Question:
The instantaneous voltages at three terminals marked $X , Y$ and $Z$ are given by
$V _{ x }= V _{0} \sin \omega t$
$V _{ y }= V _{0} \sin \left(\omega t +\frac{2 \pi}{3}\right)$ and
$V _{ z }= V _{0} \sin \left(\omega t +\frac{4 \pi}{3}\right)$
An ideal voltmeter is configured to read $rms$ value of the potential difference between its terminals. It is connected between points $X$ and $Y$ and then between $Y$ and $Z$. The reading(s) of the voltmeter will be
The instantaneous voltages at three terminals marked $X , Y$ and $Z$ are given by
$V _{ x }= V _{0} \sin \omega t$
$V _{ y }= V _{0} \sin \left(\omega t +\frac{2 \pi}{3}\right)$ and
$V _{ z }= V _{0} \sin \left(\omega t +\frac{4 \pi}{3}\right)$
An ideal voltmeter is configured to read $rms$ value of the potential difference between its terminals. It is connected between points $X$ and $Y$ and then between $Y$ and $Z$. The reading(s) of the voltmeter will be
Updated On: Jul 7, 2023
- $V^{rms}_{xy} = V_{0}\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}$
- $V^{rms}_{xy} = V_{0}\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}$
- $V^{rms}_{xy} = V_{0}$
- independent of the choice of the two terminals
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
$V _{ XYO }= V _{ Y 2 O }= V _{ ZXO }=\sqrt{3} V _{0}$
$V _{ XX }^{ ms }= V _{ YZ }^{ rms }=\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}} V _{0}$
$V _{ XX }^{ ms }= V _{ YZ }^{ rms }=\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}} V _{0}$
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on AC Voltage
- In \(AC\) circuit with source voltage \(E \) = \(20\) \(sin\; 1000 \;t\) is connected to series \(L-R\) circuit whose power factor is \(\frac{1}{\sqrt 2}\) If \(E = 25\) \(sin \;2000\) \(t\), the new power factor is :
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- AC Voltage
- Alternating voltage and current in circuit is given as \(V = (100 \;sin \;ωt)\) volt
\(I = 100\;sin\bigg(ωt+\frac{π}{3}\bigg)mA\)
Find average power dissipated in circuit.- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- AC Voltage
- A student is provided with a variable voltage source V, a test resistor Rr = 10Ω, two identical galvanometers G1 and G2 and two additional resistors, R1 = 10MΩ and R2 = 0.001Ω. For conducting an experiment to verify ohms law, the most suitable circuit is
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- AC Voltage
- The maximum and minimum voltage of an amplitude modulated signal are 60 V and 20 V, respectively. The percentage modulation index will be:
- JEE Main - 2022
- Physics
- AC Voltage
- The I–V characteristics of a p-n junction diode in forward bias is shown in the figure. The ratio of dynamic resistance, corresponding to forward bias voltage of 2 V and 4 V respectively, is
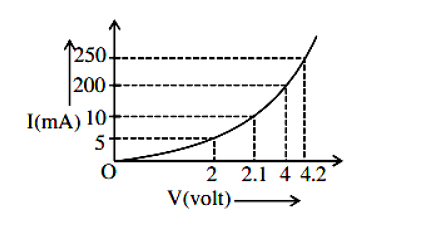
- JEE Main - 2022
- Physics
- AC Voltage
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let \(S=\left\{\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & c \\ 1 & a & d\\ 1 & b & e \end{pmatrix}:a,b,c,d,e\in\left\{0,1\right\}\ \text{and} |A|\in \left\{-1,1\right\}\right\}\), where |A| denotes the determinant of A. Then the number of elements in S is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Matrices
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- Two equilateral-triangular prisms \(P_1 \)and \(P_2\) are kept with their sides parallel to each other, in vacuum, as shown in the figure. A light ray enters prism \(P_1\) at an angle of incidence 𝜃 such that the outgoing ray undergoes minimum deviation in prism \(P_2\). If the respective refractive indices of \(P_1\) and\( P_2\) are \(√ 3 /2\) and \(√3\), then \(\theta = sin{−1}[\sqrt \frac{ 3}{ 2} sin ( \frac{\pi}{B} )],\) where the value of \(\beta\) is ______.
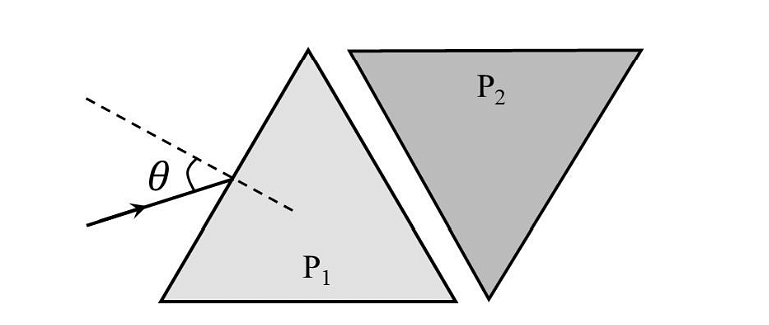
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- Let \(\overrightarrow{OP}=\frac{\alpha-1}{\alpha}\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k},\overrightarrow{OQ}=\hat{i}+\frac{\beta-1}{\beta}\hat{j}+\hat{k}\) and \(\overrightarrow{OR}=\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\frac{1}{2}\hat{k}\) be three vector where α, β ∈ R - {0} and 0 denotes the origin. If \((\overrightarrow{OP}\times\overrightarrow{OQ}).\overrightarrow{OR}=0\) and the point (α, β, 2) lies on the plane 3x + 3y - z + l = 0, then the value of l is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
AC Voltage
When voltage changes its direction after every half cycle is known as alternating voltage. The current flows in the circuit at that time are known as alternating current. The alternating current(AC) follows the sine function which changes its polarity concerning time. Most of the electrical devices are operating on the ac voltage.




