
Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Group-17 elements are also known as halogens, the whole group is known as the “Halogen Family”. The formula for general electronic configuration for Group-17 elements is ns2np5, here n represents natural numbers. The word halogen comes from Greek roots. “Halo” means salt and “genes” means producing, thus halogens are salt-producing elements. These elements when reacted with metals produce metal halide salts.
- Halogens readily react with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals to yield halide salts.
- The general electronic configuration formula for halogens is ns2np5.
- All Group-17 elements have seven valence electrons.
Read More: Nature of C-X Bond in Haloarenes
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Group-17 Elements, Halogens, Halides, Metal Halides, Electronic Configuration, Salts.
Electronic Configuration of Group-17 Elements
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The electronic configuration for Group-17 elements is ns2np5, here n represents natural numbers. Group-17 has five elements:
- Fluorine (F)
- Bromine (Br)
- Iodine (I)
- Astatine (At)
- Tennessine (Ts)
Out of these five elements on four elements are naturally occurring elements which are- Fluorine (F), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I) and Astatine (At), whereas Tennessine (Ts) is a synthetic element.

Position of Halogens in Periodic Table
The electronic configuration of Group-17 elements is shown below-
| Electronic Configuration of Group 17 Elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Electronic Configuration |
| 2 | Fluorine | F | 9 | [He]2s22p5 |
| 3 | Chlorine | Cl | 17 | [Ne]3s23p5 |
| 4 | Bromine | Br | 35 | [Ar]3d104s24p5 |
| 5 | Iodine | I | 53 | [Kr]4d105s25p5 |
| 6 | Astatine | At | 85 | [Xe]4f145d106s26p5 |
| 7 | Tennessine | Ts | 117 | [Rn]5f146d107s27p5 |
Principles for Filling Electronic Orbitals
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The electronic configuration of an element describes the arrangement of the electrons in an orbital around the atomic nucleus. Electronic configuration helps in understanding an element's physical and chemical properties. There are certain Principles that need to be followed while filling electronic orbitals. These principles are-
- Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
- Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity
- Aufbau Principle
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have identical values for the four of their quantum numbers. Simply, it can be said that:
- Only two electrons can occupy the same orbital.
- Two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins.
Mathematically, it is given as
A(x,y) = – A(y,x)
Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity
Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity states that in a given electron configuration, every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied before any orbital is doubly occupied. The term having maximum multiplicity is the lowest in energy. This means that electron pairing in p, d, or f orbitals cannot happen unless and until every orbital of the given subshell is singly occupied.
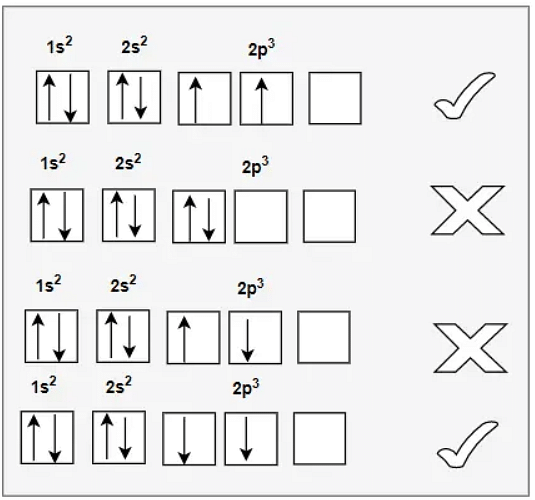
Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity
Aufbau Principle
Aufbau Principle states that in the ground state of an atom, an orbital having a lower energy state is filled before occupying orbitals having a higher energy state. The order to fill electronic orbitals is 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s and so on.

Order of filling orbitals
Interesting Facts About Group-17 Elements
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some interesting facts about Group-17 elements are-
- Halogens are highly reactive elements.
- Halogens possess high electronegativities.
- Naturally halogens occur in the form of compounds and not as pure elements.
- Fluorine is the most reactive halogen and is also considered to be a deadly gas.
- Astatine is a radioactive element.
- Astatine is utilized in medicine due to its cancer-curing properties.
- The first halogen that was discovered is chlorine.
- The name bromine is derived from the Greek word “bromos” meaning stench due to its foul odor.
- Iodine is a disinfectant and is used in antiseptics.
Things to Remember
- Group-17 elements are commonly known as Halogens.
- Group-17 has a total of five elements.
- Group-17 elements have seven electrons in their valence shells
- The general configuration of group-17 elements is ns2np5.
- Fluorine is the most electronegative element.
- Astatine and tennessine are radioactive elements.
- Tennessine is the second heaviest known element.
Check Out:
| Relevant Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Oxoacids of Halogen | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | Classification of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
Previous Year Questions
- A certain compound X when treated with copper sulphate solution yields a brown precipitate. On adding hypo solution, the precipitate turns white. The compound X is NEET - 1994
- KF combines with HF to form KHF_2. The compound contains the species: BITSAT - 2005
- Bromine is liberated, when aqueous solution of KBr is treated with: JIPMER - 1998
- Correct order of reactivity: MET - 2004
- The variation of the boiling points of the hydrogen halides is in the order HF>HI>HBr>HCl. What explains the higher boiling point of hydrogen fluoride ? NEET - 2015
- Among the following, which species represents a pseudohalide? KEAM
- The correct order of bond dissociation enthalpy of halogens is : JEE Main - 2021
Sample Questions
Ques. Write down the electronic configuration of all the Group-17 elements. (3 marks)
Ans. The electronic configuration of all the Group-17 elements is-
- The electronic configuration of fluorine is [He]2s22p5.
- The electronic configuration of chlorine is [Ne]3s23p5.
- The electronic configuration of bromine is [Ar]3d104s24p5.
- The electronic configuration of iodine is [Kr]4d105s25p5.
- The electronic configuration of astatine is [Xe]4f145d106s26p5.
- The electronic configuration of tennessine is [Rn]5f146d107s27p5.
Ques. What is the general electronic configuration of Group-17 elements? (1 mark)
Ans. The general electronic configuration of Group-17 elements is ns2np5 and n= 1,2,3 and so on.
Ques. Does Group-17 have any biological roles? (2 marks)
Ans. Yes, group-17 elements have numerous biological roles. In the human body, thyroid hormones are a class of natural iodine molecules and halogen bonds are important for their recognition. It is also an essential nutrition for animals. Chlorine is found in blood, bones, teeth, hair, and urine. Fluorine is also found in the human body.
Ques. Why does fluorine have low electron affinity compared to chlorine? (3 marks)
Ans. Fluorine is known as the most electronegative element but its electron affinity is lower compared to chlorine due to its small size. Fluorine by the virtue of its strong intermolecular forces has a small size. When an electron approaches the molecule, it faces strong repulsive forces by all the electrons. Chlorine on the other hand has a large atomic size which accommodates incoming electrons easily without much repulsive force. Thus, chlorine has a high electron affinity compared to fluorine.
Ques. What kind of bonds are formed by Halogens? (4 marks)
Ans. Halogens are responsible for forming ionic and covalent bonds. Halogens react with non-metals and bond with them by sharing electrons. The bonds are formed by sharing electrons are known as covalent bonds. Thus, halogens make covalent bonds with non-metals. For example, hydrogen chloride (HCl) also known as hydrochloric acid is an example of covalent bonding between halogen and non-metal.
Halogens when reacted with metal, bond by exchange of electrons, and such bonds are known as ionic bonds. Thus halogens form ionic bonds with metals. One such example is sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium gives one electron to chlorine to complete its octet and chlorine accepts an electron from sodium to complete its octet. Therefore the bond formed between sodium and chlorine is an ionic bond.
Ques. Why is Hydrogen fluoride a liquid at room temperature? (3 marks)
Ans. Hydrogen fluoride (HF) is a liquid at room temperature because of the high electronegativity of fluorine. Since fluorine has a high electronegativity, the hydrogen bond between hydrogen and fluorine is formed in the liquid phase. This is why only hydrogen fluoride exists as a liquid at room temperature.
Ques. What happens when Group-17 elements react with metals? Give example. (3 marks)
Ans. Group-17 elements react with metals to form metal halides. The general reaction equation is-
2M + X2 → 2MX
Some example are-
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
2K + Br2 → 2KBr
2Li + Cl2 → 2LiCl
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments