are radish and carrot the root modification?
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is: Both radish and carrot are root modifications that serve as food storage organs.
Top Questions on morphology of flowering plants
- Given below are two statements: One labelled as Assertion A and the other labelled as Reason R:
Assertion A: In gymnosperms the pollen grains are released from the microsporangium and carried by air currents.
Reason R: Air currents carry the pollen grains to the mouth of the archegonia where the male gametes are discharged and pollen tube is not formed.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Axile placentation is observed in
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Family Fabaceae differs from Solanaceae and Liliaceae. With respect to the stamens, pick out the characteristics specific to family Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Identify the correct set of statements:
- The leaflets are modified into pointed hard thorns in Citrus and Bougainvillea
- Axillary buds form slender and spirally coiled tendrils in cucumber and pumpkin
- Stem is flattened and fleshy on Opuntia and modified to perform the function of leaves
- Rhizophora shows vertically upward growing roots that help to get oxygen for respiration
- Subaerially growing stems in grasses and strawberry help in vegetative propagation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
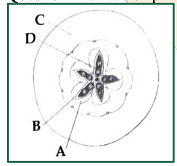
Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure makes it a false fruit?- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Questions Asked in VITEEE exam
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass 'm' resting on a smooth floor are connected by a light spring of natural length L and spring constant K, with the spring at its natural length. A third identical block 'C' (mass m) moving with a speed v along the line joining A and B collides with A. the maximum compression in the spring is
- VITEEE - 2023
- work, energy and power
- Assertion :
The binding energy of the nucleus increases with the increase in atomic number.
Reason :
Heavier elements have a greater number of non-radioactive isotopes than radioactive isotopes. - The half-life of radioactive radon is 3.8 days. The time at the end of which \(\frac{1}{20}th\) of the Radon sample will remain undecayed is (given log10e=0.4343)
- Which element has more electron gain enthalpy among chalcogen group?
- VITEEE - 2022
- sulphur
- Coin is tossed till heads is obtained what is expectation of no. of coin tosses
- VITEEE - 2022
- Random Variables
Concepts Used:
Anatomy of Flowering Plants
The anatomy of flowering plants refers to the structure and organization of various parts that make up a typical flower and plant. These structures play vital roles in reproduction, nutrient absorption, and support. Here are the key components of the anatomy of flowering plants:
Roots: Roots anchor the plant in the ground and absorb water and minerals from the soil. They often have root hairs that increase the surface area for absorption.
Stem: The stem provides support to the plant and transports water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and leaves. It also houses the vascular tissues, xylem (for water transport) and phloem (for nutrient transport).
Leaves: Leaves are the primary site for photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into chemical energy. They consist of a flattened blade, a petiole (stalk), and a network of veins that transport water, nutrients, and sugars.
Flowers: Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. They consist of sepals (protective outermost layer), petals (attractive inner layer), stamens (male reproductive organs), and pistils (female reproductive organs).
- Sepals: Sepals are usually green and protect the developing flower bud.
- Petals: Petals are often colorful and serve to attract pollinators.
- Stamens: Stamens consist of a filament and an anther. The anther produces pollen grains containing male gametes.
- Pistils: Pistils are composed of the stigma (sticky structure to receive pollen), style (connects the stigma to the ovary), and ovary (contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization).
Fruits: After fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seeds. Fruits can vary in size, shape, and texture and play a crucial role in seed dispersal by animals or wind.
Seeds: Seeds are the mature ovules that contain the embryonic plant and a food source (endosperm or cotyledons) to support its growth until it can establish itself as a new plant.
Understanding the anatomy of flowering plants is essential for various purposes, including plant identification, cultivation, and breeding. It also helps in studying the interactions between plants and their environment and provides insights into the diversity and adaptability of the plant kingdom.



