The orthocentre of the triangle with vertices $O(0, 0), A(0,3/2)$ and $B(-5, 0)$ is
The orthocentre of the triangle with vertices $O(0, 0), A(0,3/2)$ and $B(-5, 0)$ is
$(-5/2,3/4)$
$(5/2,3/4)$
$(0, 0)$
$(-5, 3/2)$
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Let, $\Delta \, AOB $ is the given triangle
Slope of $AB = \frac{\frac{3}{2}-0}{0+5} = \frac{3}{10}$
Slope of $BO = \frac{0-0}{0+54} =0$
The equation of line passing through A and perpendicular to BO is $ y-0 =- 0 \left(x - \frac{3}{2}\right) $ 
$\Rightarrow \, y = 0 \,\,\,\,\,\dots(i)$
and equation of line passing through 0 and perpendicular to AB is $y - 0 = - \frac{10}{3} (x -0)$
$\Rightarrow \; y = - \frac{10}{3} x \,\,\,\,\,\dots(ii)$
The intersection point of Eqs. (i) and (ii) (0, 0), which is the required orthocentre.
Top Questions on Three Dimensional Geometry
- A straight line drawn from the point P(1,3, 2), parallel to the line \(\frac{x-2}{1}=\frac{y-4}{2}=\frac{z-6}{1}\), intersects the plane L1 : x - y + 3z = 6 at the point Q. Another straight line which passes through Q and is perpendicular to the plane L1 intersects the plane L2 : 2x - y + z = -4 at the point R. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE ?
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let y ∈ R be such that the lines \(L_1:\frac{x+11}{1}=\frac{y+21}{2}=\frac{z+29}{3}\) and \(L_2:\frac{x+16}{3}=\frac{y+11}{2}=\frac{z+4}{\gamma}\) intersect. Let R1 be the point of intersection of L1 and L2. Let O = (0, 0 ,0), and \(\hat{n}\) denote a unit normal vector to the plane containing both the lines L1 and L2.
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entry in List-II.The correct option isList - I List - II (P) γ equals (1) \(-\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\) (Q) A possible choice for \(\hat{n}\) is (2) \(\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}\) (R) \(\overrightarrow{OR_1}\) equals (3) 1 (S) A possible value of \(\overrightarrow{OR_1}.\hat{n}\) is (4) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt6}\hat{i}-\frac{2}{\sqrt6}\hat{j}+\frac{1}{\sqrt6}\hat{k}\) (5) \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) - JEE Advanced - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let R3 denote the three-dimensional space. Take two points P = (1, 2, 3) and Q = (4, 2 ,7). Let
dist(X, Y) denote the distance between two points X and Y in R3. Let
\(S=\left\{X\in\R^3:(dist(X,P)^2)-(dist(X,Q))^2=50\right\}\ and\)
\(T=\left\{Y\in \R^3:(dist(Y,Q))^2-(dist(Y,P))^2=50\right\}\)
Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE ?- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- If the foot is perpendicular from (1, 2, 3) to the line \(\frac{x+1}{2} = \frac{y-2}{5} = \frac{z-1}{1}\) is \(( a, \beta, \gamma)\), then find \(a + \beta + \gamma\)
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Let the line / : x = \(\frac{1-y}{2}=\frac{z-3}{\lambda}, \lambda \in R\) meet the plane P : x+2y +3z = 4 at the point \((\alpha, \beta, \lambda)\). If the angle between the line I and the plane P is \(cos^{-1}\bigg(\sqrt{\frac{5}{14}}\bigg)\) then \(\alpha+2\beta+6\lambda\) is equal to______.
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Three Dimensional Geometry
Questions Asked in KCET exam
- If \(\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin(2+x)-\sin(2-x)}{x}\)= A cos B, then the values of A and B respectively are
- KCET - 2023
- limits of trigonometric functions
- The Curie temperatures of Cobalt and iron are 1400K and 1000K respectively. At T = 1600K , the ratio of magnetic susceptibility of Cobalt to that of iron is
- KCET - 2023
- Magnetism and matter
- A particle is in uniform circular motion. Related to one complete revolution of the particle, which among the stataments is incorrect ?
- KCET - 2023
- Uniform Circular Motion
- The modulus of the complex number \(\frac{(1+i)^2(1+3i)}{(2-6i)(2-2i)}\) is
- KCET - 2023
- complex numbers
- The energy gap of an LED is 2.4 eV. When the LED is switched ‘ON’, the momentum of the emitted photons is
- KCET - 2023
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
Concepts Used:
Three Dimensional Geometry
Mathematically, Geometry is one of the most important topics. The concepts of Geometry are derived w.r.t. the planes. So, Geometry is divided into three major categories based on its dimensions which are one-dimensional geometry, two-dimensional geometry, and three-dimensional geometry.
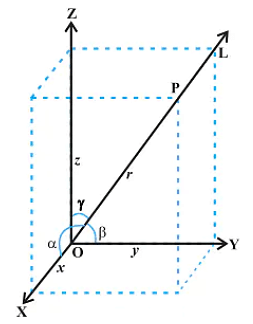
Direction Cosines and Direction Ratios of Line:
Consider a line L that is passing through the three-dimensional plane. Now, x,y and z are the axes of the plane and α,β, and γ are the three angles the line makes with these axes. These are commonly known as the direction angles of the plane. So, appropriately, we can say that cosα, cosβ, and cosγ are the direction cosines of the given line L.