Match list I with list II:
List - I List - II (a) Bronchioles (i) Dense Regular Connective Tissue (b) Goblet Cell (ii) Loose Connective Tissue (c) Tendons (iii) Glandular Tissue (d) Adipose Tissue (iv) Ciliated Epithelium
Match list I with list II:
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) | Bronchioles | (i) | Dense Regular Connective Tissue |
| (b) | Goblet Cell | (ii) | Loose Connective Tissue |
| (c) | Tendons | (iii) | Glandular Tissue |
| (d) | Adipose Tissue | (iv) | Ciliated Epithelium |
- (a)- (iv); (b) - (iii); (c) - (i);(d) - (ii)
- (a)- (i); (b) - (ii); (c) - (iii);(d) - (iv)
- (a)- (ii); (b) - (i); (c) - (iv);(d) - (iii)
- (a)- (iii); (b) - (iv); (c) - (ii);(d) - (i)
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Goblet cell - Columnar or cuboidal cells get specialised for secretion and are called glandular epithelium. Goblet cells of the alimentary canal is an example of glandular tissue.
Adipose tissue - Adipose tissue is a type of loose connective tissue located mainly beneath the skin. The cells of this tissue are specialised to store fats.
Tendons - Tendons are examples of dense regular connective tissues. They attach skeletal muscles to bones and ligaments which attach one bone to another are examples of this tissue.
Top Questions on Animal Tissues
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Ligaments are dense irregular tissue.
Statement II: Cartilage is dense regular tissue.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Animal Tissues
Match List I with List II.
List I
List II
A Mast cells I Ciliated epithelium B Inner surface II Areolar connective tissue Of bronchiole C Blood III Cuboidal epithelium D Tubular parts IV Specialised connective tissue of nephron Choose the correct answer from the options give below:
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Animal Tissues
- Which of the following statements wrongly represents the nature of smooth muscle?
- NEET (UG) - 2021
- Biology
- Animal Tissues
- Identify the types of cell junctions that help to stop the leakage of the substances across a tissue and facilitation of communication with neighbouring cells via rapid transfer of ions and molecules.
- NEET (UG) - 2021
- Biology
- Animal Tissues
- The following type of cell junction is not found in animal tissues
- KCET - 2021
- Biology
- Animal Tissues
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Match List I with List II.Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I
(Spectral Lines of Hydrogen for transitions from)List II
(Wavelength (nm))A. n2 = 3 to n1 = 2 I. 410.2 B. n2 = 4 to n1 = 2 II. 434.1 C. n2 = 5 to n1 = 2 III. 656.3 D. n2 = 6 to n1 = 2 IV. 486.1 - NEET (UG) - 2024
- Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom
- Two bodies A and B of same mass undergo completely inelastic one dimensional collision. The body A moves with velocity v1 while body B is at rest before collision. The velocity of the system after collision is v2. The ratio v1 : v2 is :
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Average Velocity and Instantaneous Velocity
- In the following circuit, the equivalent capacitance between terminal A and terminal B is :
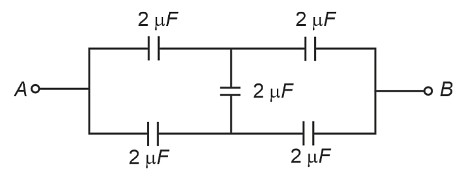
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- Match List I with List II:Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II A Citric acid cycle I Cytoplasm B Glycolysis II Mitochondrial matrix C Electron transport System III Intermembrane space of mitochondria D Proton gradient IV Inner mitochondrial membrane - NEET (UG) - 2024
- Glycolysis
- Consider the following statements A and B and identify the correct answer:

A. For a solar-cell, the I-V characteristics lies in the IV quadrant of the given graph.
B. In a reverse biased pn junction diode, the current measured in (µA), is due to majority charge carriers.- NEET (UG) - 2024
- P-N Junction
Concepts Used:
Animal Tissues
Human bodies, like most animal bodies, are made up of four different types of tissue:
Epithelial Tissue:
This tissue forms the outer layer of the body and also lines many of the body's cavities where it has a protective function.
General functions of epithelial tissue:-
- Provides a barrier between the external environment and the organ that it is covering.
- Specialized to function in secretion and absorption.
- Protects organisms from microorganisms, injury, and fluid loss.
Connective Tissue:
This tissue assists in the support and protection of organs and limbs and depending on the location in the body it may join or separate organs or parts of the body.
Muscle Tissue:
This tissue enables various forms of movement, both voluntary and involuntary.

Nerve Tissue:
This tissue is responsible for the carrying of electrical and chemical signals and impulses from the brain and central nervous system to the periphery, and vice versa.



