates from the north pole and converges at the south pole. In nature, we may isolate monopole magnets and see comparable interactions in an electric field. The electric fields of charges and magnetic fields of monopoles will function similarly, and magnetic monopoles will have a comparable electric field. Whether or not poles exist, this concept retains its effect.

North and South Poles
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- There are two poles in a magnet i.e., the North Pole and the South Pole.
- Like or similar poles repel each other while the unlike poles attract each other.
- To identify the poles in a magnet, you can place a compass near it.
- Magnetic field lines move from north to south outside the magnet whereas it is vice-versa in the case of inside the magnet.
- Magnetic field lines look like concentric circles, with no two lines crossing.
- When magnetic field lines are close to one other, they get closer, but when they are distant from the magnet, they become further apart.
Sample Questions
Ques. Which material is most magnetic in nature? (1 mark)
Ans. Neodymium magnets are the strongest permanent magnets and are constructed of a neodymium, iron, and boron alloy.
Ques. Why is it difficult to magnetize a permanent magnet? (1 mark)
Ans. Permanent magnets are difficult to magnetize because their atomic magnetic domains aren't easily aligned, unlike magnetically flexible materials, but once aligned, they stay that way eternally.
Ques. What are ferromagnetic materials? (2 mark)
Ans. Ferromagnetic materials are a class of materials that, when exposed to a magnetic field, tend to express or display significant magnetism in the direction of the field. The alignment patterns of these materials' component atoms are primarily responsible for their magnetism. These atoms tend to act like basic electromagnets.
Ques. Write 3 properties of magnetic field lines. (3 mark)
Ans. The properties of magnetic field lines are:
- When within the magnet, the magnetic field line runs from the south pole to the north pole.
- Magnetic field lines look like concentric circles, with no two lines crossing.
- When magnetic field lines are close to one other, they get closer, but when they are distant from the magnet, they become further apart.
Ques. What is Curie Temperature? (1 mark)
Ans. Temperature affects ferromagnetic properties. Ferromagnetic substances become paramagnetic when heated to a high enough temperature. Curie's temperature is the temperature at which this transition happens. It is represented by TC.
Ques. How can you determine whether the pole is a North pole or the South Pole? (2 mark)
Ans. The ways to determine the orientation of magnetic poles are:
- Placing the magnet near the compass.
- Dangling the magnet from a string.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:







Comments