The correct statement(s) related to colloids is(are)
The process of precipitating colloidal sol by an electrolyte is called peptization.
Colloidal solution freezes at higher temperature than the true solution at the same concentration.
Surfactants form micelle above critical micelle concentration (CMC). CMC depends on temperature.
Micelles are macromolecular colloids.
The Correct Option is B, C
Solution and Explanation
(a) The statement is False. Peptization refers to the process of converting a precipitate into a colloidal sol, not the other way around.
(b) The statement is True. Colloidal solutions exhibit colligative properties such as higher freezing point compared to true solutions at the same concentration due to the presence of dispersed particles.
(c) The statement is True. Surfactants form micelles above the critical micelle concentration (CMC), and CMC can indeed depend on temperature.
(d) The statement is False. Micelles are not macromolecular colloids; they are associated colloids formed by the aggregation of amphiphilic molecules in a solvent.
Top Questions on Solutions
- Which term of molar conductivity is used when the concentration of electrolyte approaches zero?
- Molal elevation constant is also known as:
- Which of the following ions will be coloured in the aqueous solution?
(A) Ti3+
(B) Nb3+
(C) Cu+
(D) Y3+
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: - Which metal is the most powerful reducing agent in aqueous solution?
- A perfectly ideal solution is rare but some solutions behave nearly ideal. Which of the following does not fall in this category?
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
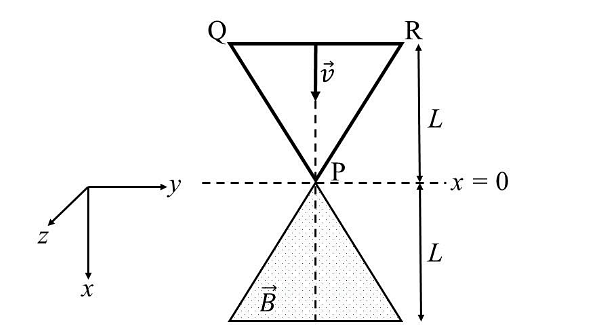
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Types of Solutions
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances, where the solute is uniformly dispersed in the solvent. Solutions can be classified into several types based on their composition and properties.
- Gas solutions: These are solutions where gases are dissolved in other gases, such as oxygen and nitrogen in air.
- Liquid solutions: These are solutions where a liquid is dissolved in another liquid, such as ethanol in water.
- Solid solutions: These are solutions where a solid is dissolved in another solid, such as an alloy of copper and zinc.
- Aqueous solutions: These are solutions where water is the solvent, such as saltwater or sugar water.
- Concentrated solutions: These are solutions where a large amount of solute is dissolved in the solvent, resulting in a high concentration.
- Dilute solutions: These are solutions where a small amount of solute is dissolved in the solvent, resulting in a low concentration.
- Saturated solutions: These are solutions where the maximum amount of solute has been dissolved in the solvent at a given temperature and pressure.
- Supersaturated solutions: These are solutions where more solute has been dissolved in the solvent than is normally possible at a given temperature and pressure.
- Colloidal solutions: These are solutions where the size of the dispersed particles is between 1 and 1000 nanometers. These solutions have unique properties such as Brownian motion and Tyndall effect.
Understanding the different types of solutions is important for understanding their properties, behavior, and applications in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and engineering.



