Question:
The equation of a plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes $x + 2y + 3z = 2$ and $x - y + z = 3$ and at a distance $\frac{2}{\sqrt 3}$ from the point $(3,1, -1)$ is
The equation of a plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes $x + 2y + 3z = 2$ and $x - y + z = 3$ and at a distance $\frac{2}{\sqrt 3}$ from the point $(3,1, -1)$ is
Updated On: Jun 14, 2022
- $5x-11y+z=17$
- $\sqrt {2x}+y = 3\sqrt 2-1$
- $ x+ y + z = \sqrt 3$
- $x -\sqrt {2y} = 1-\sqrt 2$
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
PLAN
(i) Equation of plane through intersection of two planes,
$\, \, \, \, i.e, (a_1 x + b_1 y +c_1 z +d_1)+ \lambda $
$\hspace30mm (a_2 x +b_2 y +c_2 z +d_2) = 0$
(ii) Distance of a point $(x_1,y_1,z_1)$ from
$\hspace15mm ax+by+cz+d = 0$
$\hspace50mm =\frac{|ax_1+by_1+cz_1+d|}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2}}$
Equation of plane passing through intersection of two
planes x + 2y + 3z = 2 and x - y + z = 3 is
$\, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, (x + 2y + 3z - 2) + \lambda (x - y + z - 3) = 0$
$\Rightarrow (1+ \lambda) x + (2+ \lambda) y +(3+ \lambda)z - (2+3\lambda) = 0$
whose distance from (3,1, -1) is $\frac{2}{\sqrt 3}.$
$\Rightarrow \frac{|3\, (1+ \lambda) +1. (2 - \lambda) -1\, (3+ \lambda) - (2+3\lambda)| }{\sqrt {(1+ \lambda)^2 + (2 - \lambda)^2 + (3+ \lambda)^2}} = \frac{2}{\sqrt 3}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\hspace50mm \frac{| -2 \lambda\, | }{\sqrt {3\lambda^2 + 4 \lambda^2 +14}} = \frac{2}{\sqrt 3}$
$\Rightarrow \hspace10mm 3\lambda^2=3\lambda^2+4\lambda+14 $
$\Rightarrow \hspace15mm \lambda= -\frac{7}{2} $
$\therefore \bigg( 1 -\frac{7}{2}\bigg)x +\bigg( 2 -\frac{7}{2}\bigg)y+\bigg( 3 -\frac{7}{2}\bigg)z-\bigg( 2 -\frac{21}{2}\bigg) = 0 $
$\Rightarrow \hspace40mm $ $-\frac{5x}{2}+\frac{11}{2}y-\frac{1}{2}z+\frac{17}{2}=0 $
or $\hspace50mm {5x} -{11} y +z+ 17 =0 $
(i) Equation of plane through intersection of two planes,
$\, \, \, \, i.e, (a_1 x + b_1 y +c_1 z +d_1)+ \lambda $
$\hspace30mm (a_2 x +b_2 y +c_2 z +d_2) = 0$
(ii) Distance of a point $(x_1,y_1,z_1)$ from
$\hspace15mm ax+by+cz+d = 0$
$\hspace50mm =\frac{|ax_1+by_1+cz_1+d|}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2}}$
Equation of plane passing through intersection of two
planes x + 2y + 3z = 2 and x - y + z = 3 is
$\, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, (x + 2y + 3z - 2) + \lambda (x - y + z - 3) = 0$
$\Rightarrow (1+ \lambda) x + (2+ \lambda) y +(3+ \lambda)z - (2+3\lambda) = 0$
whose distance from (3,1, -1) is $\frac{2}{\sqrt 3}.$
$\Rightarrow \frac{|3\, (1+ \lambda) +1. (2 - \lambda) -1\, (3+ \lambda) - (2+3\lambda)| }{\sqrt {(1+ \lambda)^2 + (2 - \lambda)^2 + (3+ \lambda)^2}} = \frac{2}{\sqrt 3}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\hspace50mm \frac{| -2 \lambda\, | }{\sqrt {3\lambda^2 + 4 \lambda^2 +14}} = \frac{2}{\sqrt 3}$
$\Rightarrow \hspace10mm 3\lambda^2=3\lambda^2+4\lambda+14 $
$\Rightarrow \hspace15mm \lambda= -\frac{7}{2} $
$\therefore \bigg( 1 -\frac{7}{2}\bigg)x +\bigg( 2 -\frac{7}{2}\bigg)y+\bigg( 3 -\frac{7}{2}\bigg)z-\bigg( 2 -\frac{21}{2}\bigg) = 0 $
$\Rightarrow \hspace40mm $ $-\frac{5x}{2}+\frac{11}{2}y-\frac{1}{2}z+\frac{17}{2}=0 $
or $\hspace50mm {5x} -{11} y +z+ 17 =0 $
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Three Dimensional Geometry
- A straight line drawn from the point P(1,3, 2), parallel to the line \(\frac{x-2}{1}=\frac{y-4}{2}=\frac{z-6}{1}\), intersects the plane L1 : x - y + 3z = 6 at the point Q. Another straight line which passes through Q and is perpendicular to the plane L1 intersects the plane L2 : 2x - y + z = -4 at the point R. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE ?
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let y ∈ R be such that the lines \(L_1:\frac{x+11}{1}=\frac{y+21}{2}=\frac{z+29}{3}\) and \(L_2:\frac{x+16}{3}=\frac{y+11}{2}=\frac{z+4}{\gamma}\) intersect. Let R1 be the point of intersection of L1 and L2. Let O = (0, 0 ,0), and \(\hat{n}\) denote a unit normal vector to the plane containing both the lines L1 and L2.
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entry in List-II.The correct option isList - I List - II (P) γ equals (1) \(-\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\) (Q) A possible choice for \(\hat{n}\) is (2) \(\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}\) (R) \(\overrightarrow{OR_1}\) equals (3) 1 (S) A possible value of \(\overrightarrow{OR_1}.\hat{n}\) is (4) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt6}\hat{i}-\frac{2}{\sqrt6}\hat{j}+\frac{1}{\sqrt6}\hat{k}\) (5) \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) - JEE Advanced - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let R3 denote the three-dimensional space. Take two points P = (1, 2, 3) and Q = (4, 2 ,7). Let
dist(X, Y) denote the distance between two points X and Y in R3. Let
\(S=\left\{X\in\R^3:(dist(X,P)^2)-(dist(X,Q))^2=50\right\}\ and\)
\(T=\left\{Y\in \R^3:(dist(Y,Q))^2-(dist(Y,P))^2=50\right\}\)
Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE ?- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- If the foot is perpendicular from (1, 2, 3) to the line \(\frac{x+1}{2} = \frac{y-2}{5} = \frac{z-1}{1}\) is \(( a, \beta, \gamma)\), then find \(a + \beta + \gamma\)
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let the line / : x = \(\frac{1-y}{2}=\frac{z-3}{\lambda}, \lambda \in R\) meet the plane P : x+2y +3z = 4 at the point \((\alpha, \beta, \lambda)\). If the angle between the line I and the plane P is \(cos^{-1}\bigg(\sqrt{\frac{5}{14}}\bigg)\) then \(\alpha+2\beta+6\lambda\) is equal to______.
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A closed vessel contains 10 g of an ideal gas X at 300 K, which exerts 2 atm pressure. At the same temperature, 80 g of another ideal gas Y is added to it and the pressure becomes 6 atm. The ratio of root mean square velocities of X and Y at 300 K is
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- States of matter
- Let the function \(f:[1,\infin)→\R\) be defined by
\(f(t) = \begin{cases} (-1)^{n+1}2, & \text{if } t=2n-1,n\in\N, \\ \frac{(2n+1-t)}{2}f(2n-1)+\frac{(t-(2n-1))}{2}f(2n+1) & \text{if } 2n-1<t<2n+1,n\in\N. \end{cases}\)
Define \(g(x)=\int\limits_{1}^{x}f(t)dt,x\in(1,\infin).\) Let α denote the number of solutions of the equation g(x) = 0 in the interval (1, 8] and \(β=\lim\limits_{x→1+}\frac{g(x)}{x-1}\). Then the value of α + β is equal to _____.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Integral Calculus
- A dimensionless quantity is constructed in terms of electronic charge \(e\), permittivity of free space \(\epsilon_0\) , Planck’s constant ℎ, and speed of light c. If the dimensionless quantity is written as \(e^\alpha\epsilon_0^\beta h^\gamma c^\delta\)and n is a non-zero integer, then\((\alpha, \beta,\gamma,\delta)\) is given by
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
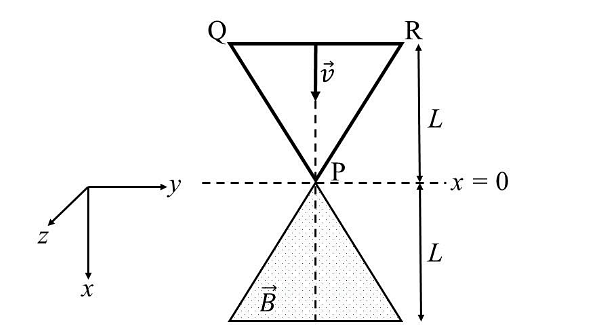
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0?
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Three Dimensional Geometry
Mathematically, Geometry is one of the most important topics. The concepts of Geometry are derived w.r.t. the planes. So, Geometry is divided into three major categories based on its dimensions which are one-dimensional geometry, two-dimensional geometry, and three-dimensional geometry.
Direction Cosines and Direction Ratios of Line:
Consider a line L that is passing through the three-dimensional plane. Now, x,y and z are the axes of the plane and α,β, and γ are the three angles the line makes with these axes. These are commonly known as the direction angles of the plane. So, appropriately, we can say that cosα, cosβ, and cosγ are the direction cosines of the given line L.