Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting paiticles that will include :
A. dipole - dipole forces. B. dipole - induced dipole forces. C. hydrogen bonding. D. covalent bonding. E. dispersion forces. Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting paiticles that will include :
A, B, C, D are correct.
A, B, C, E are correct.
A, C, D, E are correct.
B, C, D, E are correct.
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
When two or more molecules are attracted to one another, this is known as intermolecular forces.
Dipole-dipole attraction occurs when two or more polar molecules come into contact.
Dipole-induced dipole (attraction of polar and nonpolar molecules).
Dipole-dipole and ion-dipole attraction have a unique form called hydrogen bonding.
Dispersion forces (which primarily function between non-polar molecules).
Covalent bonds (which take place between atoms rather than between molecules).
Therefore, The correct option is (B): A, B, C, E are correct.
Top Questions on States of matter
- A closed vessel contains 10 g of an ideal gas X at 300 K, which exerts 2 atm pressure. At the same temperature, 80 g of another ideal gas Y is added to it and the pressure becomes 6 atm. The ratio of root mean square velocities of X and Y at 300 K is
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Number of molecules and moles in 2.8375 litre of O2 at STP.
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Which of the following is a physical change?
- NATA - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
NaOH is deliquescent
- BITSAT - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Based on the given figure, the number of correct statement/s is/are _______
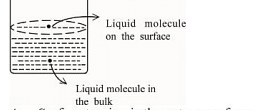
A. Surface tension is the outcome of equal attractive and repulsive forces acting on the liquid molecule in bulk
B. Surface tension is due to uneven forces acting on the molecules present on the surface
C. The molecule in the bulk can never come to the liquid surface
D. The molecules on the surface are responsible for vapour pressure if the system is a closed system- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- A thin flat circular disc of radius 4.5 cm is placed gently over the surface of water. If surface tension of water is 0.07 Nm-1, then the excess force required to take it away from the surface is :
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Surface tension
- Which of the following are required for the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
A. Light
B. Chlorophyll
C. CO2
D. ATP
E. NADPH
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
- If \(x=5\sin(\pi i+\frac{\pi}{3})m\) represents the motion of a particle executing simple harmonic motion, the amplitude and time period of motion, respectively, are :
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- simple harmonic motion
- The highest number of helium atoms is in
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Electronic configuration of atoms and ions
- \(^{290}_{82}X\stackrel{\alpha}{\rightarrow}Y\stackrel{e^+}{\rightarrow}Z\stackrel{\beta^-}{\rightarrow}P\stackrel{e^-}{\rightarrow}Q\)
In the nuclear emission stated above, the mass number and atomic number of the product Q respectively, are :- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Nuclear physics
Concepts Used:
States of Matter
The matter is made up of very tiny particles and these particles are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
There are three States of Matter:
The three states of matter are as follows:
Solid State:
- The solid-state is one of the fundamental states of matter.
- Solids differ from liquids and gases by the characteristic of rigidity.
- The molecules of solids are tightly packed because of strong intermolecular forces; they only oscillate about their mean positions.
Liquid State:
- The molecules in a liquid are closely packed due to weak intermolecular forces.
- These forces are weaker than solids but stronger than that of gases.
- There is much space in between the molecules of liquids which makes their flowing ability easy.
Gaseous State:
- In this state of matter, distances between the molecules are large (intermolecular distance is in the range of 10-7-10-5 cm.
- The intermolecular forces experienced between them are negligible.
- Thus, translatory, rotatory and vibratory motions are observed prominently in gases.



