
Exams Prep Master
Bromine, the reddish-brown color gas, is the third-largest halogen and at room temperature, it appears as a fuming red-brown liquid. The characteristic of Bromine is that it does not have a pleasant smell nor does it have a pleasing color. The smell of gasses that contain bromine irritates the nostrils and also the skin. The atomic number and the symbol of bromine is Br, and 35 respectively. The mass of Br is 79.9.4 g/mol. Let’s have a detailed discussion on bromine along with some important questions.
Read more: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
| Table of Content |
Key takeaways: Bromine, third-largest halogen, fluorine, chlorine, iodine, Isotopes, Arsenic, Phosphorus, Antimony, atomic number
What is Bromine?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The halogen, bromine, was discovered by Johan Gottlieb Gahn. When observed at room temperature it is a liquid with a fuming red-brown color. It is the third-largest halogen. Other members of the halogen family are fluorine, chlorine, and iodine. Many serious health problems can be caused by bromine yet it is very useful. Bromine is the only nonmetallic element that is liquid at room temperature.

Bromine
Bromine Structure
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
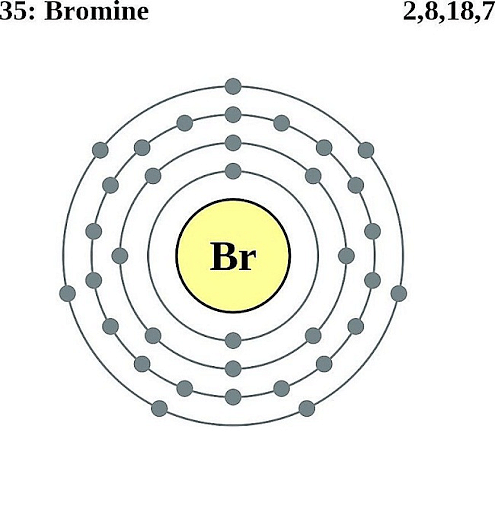
Bromine Structure
Physical Properties of Bromine
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Now that you know about Bromine let us look at the physical properties of Br. They are as follows:
- If you have to look for Br, you have to go to group 17, period 4, and block p
- The electronic configuration of Bromine is Ar 3d104s24pâµ. The atomic number mentioned above is 35.
- The melting and boiling point of Br is 266K and 332K respectively.
- The atomic weight of Br is 79.94 g/mol and the density of the element is 3.1028 g/cm3
- The color of Br is reddish brown and when seen in solid state it has a metallic luster.
- There are 29 isotopes known of Bromine, among these the two most stable isotopes are Br-79 and Br-81.
Also Read:
| Topics Related Links | ||
|---|---|---|
| Unsaturated Hydrocarbons | Boron Family | Magnesium Bromide |
Chemical Properties of Bromine
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
| Group | 17 | Melting point | −7.2°C, 19°F, 266 K |
| Period | 4 | Boiling point | 58.8°C, 137.8°F, 332 K |
| Block | p | Density (g cm−3) | 3.1028 |
| Atomic number | 35 | Relative atomic mass | 79.904 |
| State at 20°C | Liquid | Key isotopes | 79Br |
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 4s2 3d104p5 | CAS number | 7726-95-6 |
| ChemSpider ID | 4514586 | ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database | |
Now below mentioned are the chemical properties of Br:
- The electron affinity of Bromine is so high that it is equivalent to Chlorine, but the oxidizing power of Br is relatively low. The reason behind the same is the hydration of Br is relatively lower than Chloride ions.
- If you have to displace hydrogen from the saturated hydrocarbon and add it to the unsaturated hydrocarbon, then it can be done by Br. But this property is more prevalent in Chlorine.
- The reaction when observed between Br and alkali metals seems to be violent, the same when it combines with Al, Arsenic, Phosphorus, and Antimony. But with others, it reacts less violently.
- The first ionization energy of Bromine is high. The compounds like Oxygen and Fluorine which contain Br can get stabilized with appropriate ligands. All the compounds with the oxidation numbers as +1, +3, +4, +5, and +7 all form covalent bonds.
Facts about Bromine
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Bromine when found in fluid form is dangerous and the element is bleach. It can cause burns on the skin and also induces inflammatory responses in the respiratory tract of humans.
If your eye comes in contact with even a small amount that is 1ppm can lead to watering of eyes. Coughing is induced when the concentration of bromine is in concentration below 10ppm.
The rank of Br in the most abundant elements which is found in earth crust is 64th.
Also Read:
Uses of Bromine
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Even though coming in contact with Br can be dangerous when used in the appropriate amount and in the correct amount can be very useful. Some of the main uses of Bromine that have been observed are as follows:
- Bromine is used widely when it comes to the purification of water. It is said to be an alternative to chlorine. For this brominated compounds are used even in hot tubs. These compounds also help in preventing the algal and fungal growth.
- As now you know Br is poisonous it can be easily used when it comes to making pesticides.
- Brominated compounds are now used even for drug targets. These are the ingredients which can be found in analgesics, sedatives etc. Some of the drugs with brominated compounds have been observed to be helpful in curing cocaine addiction and pneumonia.
- Photography is also an area where Br is used. For obtaining the perfect photographs. If we talk about the photographic emulsion, the light sensitive part of this is made of compounds containing Bromine. This helps in adequate capturing of light for the photographs.
- It has been observed that some of the plastics also contain Bromine. The plastic which has the bromine compounds is flame resistant.
Things to Remember
- Bromine belongs to the halogen family yet has some characteristics different based on its electrode potential.
- The electronic configuration of Br is Ar 3d104s24pµ.
- Exposure to Bromine can be poisonous therefore should be handled with care.
- The location of Br is group 17, period 4, and block p.
Previous Year Questions
- Among the following oxoacids, the correct decreasing order of acidic strength is...[JEE Main 2014]
- Aluminium is usually found in +3+3 oxidation stagte. In contarast, thallium exists in +1+1 and +3+3 oxidation states. This is due to :...[JEE Main 2019]
- Which among the following is the most reactive?..[JEE Main 2015]
- Good reducing nature of H3PO2H3PO2 ttributed to the presence of:...[JEE Main 2019]
- A group 13 element 'X' reacts with chlorine gas to produce a compound XCl3.XCl3XCl3.XCl3 is electron deficient and easily reacts with NH3NH3 to form Cl3X←NH3Cl3X←NH3 adduct; however, XCl3XCl3 does not dimerise. XX is...[JEE Main 2018]
- Nitrogen and Oxygen are the main components in the atmosphere but these do not react to form oxides of nitrogen. The reaction between nitrogen and oxygen requires high temperature….[JEE Main 2015]
- C60C60, an allotrope of carbon contains :...[JEE Main 2019]
- Chlorine on reaction with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide gives :..[JEE Main 2019]
- Chlorine water on standing loses its colour and forms :….[JEE Main 2015]
- Correct statements among aa to dd regarding silicones are : (a) They are polymers with hydrophobic character (b) They are biocompatible. (c) In general, they have high thermal stability and low dielectric strenth. (d) Usually, they are resistant to oxidation and used as greases...;[JEE Main 2019]
- Diborane (B2H6)(B2H6) reacts independently with O2O2 and H2OH2O to produce, respectively….[JEE Main 2019]
- The correct order of bond dissociation enthalpy of halogens is :...[JEE Main 2021]
- Electron gain enthalpy with negative sign of fluorine is less than that of chlorine due to :...[JEE Main 2013]
- In XeO3F2XeO3F2, the number of bond pair(s), ππ-bond(s) and lone pair(s) on Xe atom respectively are :...[JEE Main 2018]
- Iodine reacts with concentrated HNO3HNO3 to yield YY along with other products. The oxidation state of iodine in YY, is :...[JEE Main 2019]
- Lithium aluminium hydride reacts with silicon tetrachloride to form :…..[JEE Main 2018]
- Xenon hexafluoride on partial hydrolysis produces compounds ?X? and ?Y?. Compounds ?X? and ?Y? and the oxidation state of Xe are respectively :...[JEE Main 2018]
- Which has trigonal bipyramidal shape ?...[JEE Main 2013]
- When metal ? MM ? is treated with NaOHNaOH, a white gelatinous precipitate ?XX? is obtained, which is soluble in excess of NaOHNaOH. Compound ?XX? when heated strongly gives an oxide which is used in chromatography as an adsorbent. The metal ?MM? is :...[JEE Main 2018]
- The least number of oxyacids are formed by :….[JEE Main 2015]
Sample Questions
Ques: Write down the electronic configuration of Br. (1 mark)
Ans: The electronic configuration of Br is Ar 3d104s24pµ
Ques: What is the position of Br in the periodic table? (1 mark)
Ans: the position of Br can be located in group 17, period 4, and block p
Ques: What are the uses of Br? (2 marks)
Ans: Some of the places where the compounds containing Br can be used are agriculture, it can be used in the swimming pools as an alternative to Chlorine. It can be used as fire retardants. Some of the Br compounds can also be used as sedatives. Sedatives are the drugs that can make you sleepy. They are a major source of analgesics and antihistamines.
Ques: where can you find Bromine? (1 mark)
Ans: Br is a naturally occurring element that can be found in the earth’s crust. The element is liquid at room temperature, you can also find them in seawater in different forms. The color of Br is brownish-red and the smell is not pleasant, somewhat like bleach.
Ques: What are the harmful effects of Bromine? (3 marks)
Ans: The poisonous nature of Br is well known. It can cause a lot of irritation and skin problems. The main target of Br is the tissue, mucous membrane, and skin. Not all exposure to Br will cause damage, but you can calculate the severity of the posing by the amount, route of exposure, and the length of Br. Chemical burns can be observed on the skin. If a large amount of inhalation of Bromine is done it can cause inflammation of the respiratory tract which will lead to choking, coughing, and shortening of breath. There can also be systemic posing in the long run due to the exposure to Bromine.
Ques: How should you handle Bromine? (2 marks)
Ans: As you know Br can be very dangerous to humans, certain measures have to be taken while handling bromine. Measures have to be taken during the transportation of Bromine. These are transported in steel tanks and have to be filled with lead. These are further protected by a metal framework. This all is done as Bromine is incompatible with many compounds both organic and inorganic.
Ques: Compare the property of Bromine with other halogens? (3 marks)
Ans: Bromine belongs to the halogen family but has properties little different in some aspects. The reactivity of Bromine is not as strong as Chlorine and Iodine. The bond energies of Br, when compared with Iodine, are higher but in comparison to Chlorine, it is lower. The oxidizing nature of Bromine is lower in comparison to Chlorine but higher when compared to Iodine. All these properties can be satisfied when observed in the standard electrode potential chart.
Ques: The two isotopes of Br are Br-79 (49.7%) and Br-81 (50.3%). Find the average atomic mass of Bromine. (3 marks)
Ans: The percentage of 79 is 49.7% and 81 is 50.3%
Average mass of an isotope = (% existence of isotope 1 * mass of isotope 1) + (% existence of the isotope 2* mass of isotope 2)/100
= (79*49.7) + (81*50.3)/100
= 3926.3/100 + 4074.3/100
= 80.006 u
Ques: How many electrons are in a Bromine atom? (1 mark)
Ans: The Br atom has 35 electrons. The distribution of electrons in the 2p orbital is 6, in 3p it is 6 and in 4p it is 5 electrons.
Ques: What is Bromine water? (1 mark)
Ans: the bromide bromate solution known by the name of Bromine water, is a yellow mixture solution. This can be prepared by mixing fumes of Bromine and water directly. As it is not safe therefore an alternative method is used. In this method breakage of sodium bromide (NaBr) in the presence of bleach and HCl.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Read:





Comments