\(∫\frac{dx}{e^x+e^{-x}}\) is equal to
Show Hint
Let's go through the steps to solve the integral using the substitution method
Given:
\[I = \int \frac{dx}{e^x + e^{-x}}\]
First, rewrite the integrand:
\[I = \int \frac{dx}{e^x + e^{-x}} = \int \frac{dx}{e^x \left(1 + e^{-2x}\right)}\]
Now, make the substitution \( e^x = t \). Therefore, \( dx = \frac{dt}{t} \):
Substitute \( e^x = t \) into the integral:
\[I = \int \frac{dt/t}{t(1 + t^{-2})} = \int \frac{dt}{t^2 + 1}\]
This simplifies to:
\[I = \int \frac{dt}{1 + t^2}\]
The integral of \(\frac{1}{1 + t^2}\) is the arctangent function:
\[I = \arctan(t) + C\]
Now, substitute back \( t = e^x \):
\[I = \arctan(e^x) + C\]
Therefore, the integral \(\int \frac{dx}{e^x + e^{-x}}\) is:
\[I = \arctan(e^x) + C\]
Hence, the correct Answer is Option A\(=tan^{-1}(e^x)+C\)
\(tan^{-1}(e^x)+C\)
\(tan^{-1}(e^{-x})+C\)
\(tan^{-1}(e^x-e^{-x})+C\)
\(log(e^x+e^{-x})+C\)
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is A:\(=tan^{-1}(e^x)+C\)
Let \(I=∫\frac{dx}{e^x+e^{-x}}dx=∫\frac{e^x}{e^{2x}+1}dx\)
Also,let \(e^x=t⇒e^x dx=dt\)
\(∴I=∫\frac{dt}{1+t^2}\)
\(=tan^{-1}+C\)
\(=tan^{-1}(e^x)+C\)
Hence,the correct Answer is A.
Top Questions on integral
- Let $f : (0, \infty) \to \mathbb{R}$ and $F(x) = \int_{0}^{x} tf(t) \, dt$. If $F(x^2) = x^4 + x^5$, then \[\sum_{r=1}^{12} f(r^2)\]is equal to:
- If \[\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{3}} \cos^4 x \, dx = a\pi + b\sqrt{3},\]where $a$ and $b$ are rational numbers, then $9a + 8b$ is equal to:
- The value of \[\int_{0}^{1} \left(2x^3 - 3x^2 - x + 1\right)^{\frac{1}{3}} \, dx\]is equal to:
- Let \( r_k = \frac{\int_{0}^{1} (1 - x^7)^k \, dx}{\int_{0}^{1} (1 - x^7)^{k+1} \, dx}, \, k \in \mathbb{N} \). Then the value of \[ \sum_{k=1}^{10} \frac{1}{7(r_k - 1)}\]is equal to ______.
- \( \int_{0}^{\pi/4} \frac{\cos^2 x \sin^2 x}{\left( \cos^3 x + \sin^3 x \right)^2} \, dx \) is equal to:
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- Find the inverse of each of the matrices,if it exists \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ 7 & 4 \end{bmatrix}\)
- For what values of x,\(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)\(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 0\\ 2 & 0 & 1 \\1&0&2 \end{bmatrix}\)\(\begin{bmatrix} 0 \\2\\x\end{bmatrix}\)=O?
What is the Planning Process?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2023
- Planning process steps
- Find the inverse of each of the matrices,if it exists. \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3\\ 5 & 7 \end{bmatrix}\)
- Find the inverse of each of the matrices, if it exists. \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3\\ 2 & 7\end{bmatrix}\)
Concepts Used:
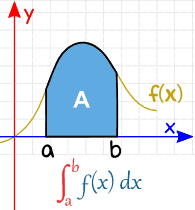
Definite Integral
Definite integral is an operation on functions which approximates the sum of the values (of the function) weighted by the length (or measure) of the intervals for which the function takes that value.
Definite integrals - Important Formulae Handbook
A real valued function being evaluated (integrated) over the closed interval [a, b] is written as :
\(\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx\)
Definite integrals have a lot of applications. Its main application is that it is used to find out the area under the curve of a function, as shown below: