Question:
The compressibility factor of an ideal gas is
The compressibility factor of an ideal gas is
Updated On: Jun 14, 2022
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 6
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
compressibility factor is defined as :
$Z=\frac{P V}{(P V) \text { ideal }}=\frac{P V}{n R T}$
for non ideal gases, $ Z \neq 1$
for ideal gases. $Z=1$
$Z=\frac{P V}{(P V) \text { ideal }}=\frac{P V}{n R T}$
for non ideal gases, $ Z \neq 1$
for ideal gases. $Z=1$
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Van Der Waals equation
- Which of the following statemnt is incorect for physisorption?
- GUJCET - 2023
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- Arrange the following gases in increasing order of van der Waals constant 'a'
A. Ar
B. CH4
C. H₂O
D. C6H6
Choose the correct option from the following.- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- At low pressure, the van der Waal's equation is reduced to
- VITEEE - 2019
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- Given van der Waals constant for NH3, H2, O2 and CO2 are respectively 4.17, 0.244, 1.36 and 3.59, which one of the following gases is most easily liquefied ?
- NEET (UG) - 2018
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- If $V$ is the volume of one molecule of gas under given conditions, the van der Waal?s constant $b$ is
- BITSAT - 2018
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
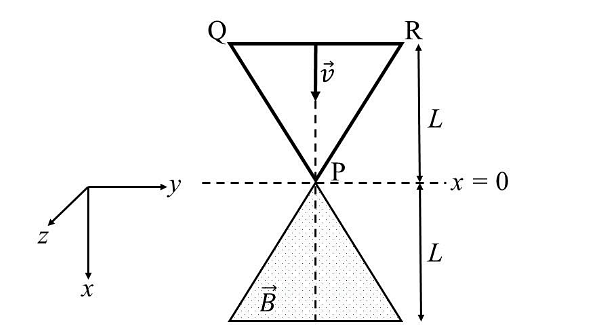
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Van Der Waals Equation
Van der Waals equation is an equation relating the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of real gases.
Read More: Derivation of Van Der Waals Equation
Derivation of Van der Waals equation:
For a real gas containing ‘n’ moles, the equation is written as
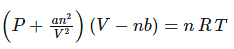
Where, P, V, T, n are the pressure, volume, temperature and moles of the gas. ‘a’ and ‘b’ constants specific to each gas.
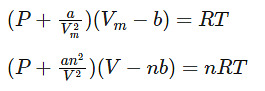
Where,
Vm: molar volume of the gas
R: universal gas constant
T: temperature
P: pressure
V: volume
Thus, Van der Waals equation can be reduced to ideal gas law as PVm = RT.
The equation can further be written as;
- Cube power of volume:
- Reduced equation (Law of corresponding states) in terms of critical constants:
Units of Van der Waals equation Constants
a: atm lit² mol-²
b: litre mol-¹



