
Content Curator
Cell Biology deals with the study of cells and its related functions. It majorly studies the cell pertaining to the aspect of their shape, size, types, composition, division, and growth. A cell is the basic and fundamental unit of life, which acts as a building block of organisms. Cells combine together to form a tissue, tissues combine together to form an organ, organs together form an organ system, organ systems and rest of the components then form an organism. Hence, a cell is the basic unit of life.
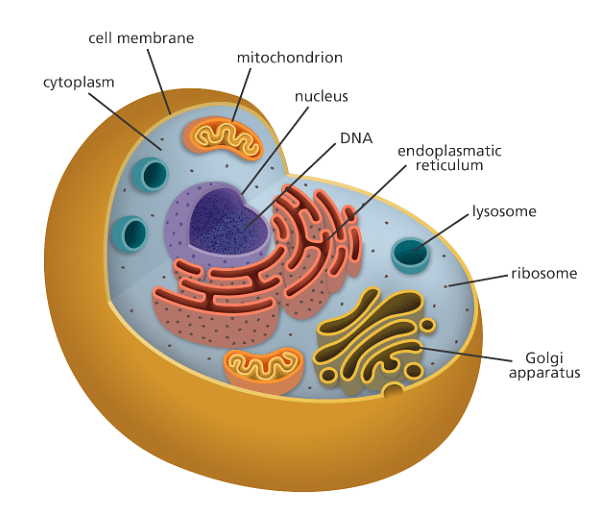
Cell Diagram
An organism can be made up of a single cell (a Unicellular organism) or many cells (Multicellular organisms). Cells are the fundamental and structural units of life. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek was the first scientist who noticed and termed the unit as a cell. The discovery of microscopes and other instruments then further helped to determine the structural components of the cell. Robert Hook later coined the term ‘nucleus’.
MCQs based on Cell Biology
Ques. What is a cell?
- The largest and basic unit of life
- Smallest and advanced unit of life
- The smallest and basic unit of life
- Largest and advanced unit of life
Click here for the answer
Ans. c) the smallest and basic unit of life.
Explanation - The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. All living things are made up of cells or groups of cells and are responsible for all the functions of life. All living organisms have cells that function as structural, functional, and biological units.
Also, read - Cell Structure
Ques. Who discovered the cell and when?
- Schwann in 1885
- Tatum in 1664
- Robert Hooke in 1665
- De Bary in 1760
Click here for the answer
Ans. c) Robert Hooke in 1965
Explanation - The cell was discovered by English botanist Robert Hooke in 1665. He used his microscope to look at cork fragments at that time. He said that the cell has a rich and fascinating history that has given many areas of modern scientific development.
Also, read - Discovery of Cell
Ques. Which of the following organisms do not have a cell?
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Algae
Click here for the answer
Ans. a) Virus
Explanation - Viruses do not have cells in them because they cannot reproduce on their own (without a host), so viruses are not considered living. Therefore, they are much smaller than living cells, and they are just packages of nucleic acids and proteins. They do not have cell membranes or other organelles (for example, ribosomes or mitochondria) that cells usually have.
Also, read - Pathogens
Ques. Who has given the cell theory?
- Robert Hooke
- Schwann and Schleiden
- Darwin and Wallace
- Watson and Crick
Click here for the answer
Ans. b) Schwann and Schleiden
Explanation - In 1838, Matthias Schleiden, a German botanist, examined a large number of plants and discovered that all plants are made up of different types of cells that make up plant tissue. Schwann (1839), a British zoologist, studied the different types of animal cells and reported that the cells have a thin outer layer today known as the ‘plasma membrane’. Therefore, Schleiden and Schwann together form a cell theory.
- What is cell biology?
- Study of plant cell
- Study of cancerous cell
- Examine of cell structure
- Study of cell structure and function
Ans. d) Study of cell structure and function
Explanation - Cell biology is the study of the structure and function of cells, and it revolves around the notion that a cell is a basic unit of life. Focusing on the cell allows for a more detailed understanding of the tissues and organisms involved in the cells. Therefore, the science of cell biology focuses on the cell structure and function of cells, ranging from the normal functions assigned to all cells to highly complex functions.
Ques. Which of the following cell organelles is present in plant cells but absent in animal cells?
- Mitochondria
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Cell wall
Ans. d) cell wall
Explanation - Animal cells do not have cell walls because they do not need them. The cell walls, which are found in plant cells, retain the shape of cells, almost as if each cell had its skeleton. This stiffness allows the plants to stand upright without the need for bones. If animals had the same cell walls as plants do, they would not be able to move.
Ques. Cell wall is mainly made up of
- Protein
- Lipid
- Cellulose
- Starch
Click here for the answer
Ans. c) cellulose
Explanation - The cell wall contains a network of cellulose molecules and connecting glycans embedded in the highly connected matrix of cellulose polysaccharides. Cellulose fibers are long polymers, specific to many aldohexose molecules. The cell wall surrounds the cytomembrane of plant cells and provides strong strength and protection against mechanical stress and proliferation.
Ques. Where is RNA present in the cell organelles?
- Golgi complex
- Cell wall
- Ribosomes
- Cytoplasm
Click here for the answer
Ans. c) Ribosomes
Explanation - Ribosomes, large protein complexes ribonucleic acid (RNA), cellular organelle are responsible for the formation of proteins. They get their ‘orders’ for protein synthesis in the nucleus where DNA is written in messenger RNA (mRNA).
Ques. Which of the following cell organelles is known as a digestive bag?
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Lysosomes
- Mitochondria
Click here for the answer
Ans. c) Lysosomes
Explanation - Lysosomes are called 'digestive bags' because they contain enzymes that play a major role in cell digestion. It will mix with food vacuole and enzymes to help the lysosome digest food in the food vacuole. Moreover, lysosomes are also known as suicide bags as these are responsible for processing the nutrients.
Ques. The membrane around the vacuole is called -
- Cytoplast
- Tonoplast
- Elaioplast
- Amyloplast
Click here for the answer
Ans. b) Tonoplast
Explanation - Tonoplast is also called the vacuolar membrane, tonoplast is a cytoplasmic-membrane around the vacuole, which separates the vacuolar content from the cell cytoplasm.
Ques. What is the function of the centrosome?
- Osmoregulation
- Secretion
- Photosynthesis
- Formation of spindle fibers
Click here for the answer
Ans. d) Formation of spindle fibers
Explanation - Centrosomes are responsible for the formation of microtubules and important spinning fibers during the cell division process. The centrosome is the main microtubule (MTOC) center for animal cells, so it regulates cell mobility, adhesion, and polarity at interphase, and facilitates the arrangement of spinning poles during mitosis.
Also, read - Cytosol and Cytoplasm
Ques. Which cell organelles are involved in apoptosis?
- Lysosomes
- Golgi
- ER
- Mitochondria
Click here for the answer
Ans. d) Mitochondria
Explanation - Apoptosis is a process of independent cell death that is activated to eliminate excess, damaged, altered, or old cells. In addition to their role as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria play a key role in regulating apoptosis. It also plays an important role in cell death.
Ques. What is the location of ribosomes in a living cell?
- Nucleolus
- Golgi complex
- Mitochondria
- Plasma membrane
Click here for the answer
Ans. a) Nucleolus
Explanation - In a eukaryotic cell, a cell with a nucleus, ribosomes originate from a special part of the nucleus called the nucleolus. Ribosomal RNA is synthesized and bound to proteins in the nucleolus, and then transported from the nucleus to form ribosomes.
Ques. Which of the following cell organelles is considered as a cell within a cell?
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Golgi complex
- Ribosome
Click here for the answer
Ans. b) Chloroplast
Explanation - Chloroplast is considered a cell within the cell because it contains its DNA. Therefore, it is a semi autonomous organelle. It helps in photosynthesis. Those organelles that have their DNA and are independent can be called cells within a cell.
Related Links:





Comments