The correct option(s) related to adsorption processes is(are)
- Chemisorption results in a unimolecular layer.
- The enthalpy change during physisorption is in the range of 100 to $140\, kJ\, mol ^{-1}$.
- Chemisorption is an endothermic process.
- Lowering the temperature favors physisorption processes.
The Correct Option is A, D
Solution and Explanation
(A) The initial assertion is accurate since chemisorption yields a monomolecular layer, while physisorption leads to a multimolecular layer.
(B) The subsequent claim is inaccurate because the enthalpy shift in physisorption typically falls within the range of (20 – 40) kJ mol–1.
(C) Chemisorption demonstrates an exothermic characteristic, with an enthalpy of adsorption ranging from (80 – 240) kJ mol–1.
(D) A reduction in temperature prompts an augmentation in the degree of physisorption.
Consequently, statements (A) and (D) are correct.
Top Questions on Surface Chemistry
- To form a complete monolayer of acetic acid on 1g of charcoal, 100 mL of 0.5M acetic acid was used. Some of the acetic acid remained unadsorbed. To neutralize the unadsorbed acetic acid, 40 mL of 1M NaOH solution was required. If each molecule of acetic acid occupies P x 10−23 m2 surface area on charcoal, the value of P is _____.
[Use given data: Surface area of charcoal = 1.5 x 102 m2g−1 ; Avogadro’s number (NA) = 6.0 x 1023 mol−1 ]- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- Surface Chemistry
Which compound is added to cement to increase its setting time?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Surface Chemistry
- What happens when lyophilic sol is added to lyophobic sol. prevention from coagulation precipitation emulsion electrophoresis
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Surface Chemistry
- During bleeding from cut \(FeCl_3\) is used to stop bleeding as
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Surface Chemistry
- Match the terms in Column-I with their description in Column-II and choose the correct option:
Column I (Chemical reactions) Column II (Enzymes used) (i) Glucose → CO2 + Ethanol a Pepsin (ii) Sucrose→Glucose + Fructose b Diastase (iii) Starch →Maltose c Zymase (iv) Protein→Amino acids d Invertase - JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Surface Chemistry
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
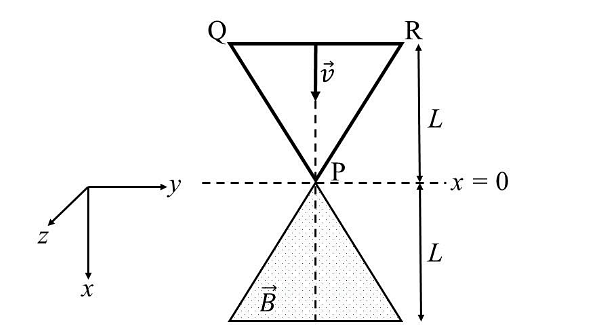
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Surface Chemistry
The study of the chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two surfaces which can be solid-liquid, solid-gas, solid-vacuum, liquid-gas, etc.
Read Also: Surface Chemistry
Applications of surface chemistry are:
Adsorption:
The process of attraction and aggregation of the molecules of a substance on the surface of a solid is known as adsorption. For Example, N2 adsorbs on the surface of activated charcoal
Two types of adsorption are:-
- Chemisorption: It is also known as Chemical Adsorption.
- Physisorption: It is also known as Physical Adsorption.
Corrosion:
The process through which the refined metals convert themselves into more stable compounds is known as corrosion.
Crystallisation:
The type of technique used in order to purify the substances to separate Solids from liquids is known as crystallisation.
Heterogeneous Catalysis:
The process wherein a catalyst is used in order to increase the rate of a chemical reaction is known as catalysis. The catalyst does not undergo any transformation and can be recovered in a chemically unchanged state.
There are two types of catalysis:-
- When the catalyst involved and the reacting substances are same states of matter or in the same phase, it is known as Homogeneous Catalysis.
- When the catalyst involved and the reacting substances are in different states of matter or different phases, it is known as Heterogeneous Catalysis.



