The reduction potential \(\left(E^0, in\ V\right)\) of \(MnO _4^{-}( aq ) / Mn ( s )\) is\(\left[ Given : E_{\left( MnO _4^-( aq ) / MnO _2( s )\right)}^0=1.68 V ; E_{\left( MnO _2( s )/ Mn ^{2+}( aq )\right)}^0=1.21 V ; E_{\left( Mn ^2( aq ) / Mn ( s )\right)}^0=-1.03 V \right]\)
Correct Answer: 0.77
Approach Solution - 1
The correct answer is 0.77
Approach Solution -2
The reduction potential (E⁰) of MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s) is indeed 0.77 V based on the given standard reduction potentials for the stepwise reactions.
Here's how to calculate it:
We can utilize the concept of standard reduction potentials to determine the overall reduction potential of a multi-step reaction. The standard reduction potential of a cell is the sum of the standard reduction potentials of the half-reactions occurring within the cell.
In this case, the reduction of MnO₄⁻ to Mn(s) involves two sequential steps:
- MnO₄⁻(aq) + 4H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → MnO₂(s) + 2H₂O(ℓ) (E⁰ = 1.68 V)
- MnO₂(s) + 4H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Mn²⁺(aq) + 2H₂O(ℓ) (E⁰ = 1.21 V)
To obtain the overall reduction potential for MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s), we need to consider the following:
- The final product in the first half-reaction (MnO₂) becomes the reactant in the second half-reaction.
- Electrons are gained (reduction) in both half-reactions.
Therefore, to get the overall reduction potential, we can directly sum the standard reduction potentials of the two half-reactions:
E⁰ (MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s)) = E⁰ (step 1) + E⁰ (step 2)
E⁰ (MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s)) = 1.68 V + 1.21 V = 2.89 V
However, there's a catch!
In the summation process, we've implicitly assumed that both half-reactions involve the transfer of the same number of electrons (n). In this case, both half-reactions involve the transfer of 2 electrons (n = 2).
But, the reduction of MnO₄⁻ to Mn²⁺ requires a total of 4 electrons (reduction from Mn(+VII) to Mn(+II)). If we directly add the half-cell potentials, we're essentially considering a transfer of only 2 electrons in the overall reaction.
To account for the total electron transfer (n = 4), we need to divide the sum of the half-cell potentials by the number of electrons transferred (n) in the overall reaction:
E⁰ (MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s)) = (1.68 V + 1.21 V) / (2)
E⁰ (MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s)) = 2.89 V / 2 = 0.77 V
Therefore, the corrected reduction potential (E⁰) of MnO₄⁻(aq) / Mn(s) is 0.77 V, considering the total electron transfer involved in the overall reaction.
Top Questions on Electrochemistry
- What is the numerical value of one Faraday in Coulombs?
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Read the following passage and answer the next five questions based on it.
Battery or cell converts chemical energy of the redox reaction to electrical energy. In fuel cells (a galvanic cell), the chemical energy of combustion of fuels like H2, ethanol, etc., is directly converted to electrical energy. In a fuel cell, H2 and O2 react to produce electricity, where H2 gas is oxidized at the anode and oxygen is reduced at the cathode, and the reactions involved are:
Anode reaction: H2 + 2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Cathode reaction: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
67.2 L of H2 at STP reacts in 15 minutes.
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- In the cell reaction
P+(𝑎𝑞)+Q(𝑠)→P(𝑠)+Q+(𝑎𝑞)
the EMF of the cell, 𝐸𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑙 is zero. The standard EMF of the cell, 𝐸𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑙 is
[Given:
Activities of all solids are unity.
Activity of P+(𝑎𝑞) is 2 M. Activity of Q+(𝑎𝑞) is 1 M.
𝑅 = universal gas constant; 𝑇 = temperature; 𝐹 = Faraday constant]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- A salt QCl of a certain metal Q is electrolyzed to its elements. 40 g of metal Q is formed at an electrode. The volume of Cl2 formed at the other electrode at 1 atm pressure and 298 K is _______ litres. (rounded off to one decimal place)
[Given: The gas constant 𝑅 = 0.082 L atm mol−1 K−1 , the molar mass of Q is 40 g mol−1 and Cl2 is assumed to be an ideal gas]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Mobility of ions Li+ , Na+ , K+ , Ag+ in water at 298 K follows the order
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
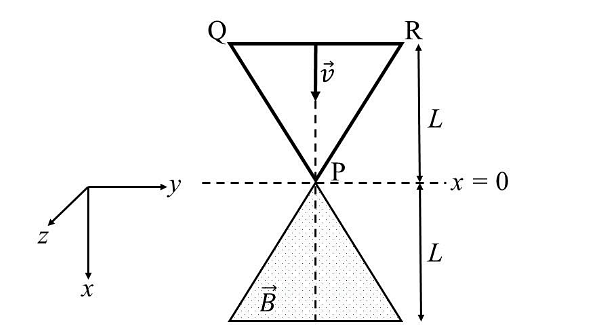
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Electrochemical Cells
An electrochemical cell is a device that is used to create electrical energy through the chemical reactions which are involved in it. The electrical energy supplied to electrochemical cells is used to smooth the chemical reactions. In the electrochemical cell, the involved devices have the ability to convert the chemical energy to electrical energy or vice-versa.
Classification of Electrochemical Cell:
Cathode
- Denoted by a positive sign since electrons are consumed here
- A reduction reaction occurs in the cathode of an electrochemical cell
- Electrons move into the cathode
Anode
- Denoted by a negative sign since electrons are liberated here
- An oxidation reaction occurs here
- Electrons move out of the anode
Types of Electrochemical Cells:
Galvanic cells (also known as Voltaic cells)
- Chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy.
- The redox reactions are spontaneous in nature.
- The anode is negatively charged and the cathode is positively charged.
- The electrons originate from the species that undergo oxidation.
Electrolytic cells
- Electrical energy is transformed into chemical energy.
- The redox reactions are non-spontaneous.
- These cells are positively charged anode and negatively charged cathode.
- Electrons originate from an external source.



