In a galvanic cell, the salt bridge
- does not participate chemically in the cell reaction
- stops the diffusion of ions from one electrode to another
- is necessary for the occurrence of the cell reaction
- ensures mixing of the two electrolytic solutions
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
In a galvanic cell, the salt bridge does not participate chemically in the cell reaction. The salt bridge is a device used to provide electrical contact between the two solutions and therefore it completes the electrical circuit. In other words, it connects the oxidation and reduction half-cells of a galvanic cell. It maintains electrical neutrality in both the solutions by a flow of ions.
The ions of the electrolyte present in the salt bridge neither react with the ions of the electrode solutions, nor gets oxidized or reduced at the electrodes. In the absence of salt bridge, the solution in one-half would accumulate positive charge and the other half would accumulate negative charge, which will eventually result in preventing the reaction and thus electricity generation.
Top Questions on Electrochemistry
- The amount of electricity in Coulomb required for the oxidation of 1 mol of \( \text{H}_2\text{O} \) to \( \text{O}_2 \) is \[\_ \times 10^5 \, \text{C}.\]
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- The strongest reducing agent amont the following is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- A conductivity cell with two electrodes (dark side) are half filled with infinitely dilute aqueous solution of a weak electrolyte. If volume is doubled by adding more water at constant temperature, the molar conductivity of the cell will -

- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- How can an electrochemical cell be converted into an electrolytic cell ?
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- For the electrochemical cell
M|M$^{2+}$||X$^{2-}$|X
If $E^0_{(M^{2+}/M)} = 0.46$ V and $E^0_{(X/X^{2-})} = 0.34$ V.
Which of the following is correct?- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A closed vessel contains 10 g of an ideal gas X at 300 K, which exerts 2 atm pressure. At the same temperature, 80 g of another ideal gas Y is added to it and the pressure becomes 6 atm. The ratio of root mean square velocities of X and Y at 300 K is
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- States of matter
- Let the function \(f:[1,\infin)→\R\) be defined by
\(f(t) = \begin{cases} (-1)^{n+1}2, & \text{if } t=2n-1,n\in\N, \\ \frac{(2n+1-t)}{2}f(2n-1)+\frac{(t-(2n-1))}{2}f(2n+1) & \text{if } 2n-1<t<2n+1,n\in\N. \end{cases}\)
Define \(g(x)=\int\limits_{1}^{x}f(t)dt,x\in(1,\infin).\) Let α denote the number of solutions of the equation g(x) = 0 in the interval (1, 8] and \(β=\lim\limits_{x→1+}\frac{g(x)}{x-1}\). Then the value of α + β is equal to _____.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Integral Calculus
- A dimensionless quantity is constructed in terms of electronic charge \(e\), permittivity of free space \(\epsilon_0\) , Planck’s constant ℎ, and speed of light c. If the dimensionless quantity is written as \(e^\alpha\epsilon_0^\beta h^\gamma c^\delta\)and n is a non-zero integer, then\((\alpha, \beta,\gamma,\delta)\) is given by
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
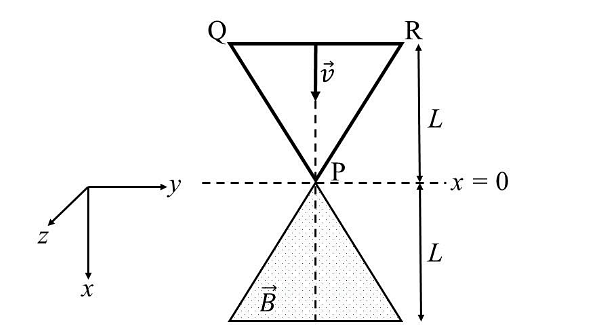
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0?
Concepts Used:
Electrochemical Cells
An electrochemical cell is a device that is used to create electrical energy through the chemical reactions which are involved in it. The electrical energy supplied to electrochemical cells is used to smooth the chemical reactions. In the electrochemical cell, the involved devices have the ability to convert the chemical energy to electrical energy or vice-versa.
Classification of Electrochemical Cell:
Cathode
- Denoted by a positive sign since electrons are consumed here
- A reduction reaction occurs in the cathode of an electrochemical cell
- Electrons move into the cathode
Anode
- Denoted by a negative sign since electrons are liberated here
- An oxidation reaction occurs here
- Electrons move out of the anode
Types of Electrochemical Cells:
Galvanic cells (also known as Voltaic cells)
- Chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy.
- The redox reactions are spontaneous in nature.
- The anode is negatively charged and the cathode is positively charged.
- The electrons originate from the species that undergo oxidation.
Electrolytic cells
- Electrical energy is transformed into chemical energy.
- The redox reactions are non-spontaneous.
- These cells are positively charged anode and negatively charged cathode.
- Electrons originate from an external source.



