Among the following, which one is a disaccharide?
- Glucose
- Glycogen
- Maltose
- Starch
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules linked together by a glycosidic bond. It is commonly found in germinating seeds and is produced during the breakdown of starch by the enzyme amylase.
Glucose is a monosaccharide, which means it consists of a single sugar molecule.
Glycogen is a polysaccharide, which is a complex carbohydrate composed of multiple glucose units linked together.
Starch is also a polysaccharide composed of glucose units and serves as a storage form of energy in plants.
Therefore, the correct option is (C): Maltose.
Top Questions on Biomolecules
- Match List-I with List-II:

- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- For a double strand DNA, one strand is given below:
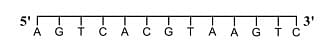
The amount of energy required to split the double strand DNA into two single strands is _____ kcal mol−1.
[Given: Average energy per H-bond for A-T base pair = 1.0 kcal mol−1, G-C base pair = 1.5 kcal mol−1, and A-U base pair = 1.25 kcal mol−1. Ignore electrostatic repulsion between the phosphate groups.]- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Aspartame, an artificial sweetener, is a dipeptide aspartyl phenylalanine methyl ester. The structure of aspartame is
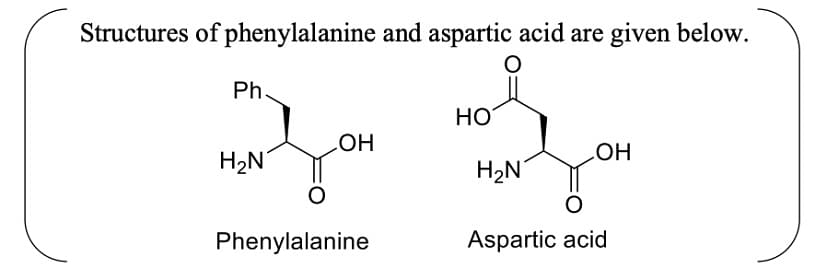
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: A unit formed by the attachment of a base to 1' position of sugar is known as nucleoside.Statement II: When nucleoside is linked to phosphorous acid at 5 -position of sugar moiety, we get neucleotide.In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- How many of the following- amino acids contain sulphur?
Lysine; Methionine; Glutamic acid; Threonine
Arginine; Cysteine; Tyrosine; Isoleucine- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Questions Asked in CUET exam
- If the energy of incident radiation is increased by $25\%$, the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted increases from 0.6 eV to 0.9 eV. The work function of the metal is:
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Dual nature of matter
- Read the following passage and answer the next five questions based on it.
Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions due to steric and electronic reasons. Sterically, the presence of two large groups in ketones hinders the attack of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon than in aldehydes. Electronically, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones because two alkyl groups reduce the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon more effectively than in the former- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Match List-I with List-II:
List-I List-II (A) Mn2+ (I) Pyrolusite ore (B) Spin only Magnetic Moment (II) An alloy of 4f metal, iron and traces of S, C, Al and Ca (C) MnO2 (III) μs = √n(n + 2) BM (D) Misch metal (IV) Highest oxidation states
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Magnetic moment
- Read the following passage and answer the next five questions based on it.
The transition metals are very hard and have low volatility. Their melting and boiling points are high. In any row, the melting points of these metals rise to a maximum at d5 and fall regularly as atomic number increases. The high melting points of these metals are attributed to the involvement of greater number of electrons from (n– 1)d in addition to ns electrons in the interatomic metallic bonding.- CUET (UG) - 2024
- General Properties of the Transition Elements (d-Block)
- Match List-I with List-II:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Concepts Used:
Biomolecules
Biomolecules are the most essential organic molecules, which are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. These non-living molecules are the actual foot-soldiers of the battle of sustenance of life.
There are four major classes of Biomolecules – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids and Lipids.
- Carbohydrates are chemically defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds which produce them on hydrolysis.
- Proteins are another class of indispensable biomolecules, which make up around 50per cent of the cellular dry weight. Proteins are polymers of amino acids arranged in the form of polypeptide chains. The structure of proteins is classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary in some cases.
- Nucleic acids refer to the genetic material found in the cell that carries all the hereditary information from parents to progeny. There are two types of nucleic acids namely, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The main function of nucleic acid is the transfer of genetic information and synthesis of proteins by processes known as translation and transcription.
- Lipids are organic substances that are insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents, are related to fatty acids and are utilized by the living cell.



