The input resistance of a silicon transistor is $665 \,\Omega$. Its base current is changed by $15 \, \mu \,A$ which results in the change in collector current by $2 \,mA$. This transistor is used as a common emitter amplifier with a load resistance of $5\, k\,\Omega$. What is the voltage gain of the amplifier?
- 1002.5
- 1232.8
- 7235.9
- 9879.3
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
$\Delta I_{C}=2 mA = 2 \times10^{-3} A ,R_{L}=5 k\Omega =5\times10^{3} \Omega$
$\beta=\frac{\Delta I_{C}}{\Delta I_{B}} =\frac{2\times10^{-3}}{15\times10^{-6}} =\frac{400}{3} $
Voltage gain, $A_{V }=\beta. \frac{R_{L}}{R_{i}}$
$ A_{V}=\frac{400}{3}\times\frac{5\times10^{3}}{665}=1002.5$
Top Questions on Transistors
- The typical biasing of a silicon transistor is shown in the figure.
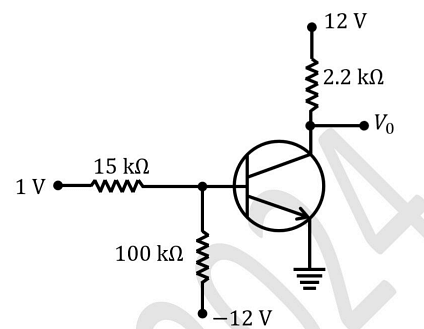
The value of the common-emitter current gain \( \beta \) for the transistor is 100. Ignore reverse saturation current. The output voltage \( V_o \) (in V) is ____ (in integer).- GATE PH - 2024
- Physics
- Transistors
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I : In a typical transistor, all three regions emitter, base and collector have same doping level.
Statement II : In a transistor, collector is the thickest and base is the thinnest segment.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Transistors
- In an n-p-n common emitter (CE) transistor the collector current changes from 5 m A to 16 mA for the change in base current from 100 μ A and 200 μA , respectively. The current gain of transistor is Options 1. 110 2. 0.9 3. 210 4. 9
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Transistors
- The purpose of a coupling capacitor in a transistor amplifier is to___
- CUET (PG) - 2023
- Physics
- Transistors
- If the power and current gains of a transistor amplifier are 16500 and 100 respectively, then voltage gain is___
- CUET (PG) - 2023
- Physics
- Transistors
Questions Asked in JIPMER exam
- Binomial nomenclature was first introduced by
- JIPMER - 2015
- KCET - 2022
- Diversity In The Living World
- A convex lens $'A'$ of focal length $20\, cm$ and a concave lens $'B'$ of focal length $5\, cm$ are kept along the same axis with a distance $'d'$ between them. If a parallel beam of light falling on $'A'$ leaves $'B'$ as a parallel beam, then the distance $'d'$ in cm will be :
- JIPMER - 2021
- Spherical Mirrors
- A bacterial flagellum is composed of
- JIPMER - 2021
- Prokaryotic Cells
- $2,4-DNP $ test can be used to identify :
- JIPMER - 2021
- Chemical Reactions
- How many moles of acidified $K_2Cr_2O_7$ is required to liberate $6$ moles of $I_2$ from an aqueous solution of $I^-$ ?
- JIPMER - 2020
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
Concepts Used:
Transistors
Transistor
A transistor is a type of semiconductor device that can be used to both conduct and insulate electric current or voltage. A transistor basically acts as a switch and an amplifier. In simple words, we can say that a transistor is a miniature device that is used to control or regulate the flow of electronic signals.
Parts of a Transistor:
A transistor is a combination of three terminals made of semiconducting materials that help in making a connection to an external circuit and allow current to flow. The three terminals are:
- Base: The base activates the transistor. It is thin and lightly doped. It is put in the centre of the transistor.
- Emitter: The emitter is the negative terminal of the transistor. It is heavily doped and is moderately sized.
- Collector: The collector is the negative terminal of the transistor. It is located on the right side of a transistor and is moderately doped. It is larger than the emitter.
Read More: Difference Between NPN and PNP Transistor
Types of Transistors:
A transistor is a type of electronic device which is formed by p-type and n-type semiconductors.
NPN Transistor
- NPN transistor is a type of Bipolar Junction Transistor.
- In this, electrons are major current carriers, and minor ones are holes.
- Their arrangement is in such a way that N-type doped semiconductors are separated by the layer of P-type doped semiconductors which is a thin layer of material embedded between them.
- Emitter Current = Collector Current + Base Current
PNP Transistor
- PNP transistor is also a type of Bipolar Junction Transistor.
- In these, holes are the major source that carries current, and electrons are minor.
- Their arrangement is in a way that P-type doped semiconductor is separated by N-type doped semiconductor material which is a thin layer.
- Emitter Current = Collector Current + Base Current
Read More: Characteristics of a Transistor
Configurations of a Transistor:
Using the three types of configuration can be used to design any transistor circuit. The three types of configuration of a transistor are:
- Common Emitter Transistor
- Common Base Transistor
- Common Collector Transistor
Common Emitter (CE) Configuration of a Transistor
In Common Emitter Configuration, the transistor’s emitter terminal will be connected common between the output terminal and the input terminal.
Input Characteristics
- Variation of emitter current (IB) with Base-Emitter voltage (VBE) when Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE) is held constant.
- Rin = ΔVBE/ΔIB | VCE = Constant
Output Characteristics
- Variation of collector current (IC) with Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE) when the base current (IB) is held constant.
- Rout = ΔVCE/ΔIC | IB = Constant
Current Transfer Characteristics
- The variation of the collector current (IC) with the base current (IB) when the collector-emitter voltage (VCE) is constant.
- α = ΔIC/ΔIB | VCB = Constant
Common Base (CB) Configuration of a Transistor
In Common Base Configuration, the transistor’s base terminal will be connected common between the output terminal and the input terminal.
Input Characteristics
- Variation of emitter current (IE) with Base-Emitter voltage (VBE) when the Collector Base voltage (VCB) is held constant.
- Rin = ΔVBE/ΔIE | VCB = Constant
Output Characteristics
- Variation of collector current (IC) with Collector-Base voltage (VCB) when the emitter current (IE) is held constant.
- Rout = ΔVCB/ΔIB | IE = Constant
Current Transfer Characteristics
- The variation of the collector current (IC) with the emitter current (IE) when the Collector Base voltage (VCB) is constant.
- α = ΔIC/ΔIE | VCB = Constant
Common Collector Configuration of a Transistor
In Common Collector Configuration, the transistor’s collector terminal will be connected common between the output terminal and the input terminal.
Input Characteristics
- Variation of emitter current (IB) with Collector-Base voltage (VCB) when the Collector Base voltage (VCB) is held constant.
Output Characteristics
- Variation of emitter current (IE) with Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE) when the base current (IB) is held constant.
Current Transfer Characteristics
- The variation of the collector current (IE) with the base current (IB) when the Collector-Emitter voltage (VCE) is constant.



