Question:
Number of molecules and moles in 2.8375 litre of O2 at STP.
Number of molecules and moles in 2.8375 litre of O2 at STP.
Show Hint

Updated On: Oct 16, 2024
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Approach Solution - 1
Number of moles = 0.1266 moles
Number of molecules = 0.7625 × 1023
Number of molecules = 0.7625 × 1023
Was this answer helpful?
6
9
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Approach Solution -2
At STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure), the temperature is 273.15 K and the pressure is 1 atm.
The molar volume of any ideal gas at STP is 22.4 \(\frac{L}{mol}\).
Therefore, we can use the following formula to calculate the number of moles of O2 :
⇒ n = \(\frac{V}{V_M}\) ,
where n is the number of moles,
V is the volume of the gas (2.8375 L)
\(V_M \)is the molar volume of the gas at STP (22.4 \(\frac{L}{mol}\)).
n = \(\frac{2.8375}{22.4}\) \(\frac{L}{mol}\)
n = 0.1266 mol
We can use the Avogadro's number (6.022 x \(10^{23}\)) to calculate the number of molecules:
Number of molecules = n x \(N_A\)
where NA is Avogadro's number.
Number of molecules = 0.1266 mol x 6.022 x 1023\(\frac{L}{mol}\)
Number of molecules = 7.614 x 1022 molecules
Therefore, there are 0.1266 moles and 7.614 x 1022 molecules of O2 in 2.8375 L of \(O_2\) at STP.
Number of moles = 0.1266 moles
Number of molecules = 0.7625 × 1023
The molar volume of any ideal gas at STP is 22.4 \(\frac{L}{mol}\).
Therefore, we can use the following formula to calculate the number of moles of O2 :
⇒ n = \(\frac{V}{V_M}\) ,
where n is the number of moles,
V is the volume of the gas (2.8375 L)
\(V_M \)is the molar volume of the gas at STP (22.4 \(\frac{L}{mol}\)).
n = \(\frac{2.8375}{22.4}\) \(\frac{L}{mol}\)
n = 0.1266 mol
We can use the Avogadro's number (6.022 x \(10^{23}\)) to calculate the number of molecules:
Number of molecules = n x \(N_A\)
where NA is Avogadro's number.
Number of molecules = 0.1266 mol x 6.022 x 1023\(\frac{L}{mol}\)
Number of molecules = 7.614 x 1022 molecules
Therefore, there are 0.1266 moles and 7.614 x 1022 molecules of O2 in 2.8375 L of \(O_2\) at STP.
Number of moles = 0.1266 moles
Number of molecules = 0.7625 × 1023
Was this answer helpful?
42
25
Top Questions on States of matter
- A closed vessel contains 10 g of an ideal gas X at 300 K, which exerts 2 atm pressure. At the same temperature, 80 g of another ideal gas Y is added to it and the pressure becomes 6 atm. The ratio of root mean square velocities of X and Y at 300 K is
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Which of the following is a physical change?
- NATA - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
NaOH is deliquescent
- BITSAT - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting paiticles that will include :
A. dipole - dipole forces.B. dipole - induced dipole forces.C. hydrogen bonding.D. covalent bonding.E. dispersion forces.Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Based on the given figure, the number of correct statement/s is/are _______
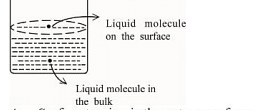
A. Surface tension is the outcome of equal attractive and repulsive forces acting on the liquid molecule in bulk
B. Surface tension is due to uneven forces acting on the molecules present on the surface
C. The molecule in the bulk can never come to the liquid surface
D. The molecules on the surface are responsible for vapour pressure if the system is a closed system- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Let \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}, \quad \vec{b} = -\hat{i} - 8\hat{j} + 2\hat{k}, \quad \text{and} \quad \vec{c} = 4\hat{i} + c_2\hat{j} + c_3\hat{k} \]be three vectors such that \[\vec{b} \times \vec{a} = \vec{c} \times \vec{a}.\]If the angle between the vector $\vec{c}$ and the vector $3\hat{i} + 4\hat{j} + \hat{k}$ is $\theta$, then the greatest integer less than or equal to $\tan^2 \theta$ is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- 10 mL of gaseous hydrocarbon on combustion gives 40 mL of CO\(_2\)(g) and 50 mL of water vapour. The total number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon is ______ .
- JEE Main - 2024
- Hydrocarbons
- If each term of a geometric progression \( a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots \) with \( a_1 = \frac{1}{8} \) and \( a_2 \neq a_1 \), is the arithmetic mean of the next two terms and \( S_n = a_1 + a_2 + \dots + a_n \), then \( S_{20} - S_{18} \) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Arithmetic Mean
A body of mass 1000 kg is moving horizontally with a velocity of 6 m/s. If 200 kg extra mass is added, the final velocity (in m/s) is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- speed and velocity
- $\textbf{Choose the correct statements about the hydrides of group 15 elements.}$
A. The stability of the hydrides decreases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 > \text{PH}_3 > \text{AsH}_3 > \text{SbH}_3 > \text{BiH}_3\)
B. The reducing ability of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
C. Among the hydrides, \(\text{NH}_3\) is a strong reducing agent while \(\text{BiH}_3\) is a mild reducing agent.
D. The basicity of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
Choose the most appropriate from the option given below:- JEE Main - 2024
- p -Block Elements
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
States of Matter
The matter is made up of very tiny particles and these particles are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
There are three States of Matter:
The three states of matter are as follows:
Solid State:
- The solid-state is one of the fundamental states of matter.
- Solids differ from liquids and gases by the characteristic of rigidity.
- The molecules of solids are tightly packed because of strong intermolecular forces; they only oscillate about their mean positions.
Liquid State:
- The molecules in a liquid are closely packed due to weak intermolecular forces.
- These forces are weaker than solids but stronger than that of gases.
- There is much space in between the molecules of liquids which makes their flowing ability easy.
Gaseous State:
- In this state of matter, distances between the molecules are large (intermolecular distance is in the range of 10-7-10-5 cm.
- The intermolecular forces experienced between them are negligible.
- Thus, translatory, rotatory and vibratory motions are observed prominently in gases.



