A disaccharide X cannot be oxidised by bromine water. The acid hydrolysis of X leads to a laevorotatory solution. The disaccharide X is
A disaccharide X cannot be oxidised by bromine water. The acid hydrolysis of X leads to a laevorotatory solution. The disaccharide X is
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Sucrose is a non-reducing disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose units joined together by a glycosidic bond. It cannot be oxidized by bromine water because it does not have a reducing group (such as an aldehyde or a ketone) that can be oxidized.
When sucrose undergoes acid hydrolysis, it breaks down into its constituent monosaccharides, glucose, and fructose. This hydrolysis reaction occurs due to the cleavage of the glycosidic bond. The resulting mixture of glucose and fructose is known as invert sugar and it is laevorotatory, meaning it rotates plane-polarized light to the left.
Therefore, the disaccharide X is most likely sucrose.
Top Questions on Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- The compound that will undergo SN1 reaction with the fastest rate is
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Match List I with List II
List-I
(Conversion)List-II
(Shape/geometry)(A) 1 mol of H2O to O2 (I) 3F (B) 1 mol of MnO-4 to Mn2+ (II) 2F (C) 1.5 mol of Ca from molten CaCl2 (III) 1F (D) 1 mol of FeO to Fe2O3 (IV) 5F
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Which is following compound is easily attacked by electrophile?
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- The option(s) with correct sequence of reagents for the conversion of P to Q is(are)
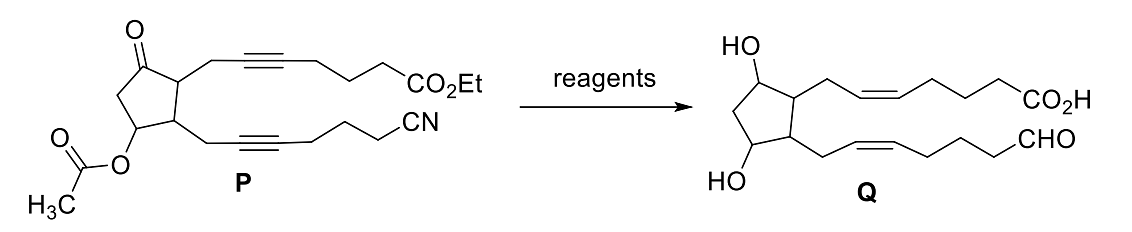
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Match List I with List II
List-I
(Complex)List-II
(Type of isomerism)(A) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 (I) Solvate isomerism (B) [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Br (II) Linkage isomerism (C) [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] (III) Ionization isomerism (D) [Co(H2O)6]Cl3 (IV) Coordination isomerism
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
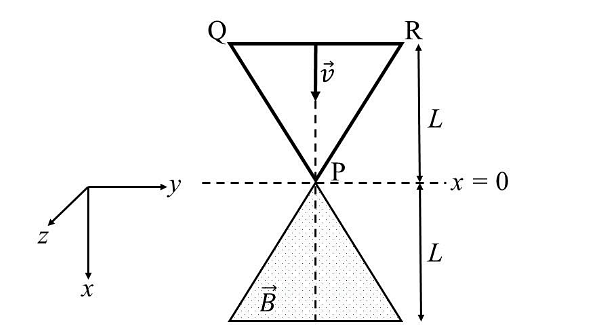
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Organic Chemistry is a subset of chemistry dealing with compounds of carbon. Therefore, we can say that Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds and is 200-225 years old. Carbon forms bond with itself to form long chains of hydrocarbons, e.g.CH4, methane and CH3-CH3 ethane. Carbon has the ability to form carbon-carbon bonds quite elaborately. Polymers like polyethylene is a linear chain where hundreds of CH2 are linked together.
Read Also: Organic Compounds
Importance of Organic Chemistry:
Organic chemistry is applicable in a variety of areas including-
- Medicines: Example- Aspirin which is a headache medicine and Ibuprofen is a painkiller, both are organic compounds. Other examples include paracetamol.
- Food: Example- Starch which is a carbohydrate is an organic compound and a constituent of rice and other grains. It is the source of energy.
- Clothing: Example- Nylon, Polyester and Cotton are forms of organic compounds.
- Fuels: Examples- Gasoline, Petrol and Diesel are organic compounds used in the automobile industry at large.







