The total number of chiral molecules formed from one molecule of $P$ on complete ozonolysis $\left( O _3, Zn / H _2 O \right)$ is_____


Correct Answer: 2
Solution and Explanation
Only 2 chiral molecules are formed.
Top Questions on Ozonolysis
- Which among the following pairs of the structures will give different products onozonolysis? (Consider the double bonds in the structures are rigid and not delocalized)
- JEE Main - 2022
- Chemistry
- Ozonolysis
- Ozonolysis of an organic compound gives formaldehyde as one of the products. This confirms the presence of
- SRMJEEE - 2018
- Chemistry
- Ozonolysis
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
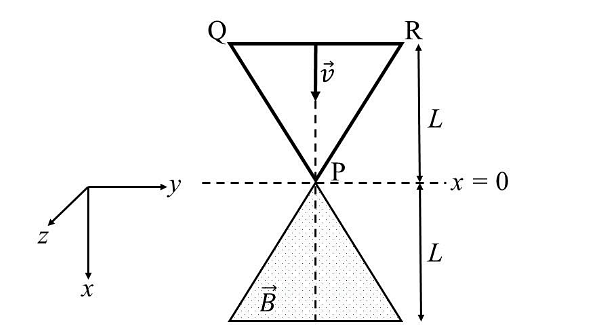
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Hydrocarbons - Reaction Mechanism
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are entirely made up of only two kinds of atoms – carbon and hydrogen. Typically, hydrocarbons are colourless gases that have very weak odours.
Mechanism of electrophilic substitution reactions:
According to experimental evidences, SE (S = substitution; E = electrophilic) reactions are supposed to proceed via the following three steps:
- Generation of the electrophile
- Formation of carbocation intermediate
- Removal of proton from the carbocation interm
Hydrocarbons - Classification
Types of Hydrocarbons:
Hydrocarbons are classified under the special heads as stated below:
Saturated hydrocarbons-
Those compounds where there is a single bond present between carbon atoms and are saturated with atoms of hydrogen are saturated hydrocarbons. They are the prime component of petroleum fuel. Carbon atoms bond themselves to as many hydrogen atoms as they can. They undergo the process of hybridization, and also, do not have double or triple bonds. The formula for alkanes which is the most common hydrocarbon is CnH2n+2. Saturated hydrocarbons have an akin molecular formula as hydrocarbons.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons-
Hydrocarbons comprise at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms known as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes are organic compounds that comprise double bonds, whereas alkynes are triple bonded. Here, the situation is the opposite of saturated hydrocarbons as the carbon atoms don't bond themselves with as many hydrogen atoms as possible. When it comes to hydrogen atoms, they are unsaturated.
Aliphatic hydrocarbons-
The term denotes the hydrocarbons formed as a result of the chemical degradation of fats. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are generally chemical compounds. Their structure includes one or more hydrogen atoms which are replaced with a halogen. They are linked in chains in single, double, or triple bonds without any rings. Propane, butane, methane, and ethane serve as good examples of aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Aromatic hydrocarbons-
They are discriminated against because of the benzene rings present in them. They give away different types of aroma. These hydrocarbons comprise only hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are used extensively in fields of medicine, hygiene, and fashion.
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons can be described as organic compounds that consists only hydrogen and carbon atoms. These compounds are of different types and thereby have distinct natures. Hydrocarbons are colorless gases and are known for discharging faint odours. These have been categorized under four major classes named as alkynes, alkanes, alkenes, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Types of Hydrocarbons
- Saturated hydrocarbons - Saturated hydrocarbons are those compounds where there is a single bond exists between carbon atoms and are saturated with atoms of hydrogen.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons - Hydrocarbons comprises of at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms are known as unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- Aliphatic hydrocarbons - The term denotes the hydrocarbons formed as an outcome of the chemical degradation of fats. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are basically chemical compounds.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons - They are distinguished because of the presence of benzene rings in them. They give away distinct types of aroma. These hydrocarbons comprises of only hydrogen and carbon atoms.



