Leaching of gold with dilute aqueous solution of NaCN in presence of oxygen gives complex [A], which on reaction with zinc forms the elemental gold and another complex [B]. [A] and [B], respectively are :
- \([Au(CN)_4]^–\) and \([Zn(CN)_2 (OH)_2]^{2-}\)
- \([Au(CN)_2]^–\) and \([Zn (OH)_4]^{2-}\)
- \([Au(CN)_2]^–\) and \([Zn (CN)_4]^{2-}\)
- \([Au(CN)_4]^{2-}\) and \([Zn (CN)_6]^{4-}\)
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
In the metallurgy of gold
\(4Au + 8CN^– + 2H_2O + O_2 → 4[Au(CN)_2]^– + 4OH^–\)
\(2[Au(CN)_2]^– + Zn → [Zn(CN)_4]^{2–} + 2Au\)
So, the correct option is (C): \([Au(CN)_2]^–\) and \([Zn (CN)_4]^{2-}\)
Top Questions on Concentration of ores
- Given below are two statements:
Statement I : In froth floatation method a rotating paddle agitates the mixture to drive air out of it.
Statement II : Iron pyrites are generally avoided for extraction of iron due to environmental reasons.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- Ferric oxide in blast furnace's upper half is mainly reduced by:
- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- Extraction of which one of the following metals involves concentration of the ore by leaching?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- The methods NOT involved in concentration of ore are
A Liquation
B Leaching
C Electrolysis
D Hydraulic washing
E Froth floatation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
- Match List-I with List-II.
List-I
List-II
(A) Aluminium (I) Calamine (B) Iron (II) Bauxite (C) Copper (III) Malachite (D) Zinc (IV) Siderite
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Chemistry
- Concentration of ores
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Let \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}, \quad \vec{b} = -\hat{i} - 8\hat{j} + 2\hat{k}, \quad \text{and} \quad \vec{c} = 4\hat{i} + c_2\hat{j} + c_3\hat{k} \]be three vectors such that \[\vec{b} \times \vec{a} = \vec{c} \times \vec{a}.\]If the angle between the vector $\vec{c}$ and the vector $3\hat{i} + 4\hat{j} + \hat{k}$ is $\theta$, then the greatest integer less than or equal to $\tan^2 \theta$ is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- 10 mL of gaseous hydrocarbon on combustion gives 40 mL of CO\(_2\)(g) and 50 mL of water vapour. The total number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon is ______ .
- JEE Main - 2024
- Hydrocarbons
- If each term of a geometric progression \( a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots \) with \( a_1 = \frac{1}{8} \) and \( a_2 \neq a_1 \), is the arithmetic mean of the next two terms and \( S_n = a_1 + a_2 + \dots + a_n \), then \( S_{20} - S_{18} \) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Arithmetic Mean
A body of mass 1000 kg is moving horizontally with a velocity of 6 m/s. If 200 kg extra mass is added, the final velocity (in m/s) is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- speed and velocity
- $\textbf{Choose the correct statements about the hydrides of group 15 elements.}$
A. The stability of the hydrides decreases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 > \text{PH}_3 > \text{AsH}_3 > \text{SbH}_3 > \text{BiH}_3\)
B. The reducing ability of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
C. Among the hydrides, \(\text{NH}_3\) is a strong reducing agent while \(\text{BiH}_3\) is a mild reducing agent.
D. The basicity of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
Choose the most appropriate from the option given below:- JEE Main - 2024
- p -Block Elements
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
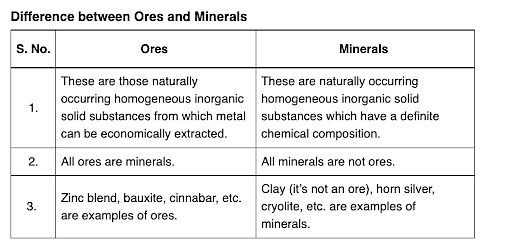
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal



