Question:
According to kinetic theory of gases
According to kinetic theory of gases
Updated On: May 20, 2024
- collisions are always elastic
- heavier molecules transfer more momentum to the wall of the container
- only a small number of molecules have very high velocity
- between collisions, the molecules move in straight lines with constant velocities
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
(a) According to a postulate of kinetic theory of gases, collision between the molecules as well as with the wall of container is perfectly elastic in nature.
(b) If a gas molecule of mass m moving with speed u collide to the wall of container, the change in momentum is $\Delta $p = - 2mu. Therefore, heavier molecule will transfer more momentum to the wall as there will be greater change in momentum of the colliding gas molecule. However, this is not postulated in kinetic theory.
(c) According to Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of molecular speed, very few molecules have either very high or very low speeds. Most of the molecules moves in a specific, intermediate speed range.
(d) According to kinetic theory of gases, a gas molecule moves in straight line unless it collide with another molecule or to the wall of container and change in momentum is observed only after collision.
(b) If a gas molecule of mass m moving with speed u collide to the wall of container, the change in momentum is $\Delta $p = - 2mu. Therefore, heavier molecule will transfer more momentum to the wall as there will be greater change in momentum of the colliding gas molecule. However, this is not postulated in kinetic theory.
(c) According to Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of molecular speed, very few molecules have either very high or very low speeds. Most of the molecules moves in a specific, intermediate speed range.
(d) According to kinetic theory of gases, a gas molecule moves in straight line unless it collide with another molecule or to the wall of container and change in momentum is observed only after collision.
Was this answer helpful?
0
1
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Approach Solution -2
According to the principles of the kinetic theory of gases, gas molecules interact by colliding with each other and with the walls of their container. These collisions are completely elastic, meaning that no energy is lost during the interaction.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on States of matter
- A closed vessel contains 10 g of an ideal gas X at 300 K, which exerts 2 atm pressure. At the same temperature, 80 g of another ideal gas Y is added to it and the pressure becomes 6 atm. The ratio of root mean square velocities of X and Y at 300 K is
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Number of molecules and moles in 2.8375 litre of O2 at STP.
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Which of the following is a physical change?
- NATA - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
NaOH is deliquescent
- BITSAT - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting paiticles that will include :
A. dipole - dipole forces.B. dipole - induced dipole forces.C. hydrogen bonding.D. covalent bonding.E. dispersion forces.Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Chemistry
- States of matter
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let the function \(f:[1,\infin)→\R\) be defined by
\(f(t) = \begin{cases} (-1)^{n+1}2, & \text{if } t=2n-1,n\in\N, \\ \frac{(2n+1-t)}{2}f(2n-1)+\frac{(t-(2n-1))}{2}f(2n+1) & \text{if } 2n-1<t<2n+1,n\in\N. \end{cases}\)
Define \(g(x)=\int\limits_{1}^{x}f(t)dt,x\in(1,\infin).\) Let α denote the number of solutions of the equation g(x) = 0 in the interval (1, 8] and \(β=\lim\limits_{x→1+}\frac{g(x)}{x-1}\). Then the value of α + β is equal to _____.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Integral Calculus
- A dimensionless quantity is constructed in terms of electronic charge \(e\), permittivity of free space \(\epsilon_0\) , Planck’s constant ℎ, and speed of light c. If the dimensionless quantity is written as \(e^\alpha\epsilon_0^\beta h^\gamma c^\delta\)and n is a non-zero integer, then\((\alpha, \beta,\gamma,\delta)\) is given by
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
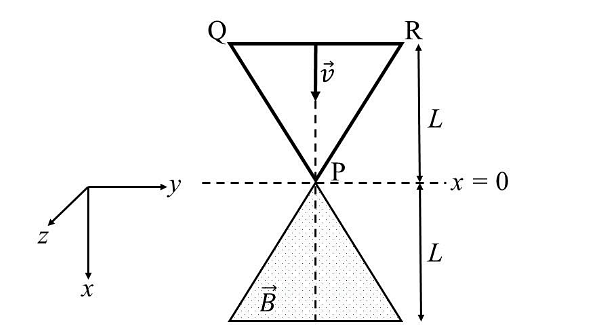
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
States of Matter
The matter is made up of very tiny particles and these particles are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
There are three States of Matter:
The three states of matter are as follows:
Solid State:
- The solid-state is one of the fundamental states of matter.
- Solids differ from liquids and gases by the characteristic of rigidity.
- The molecules of solids are tightly packed because of strong intermolecular forces; they only oscillate about their mean positions.
Liquid State:
- The molecules in a liquid are closely packed due to weak intermolecular forces.
- These forces are weaker than solids but stronger than that of gases.
- There is much space in between the molecules of liquids which makes their flowing ability easy.
Gaseous State:
- In this state of matter, distances between the molecules are large (intermolecular distance is in the range of 10-7-10-5 cm.
- The intermolecular forces experienced between them are negligible.
- Thus, translatory, rotatory and vibratory motions are observed prominently in gases.



