The $pH$ of $10^{-8}\, M \,HCl $ solution is
- 8
- more than 8
- between 6 and 7
- slightly more than 7
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
From $HCI, [H^+] = 1 \times 10 ^{-8}\, M $
Total $ {[H^+] = (1 \times 10^{-7} + 1 \times 10^{-8}}) }$M
$= (1 \times 10^{-7} + 0.1 \times 10^{-7} ) $M
$= 1.1 \times 10^{-7} $ M
$pH = - log (1.1 \times 10^{-7} )$ = 6.9586
Top Questions on Acids and Bases
- Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R)
Assertion (A): Ketoses give Seliwanoff's test faster than Aldoses
Reason (R): Ketoses undergo $\beta$-elimination followed by formation of furfural
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
- Incorrect statement for the use of indicators in acid-base titration is :
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled asReason (R)
Assertion (A): $\alpha$-halocarboxylic acid on reaction with dil $NH _3$ gives good yield of $\alpha$-aminocarboxylic acid whereas the yield of amines is very low when prepared from alkyl halides
Reason (R): Amino acids exist in zwitter ion form in aqueous medium
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
- When the hydrogen ion concentration $\left[ H ^{+}\right]$changes by a factor of $1000$ , the value of $pH$ of the solution_____
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
- In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant becomes 0.0625 of its initial concentration after 2 hours. The half-life of the reaction is given by
- WBJEE JENPAS UG - 2023
- Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
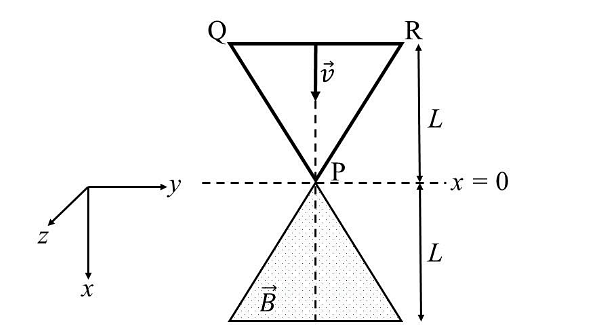
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Acids and Bases
Acid is any hydrogen-containing substance that is capable of donating a proton (hydrogen ion) to another substance. Base is an ion or molecule capable of accepting a hydrogen ion from acid.
Physical Properties of Acids and Bases
| Physical Properties | ACIDS | BASES |
| Taste | Sour | Bitter |
| Colour on Litmus paper | Turns blue litmus red | Turns red litmus blue |
| Ions produced on dissociation | H+ | OH- |
| pH | <7 (less than 7) | >7 (more than 7) |
| Strong acids | HCl, HNO3, H2SO4 | NaOH, KOH |
| Weak Acids | CH3COOH, H3PO4, H2CO3 | NH4OH |
Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
| Type of Reaction | Acid | Bases |
| Reaction with Metals | Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas (H2) E.g., Zn(s)+ dil. H2SO4 → ZnSO4 (Zinc Sulphate) + H2 | Base + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas (H2) E.g., 2NaOH +Zn → Na2ZnO2 (Sodium zincate) + H2 |
| Reaction with hydrogen carbonates (bicarbonate) and carbonates | Metal carbonate/Metal hydrogen carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water E.g., HCl+NaOH → NaCl+ H2O 2. Na2CO3+ 2 HCl(aq) →2NaCl(aq)+ H2O(l) + CO2(g) 3. Na2CO3+ 2H2SO4(aq) →2Na2SO4(aq)+ H2O(l) + CO2(g) 4. NaHCO3+ HCl → NaCl+ H2O+ CO2 | Base+ Carbonate/ bicarbonate → No reaction |
| Neutralisation Reaction | Base + Acid → Salt + Water E.g., NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) | Base + Acid → Salt + Water E.g., CaO+ HCl (l) → CaCl2 (aq)+ H2O (l) |
| Reaction with Oxides | Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water E.g., CaO+ HCl (l) → CaCl2 (aq)+ H2O (l) | Non- Metallic oxide + Base → Salt + Water E.g., Ca(OH)2+ CO2 → CaCO3+ H2O |
| Dissolution in Water | Acid gives H+ ions in water. E.g., HCl → H+ + Cl- HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl– | Base gives OH- ions in water. |
Read more on Acids, Bases and Salts



