
Correct match of the C–H bonds (shown in bold) in Column J with their BDE in Column K is
Column J
Molecule
Column K
BDE (kcal mol–1 )
P \(\text{H--CH(CH}_3\text{)}_2\) i 132 Q \(\text{H--CH}_2\text{Ph}\) ii 110 R \(\text{H--CH}=CH_2\) iii 95 S \(\text{H--C≡CH}\) iv 88
Column J | Column K | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| P | \(\text{H--CH(CH}_3\text{)}_2\) | i | 132 |
| Q | \(\text{H--CH}_2\text{Ph}\) | ii | 110 |
| R | \(\text{H--CH}=CH_2\) | iii | 95 |
| S | \(\text{H--C≡CH}\) | iv | 88 |
P – iii, Q – iv, R – ii, S – i
P – i, Q – ii, R – iii, S – iv
P – iii, Q – ii, R – i, S – iv
P – ii, Q – i, R – iv, S – iii
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation

Order of stability of free radical
\(Q > P > R > S\)
\(\text{Stability of free radical } \alpha \frac{1}{\text{Bond energy}}\)
∴ Order of bond energy :
\(S > R > P > Q\)
For the following reaction,
\(\text{CH}_4\text{(g)} + \text{Cl}_2\text{(g)} \overset{\text{light}}{\longrightarrow} \text{CH}_3\text{Cl (g)} + \text{HCl(g)}\)
the correct statement is
\(\text{CH}_4\text{(g)} + \text{Cl}_2\text{(g)} \overset{\text{light}}{\longrightarrow} \text{CH}_3\text{Cl (g)} + \text{HCl(g)}\)
the correct statement is
Initiation step is exothermic with \(\Delta\)H° = –58 kcal mol–1
Propagation step involving ·CH3 formation is exothermic with \(\Delta\)H° = –2 kcal mol–1
Propagation step involving CH3Cl formation is endothermic with \(\Delta\)H° = +27 kcal mol–1
The reaction is exothermic with \(\Delta\)H° = –25 kcal mol–1
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation

Step (1) → Endothermic (bond breaking)
Step (2) → ∆H = 105 – 103 = 2 kcal/mol (Endothermic)
Step (3) → ∆H = 58 – 85 = –27 kcal/mol (Exothermic)
For complete reaction
\(\text{CH}_4\text{(g)} + \text{Cl}_2\text{(g)} \overset{\text{light}}{\longrightarrow} \text{CH}_3\text{Cl (g)} + \text{HCl(g)}\)
∆H = 58 + 105 – 85 – 103
= –25 kcal/mol
Top Questions on Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Arrange the following in decreasing order of the number of molecules contained in: (A) 16 g of O$_2$, (B) 16 g of CO$_2$, (C) 16 g of CO, (D) 16 g of H$_2$
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- The total number of sigma bonds in P$_4$O$_{10}$ is:
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Ionic character of the covalent bonds in the compounds Cl2, HCl, NaCl, NaF follows the order
- IIT JAM BT - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- The N–O bond order in [NO]− is _______
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Zn–C bond polarity in the compounds below

follows the order- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
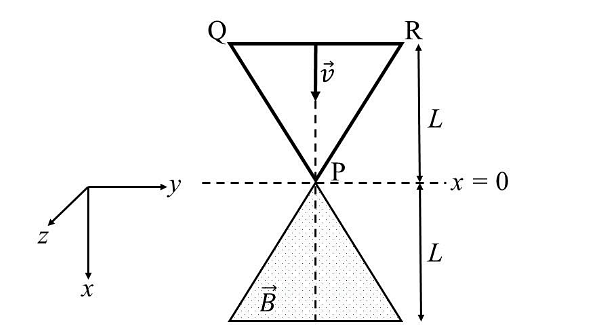
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability



