Question:
A solution is prepared by dissolving $10 \,g$ of a non-volatile solute (molar mass, $'M^{\prime} g mol ^{-1}$ ) in $360\, g$ of water. What is the molar mass in $g\, mol ^{-1}$ of solute if the relative lowering of vapour pressure of solution is $5 \times 10^{-3}$ ?
A solution is prepared by dissolving $10 \,g$ of a non-volatile solute (molar mass, $'M^{\prime} g mol ^{-1}$ ) in $360\, g$ of water. What is the molar mass in $g\, mol ^{-1}$ of solute if the relative lowering of vapour pressure of solution is $5 \times 10^{-3}$ ?
Updated On: May 6, 2024
- 199
- 99.5
- 299
- 149.5
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Given,
Mass of solute $\left(w_{B}\right)=10 \,g$
Molar mass of solute $\left(M_{B}\right)=M_{B}$
Mass of solvent $\left(w_{A}\right)=360 \,g$
Relative lowering in vapour pressure of solution
$=5 \times 10^{-3}$
Molar mass of water $\left(M_{A}\right)=18 \,g \,mol ^{-1}$
$\because \frac{\Delta p}{p^{\circ}}=$ Relative lower in vapour-pressure of solution.
$\frac{\Delta p}{p^{\circ}}=\chi_{B} $
$\Rightarrow \frac{n_{B}}{n_{A}+n_{B}}=5 \times 10^{-3}$
where, $n_{A}$ and $n_{B}$ are number of moles of solvent
(A) and solute $(B)$ respectively.
$n_{A}=\frac{360}{18}=20$
$n_{B}=\frac{w_{B}}{M_{B}}=\frac{10}{M_{B}}$
$ \because 5 \times 10^{-3}=\chi_{B}=\frac{\frac{10}{M_{B}}}{20+\frac{10}{M_{B}}}$
$5 \times 10^{-3}=\frac{\frac{10}{M_{B}}}{\frac{20 M_{B}+10}{M_{B}}}$
$5 \times 10^{-3}=\frac{10}{20\, M_{B}+10}$
$\left(20\, M_{B}+10\right) 5 \times 10^{-3} =10 $ or,
$20\, M_{B}+10 =\frac{10}{5} \times 10^{3} $
$20 M_{B}+10 =2000 $
$\Rightarrow 20 \,M_{B}=1990 $
$ M_{B} =\frac{1990}{20}=99.5 \,g \,mol ^{-1}$
Was this answer helpful?
3
1
Top Questions on Solutions
- Which of the following solutions shows positive deviation from Raoult's law?
- IUPAC name of compound
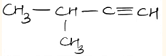
- A saturated \(CaCO_3 \)stock solution is existing at 25°C. In one experiment (i) 25 g \(Na_2CO_3 \)is added to the stock solution. In another experiment (ii) 25 g \(Na_2SO_4\) is added to the stock solution. Select the correct statement from the following.
- The ionic strength of a solution containing 0.01M of $CaCl_2$ and 0.001M of $Na_2SO_4$ is _____ M (rounded off to 3 decimal places)
- The pH of a solution containing 0.1M of acetic acid and 0.05 M of sodium acetate is ________ (rounded off to 2 decimal places).
The $pK_a$ value of ionization of acetic acid is 4.76.
View More Questions
Questions Asked in AP ECET exam
- Let $M$ and $m$ respectively denote the maximum and the minimum values of $[f(\theta)]^{2}$, where $f(\theta)=\sqrt{a^{2} \cos ^{2} \theta+b^{2} \sin ^{2} \theta}$ $+\sqrt{a^{2} \sin ^{2} \theta+b^{2} \cos ^{2} \theta}$. Then $M-m=$
- AP ECET - 2019
- Application of derivatives
- The half-life periods of a first order reaction at $300\, K$ and $400\, K$ are $50\, s$ and $10\, s$ respectively. The activation energy of the reaction in $kJ \; mol^{-1}$ is (log 5 = 0.70)
- AP ECET - 2019
- Chemical Kinetics
- If $I_{n} = \int \frac{\sin nx}{\sin x} dx $ for $n = 1, 2 , 3,...,$ then $I_6$ =
- AP ECET - 2019
- integral
- A solid copper sphere of density $\rho$, specific heat capacity $C$ and radius $r$ is initially at $200\, K$. It is suspended inside a chamber whose walls are at $0\, K$. The time required (in (is) for the temperature of the sphere to drop to $100 \,K$ is ($\sigma$ is Stefan's constant and all the quantities are in SI units)
- AP ECET - 2019
- radiation
- Let $A, G, H$ and $S$ respectively denote the arithmetic mean, geometric mean, harmonic mean and the sum of the numbers $a_1 , a_2 , a_3 ....., a_n$ . Then the value of at which the function $f(x) =\displaystyle \sum^n_{k =1} (x -a_k)^2$ has minimum is
- AP ECET - 2019
- Arithmetic Progression
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Solutions
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components in which the particle size is smaller than 1 nm.
For example, salt and sugar is a good illustration of a solution. A solution can be categorized into several components.
Types of Solutions:
The solutions can be classified into three types:
- Solid Solutions - In these solutions, the solvent is in a Solid-state.
- Liquid Solutions- In these solutions, the solvent is in a Liquid state.
- Gaseous Solutions - In these solutions, the solvent is in a Gaseous state.
On the basis of the amount of solute dissolved in a solvent, solutions are divided into the following types:
- Unsaturated Solution- A solution in which more solute can be dissolved without raising the temperature of the solution is known as an unsaturated solution.
- Saturated Solution- A solution in which no solute can be dissolved after reaching a certain amount of temperature is known as an unsaturated saturated solution.
- Supersaturated Solution- A solution that contains more solute than the maximum amount at a certain temperature is known as a supersaturated solution.



