
Content Writer
Heat and Temperature are interrelated terms, but contrary to popular belief, they are two different quantities. Heat and Temperature are closely related to each other in day-to-day applications which often leads to confusion between both terms.
- Heat is a form of energy transferred between two bodies because of a temperature difference existing between them.
- Temperature is a measure of the degree of hotness or coolness of any object.
The main difference between heat and temperature is that heat is the form of energy that transfers from a hot state to a cold state, whereas temperature is an objective measure of the heat energy contained in a body. Heat deals with thermal energy, whereas temperature is more related to molecular kinetic energy.
Key Terms: Heat, Temperature, Thermal Energy, Kinetic Energy, Joules, Kelvin, Calorimeter, Conduction, Convection, Radiation
What is Heat?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Heat is a form of thermal energy that is transferred between systems or objects with different temperatures.
- Heat increases with the increase in temperature and decreases with the decrease in temperature.
- The direction of flow of energy is from the substance of higher temperature to the substance of lower temperature.
- Heat is measured in units of energy, usually Joules or Calories.
- The SI unit of Heat is Joule.
- When atoms and molecules of a body move, they possess kinetic energy and result in the formation of heat on collision.
Example: When we put water in a vessel and put it on the stove, the water gets warm. The reason is that the molecules of water move uniformly around all directions and collide with each other, resulting in a rise in the temperature of the water.

Read More:
Heat Transfer
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Heat is a form of energy that can be transferred from one type to another. Heat Transfer takes place through three processes namely conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction
Conduction is the process of transmission of energy from one particle of the medium to another with the particles being in direct contact with each other.
Example: On ironing clothes, the heat is conducted from the iron to the clothes.

Convection
Convection is how heat flows through liquids and gases. It is the movement of fluid molecules from higher-temperature regions to lower-temperature regions.
Example: When boiling water, the denser molecules move at the bottom while lighter molecules move upwards to heat up the water.

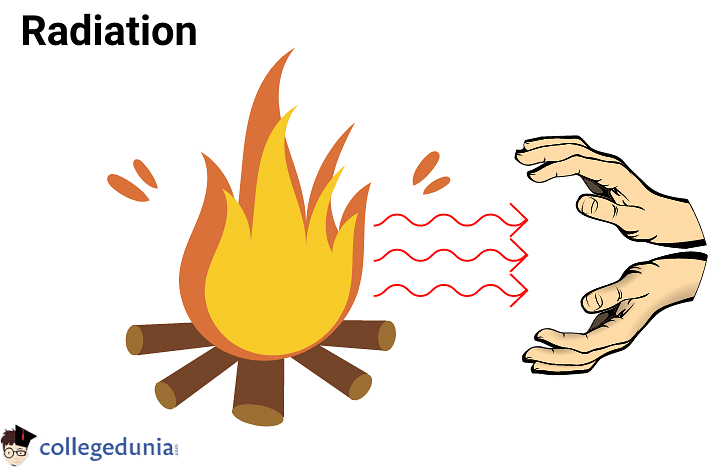
Radiation
Radiation is a process that involves the transfer of heat by means of electromagnetic waves or radio waves.
Example: Earth is heated through thermal radiation from the Sun. Another example is that our hands get heated when we try to warm them up in front of the fire.
Heat Transfer PDF: Click Here to Download
What is Temperature?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Temperature is the measure of the average heat of the molecules in a substance. It gives the degree of hotness or coldness of the substance. The magnitude of temperature indicates the average energy of molecules in the given substance. The SI unit of temperature is Kelvin.
There are two commonly used ways to measure the temperature of the body:
- Celsius Scale: In the Celsius scale, the freezing point of water is 0oC and the boiling point of water is 100oC.
- Kelvin Scale: The Kelvin scale has an absolute zero on its scale. It is denoted by K.

Conversion of Celsius to Kelvin
To convert Celsius to kelvin degrees, just add 273 to that temperature.
| K = oC + 273 |
For instance, if we have to convert 27°C to kelvin, then add 273 to it and get the resultant to 300K.
Conversion of Kelvin to Celsius
Similarly, to convert the Kelvin degree to Celsius degree, just subtract 273 from that temperature.
| oC = K – 273 |
For instance, to convert 278k to degrees Celsius. Then we subtract 273 from it, which results in 5°C.
Also Check:
Difference Between Heat and Temperature
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Though heat and temperature are often confused with each other, they are two different concepts. The differences between Heat and Temperature are as follows:
| Heat | Temperature |
|---|---|
| Heat is the amount of energy stored in an object. | Temperature is a measure of the thermal energy in a substance. |
| The SI unit of heat is Joules. | The SI unit of temperature is Kelvin. |
| The other unit for measuring heat is Calories. | The other units for measuring heat are Fahrenheit and Celsius. |
| The symbol of heat is Q. | The symbol of temperature is T. |
| Heat stored in an object depends on the mass, temperature, and material of the object. | Temperature depends on the average kinetic energy of the molecules or particles of a body. |
| Heat is measured by Calorimeter using the principle of calorimetry. | Temperature is measured using a thermometer. |
| Two bodies with a similar amount of heat can differ in their temperature. | Two bodies with a similar temperature can contain different amounts of heat energy. |
| When two bodies are in contact with each other, the sum of the heat energy of both objects would be the total heat energy. | If two objects with different temperatures are in contact with each other, the resultant temperature will be the temperature between the two temperatures. |
| Heat has the ability to do work. | Temperature is only used to measure the degree of heat. |
| Heat flows from hotter objects or regions to colder regions or objects. | Temperature increases when there is more heat and decreases when cooled. |
Things to Remember
- Heat is a form of energy while temperature is a measurement of hotness or coldness.
- Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between molecules within a system.
- Heat can be transferred in three ways namely Conduction, Convection, and Radiation.
- Temperature is the average kinetic energy of molecules within a material or system.
- Temperature can be measured on two scales namely Celsius Scale and Kelvin scale.
- The SI units of Heat and Temperature are Joule and Kelvin respectively.
- Heat is measured by a calorimeter and temperature is measured by a thermometer.
- The value of heat is always positive while the temperature can be positive as well as negative.
Previous Years’ Questions
- Consider a pair of insulating blocks with thermal resistances… [VITEEE 2019]
- Four rods with different radii r and length l are used to connect two… [NEET 2016]
- The total radiant energy per unit area, normal to the direction of incidence… [NEET 2010]
- If the radius of a star is R and it acts as a black body, what would be the… [NEET 2012]
- Certain quantity of water cools from 70∘C to 60∘C in the first 5 minutes and… [NEET 2014]
- Two metal rods 1 and 2 of the same length have the same temperature difference… [NEET 2013]
- A black body is at a temperature of… [NEET 2016]
- A body cools from a temperature of 3T to 2T in 10 minutes… [NEET 2016]
- Two rods A and B of different materials are welded together… [NEET 2017]
- A copper rod of 88cm and an aluminum rod of unknown length… [NEET 2019]
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Heat? (3 Marks)
Ans. Heat is the thermal energy that is transferred between molecules in a system due to the difference in temperature. It is the total kinetic energy and potential energy obtained by molecules in an object. Heat flows from the hotter to the colder region and has a working capacity. Heat is measured in Joules using a Calorimeter. The other unit of heat is Calories (Cal).
Ques. What is Temperature? (3 Marks)
Ans. Temperature is the thermal condition of a body that determines the direction of heat flow. The temperature of a body determines whether the body will receive heat from another body or it will give heat to the same. The SI unit of the temperature is Kelvin, but it is usually measured in Celcius and Fahrenheit. Temperature is measured using a thermometer.
Ques. State the main difference between heat and temperature. (1 Mark)
Ans. The main difference between heat and temperature is that heat is a form of energy that can be transferred from a hot to a cool temperature object while the temperature of an object measures the degree of hotness or coolness.
Ques. Convert the following into degrees Celsius.
a. 254K
b. 273K
c. 300K (2 Marks)
Ans. To convert the measures into degrees Celsius then, we have to subtract from 273.
- 273- 254 = 19°C.
- 273 – 273 = 0°C.
- 273 – 300 = -27°C
Ques. Mention the direction of the flow of heat and the methods of transmission of heat. (1 Mark)
Ans. The heat gets transferred in the direction of the higher level to the lower level. The methods for the transmission of heat are Conduction, Convection, and radiation.
Ques. How to calculate the total amount of heat energy and resultant temperature when two bodies are in contact with each other? (2 Marks)
Ans. When the two bodies are kept in contact, the total amount of heat energy is the sum of the heat energy of both objects. On the other hand, when the two bodies with different temperatures are kept in contact, then the resultant temperature will be the temperature between the two bodies.
Ques. What is the SI unit of heat and temperature? (1 Mark)
Ans. The SI unit of heat is Joules while the SI unit of Temperature is Kelvin.
Ques. How to convert Celsius into kelvin and vice versa? (3 Marks)
Ans. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, we need to add 273 to the temperature in Celsius. For example, if we need to convert 5°C to Kelvin, add 5+273 = 278. Thus, the temperature in Kelvin would be 275°K.
To convert Kelvin to Celsius, we need to subtract 273 from the number in Kelvin. For example, if we need to convert 400°K to Celsius, subtract 400 - 273 = 127. Therefore, the temperature in Celcius would be 27°C.
Ques. What are the methods of heat transfer? (3 Marks)
Ans. There are three main methods of heat transfer namely Conduction, Convection, and Radiation.
- Conduction is the process in which heat transfer happens between molecules that are in direct contact with each other without the particles moving.
- Convection is the transfer of heat because of the movement of particles from one place to another.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic or radio waves.
Ques. Give an example of heat. (2 Marks)
Ans. The boiling of water is an excellent example of heating. When we fill a container with water and place it on the stove, the container heats up. The reason for the heating up of the container is that water molecules flow in all directions equally and clash with one another. This causes the temperature of water to rise and grow hotter.
Check-Out:





Comments