The following carbohydrate is

The following carbohydrate is

Show Hint
There is hydrogen at first carbon (Anomeric C) for aldohexose while alkyl group for ketohexose.
a ketohexose
- an aldohexose
an α-furanose
an α-pyranose
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
As the carbohydrate has six carbons, it is a hexose. Also, it has hydrogen at anomeric carbon (first carbon).
- Anomeric C is the new chiral centre that is formed after cyclization.
- It is the cyclic form of D-glucose.
- As glucose has aldehyde functionality, the structure is aldohexose.
Approach Solution -2
Carbohydrates are polysaccharides.
- In the question, we first need to identify the given structure and then explain the name carbohydrate.
- The beta position of the compound is the position where the functional group is attached in the same direction.
- The alpha position is in which the functional group is attached in the opposite direction.
- In the given structure, the beta position is present as the -OH group at 1st carbon and 5th carbon are attached to the same upper direction as shown -

Hence, options C and D are incorrect.
Now, between options A and B, a hexose is a 6-membered ring structure, also known as furanose.
- Now, the 'Aldo' group is used when an aldehyde group is present and the 'keto' is used when the functional group ketone i.e. -C=O is present.
- So, at the 6th carbon, the aldehyde group is attached due to which the complete name of the compound becomes aldohexose.
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note: For the keto group there should be the presence of a double bond between carbon and oxygen that was not present.
Top Questions on Biomolecules
- The number of tripeptides formed by three different amino acids using each amino acid once is ______.
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- DNA molecule contains 4 bases whoes structure are shown below. One of the structure is not correct, identify the incorrect base structure.
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Coagulation of egg, on heating is because of :
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Which of the following is the correct structure of L-Glucose ?
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Vanillin compound obtained from vanilla beans, has total sum of oxygen atoms and \( \pi \) electrons is ______
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A closed vessel contains 10 g of an ideal gas X at 300 K, which exerts 2 atm pressure. At the same temperature, 80 g of another ideal gas Y is added to it and the pressure becomes 6 atm. The ratio of root mean square velocities of X and Y at 300 K is
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- States of matter
- Let the function \(f:[1,\infin)→\R\) be defined by
\(f(t) = \begin{cases} (-1)^{n+1}2, & \text{if } t=2n-1,n\in\N, \\ \frac{(2n+1-t)}{2}f(2n-1)+\frac{(t-(2n-1))}{2}f(2n+1) & \text{if } 2n-1<t<2n+1,n\in\N. \end{cases}\)
Define \(g(x)=\int\limits_{1}^{x}f(t)dt,x\in(1,\infin).\) Let α denote the number of solutions of the equation g(x) = 0 in the interval (1, 8] and \(β=\lim\limits_{x→1+}\frac{g(x)}{x-1}\). Then the value of α + β is equal to _____.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Integral Calculus
- A dimensionless quantity is constructed in terms of electronic charge \(e\), permittivity of free space \(\epsilon_0\) , Planck’s constant ℎ, and speed of light c. If the dimensionless quantity is written as \(e^\alpha\epsilon_0^\beta h^\gamma c^\delta\)and n is a non-zero integer, then\((\alpha, \beta,\gamma,\delta)\) is given by
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
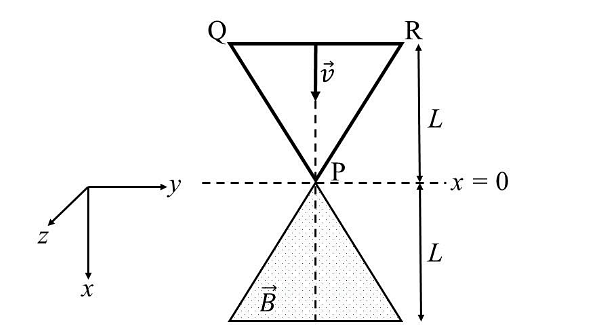
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0?
Concepts Used:
Biomolecules
Biomolecules are the most essential organic molecules, which are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. These non-living molecules are the actual foot-soldiers of the battle of sustenance of life.
There are four major classes of Biomolecules – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids and Lipids.
- Carbohydrates are chemically defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds which produce them on hydrolysis.
- Proteins are another class of indispensable biomolecules, which make up around 50per cent of the cellular dry weight. Proteins are polymers of amino acids arranged in the form of polypeptide chains. The structure of proteins is classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary in some cases.
- Nucleic acids refer to the genetic material found in the cell that carries all the hereditary information from parents to progeny. There are two types of nucleic acids namely, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The main function of nucleic acid is the transfer of genetic information and synthesis of proteins by processes known as translation and transcription.
- Lipids are organic substances that are insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents, are related to fatty acids and are utilized by the living cell.



