In the circuit shown in the figure, the capacitor is initially uncharged and the key K is initially open in this condition, a current of 1 A flows through the 1 Ω resistor. The key is closed at a time t=t0. Choose the correct options(given \(e^{-1}=0.36\))
- R=3Ω
- Before t=t0, i1-2A
- At t=t0+7.2μ sec. current in the capacitor =0.6A
- At t→∞, charge on the capacitor is 12μC
The Correct Option is A, B, C, D
Solution and Explanation

\(\frac{x-5}{1}\Rightarrow\,\,x=+6\,,\,i_1=volt,\frac{6-0}{3}=2A\)
R=\(\frac{15-6}{3}\)=3\(\Omega\)
after switching on :  \(\Rightarrow\)
\(\Rightarrow\) 
\(\varepsilon_{eq}=\frac{\frac{15}{3}+\frac{5}{1}+\frac{0}{3}}{\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{1}+\frac{1}{3}}=6\,volt\)
\(\frac{1}{r_{eq}}=\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{1}+\frac{1}{3}\Rightarrow\frac{3}{5}\Omega\)
Steady-state charge on the capacitor
q=CV=(\(2\mu\))\((6)=12\mu c\)
\(R_{eq}=\frac{3}{5}+3=\frac{18}{5}\Omega,\,i_{max}=\frac{\varepsilon_{eq}}{R_{eq}}=\frac{6}{\frac{18}{5}}=\frac{5}{3}A\)
\(R_{eq}C=\frac{18}{5}\times2\Omega=\frac{36}{5}\mu\,sec.\)
\(\frac{t}{R_c}=\frac{7.2}{\frac{36}{5}}\mu=1\)
\(i(t)=\frac{\varepsilon_{eq}}{R_{eq}}e^-{\frac{t}{R_{eq}C}}=\frac{5}{3}e^{-1}=\frac{5}{3}\times0.36\)
\(i=0.6A\)
At steady state, voltage across capacitor = 6 V
Therefore, Q = 6 × 2 = 12μC
So, all the options are correct.
Top Questions on Combination of capacitors

Find the equivalent capacitance across points A and B in the given electric circuit.
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Combination of capacitors
- As shown in the figure, two parallel plate capacitors having equal plate area of 200 cm2 are joined in such a way that a ≠ b. The equivalent capacitance of the combination is x ∈0 F. The value of x is_____.

- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Combination of capacitors
- A parallel plate capacitor has plate area $40\, cm ^2$ and plates separation $2\, mm$ The space between the plates is filled with a dielectric medium of a thickness $1 \,mm$ and dielectric constant $5$ The capacitance of the system is :
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Combination of capacitors
- The liquid is raising at a rate of 250\(cm^3s^{-1}\) in the container. Value of the capacitance of the container after 10 sec.? (\(\varepsilon_0=9 \times10^{12}C^2N^{-1}m^{-2}\))
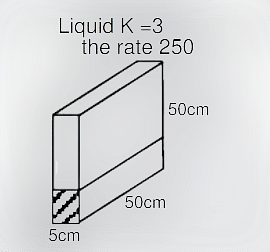
- JEE Advanced - 2023
- Physics
- Combination of capacitors
- A capacitor C1 of capacitance 5 μF is charged to a potential of 30 V using a battery. The battery is then removed and the charged capacitor is connected to an uncharged capacitor C2 of capacitance 10 μF as shown in figure. When the switch is closed charge flows between the capacitors. At equilibrium, the charge on the capacitor C2 is ____ μC.

- JEE Main - 2022
- Physics
- Combination of capacitors
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let the function \(f:[1,\infin)→\R\) be defined by
\(f(t) = \begin{cases} (-1)^{n+1}2, & \text{if } t=2n-1,n\in\N, \\ \frac{(2n+1-t)}{2}f(2n-1)+\frac{(t-(2n-1))}{2}f(2n+1) & \text{if } 2n-1<t<2n+1,n\in\N. \end{cases}\)
Define \(g(x)=\int\limits_{1}^{x}f(t)dt,x\in(1,\infin).\) Let α denote the number of solutions of the equation g(x) = 0 in the interval (1, 8] and \(β=\lim\limits_{x→1+}\frac{g(x)}{x-1}\). Then the value of α + β is equal to _____.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Integral Calculus
- A dimensionless quantity is constructed in terms of electronic charge \(e\), permittivity of free space \(\epsilon_0\) , Planck’s constant ℎ, and speed of light c. If the dimensionless quantity is written as \(e^\alpha\epsilon_0^\beta h^\gamma c^\delta\)and n is a non-zero integer, then\((\alpha, \beta,\gamma,\delta)\) is given by
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
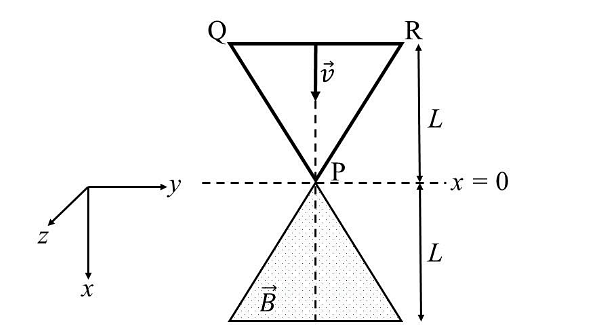
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
Concepts Used:
Capacitor
Capacitors commonly known as Condensers are passive components, similar to a resistor. In capacitors, charges are usually stored in the form of an "electrical field". Electrical and electronic circuits depend on the same which is made up of two parallel metal plates that are not connected to one another. The two plates are separated by a non-conducting insulating medium called dielectric.
Uses of Capacitors:
- DC blocking capacitors block the DC and allows only AC to certain parts of the circuit.
- These are main elements of filters.
- They possess the ability to couple a section of the circuit to another.
Types of Capacitors:
- Ceramic capacitors are created by covering two sides of their tiny ceramic disc with silver and stacking them together.
- Film Capacitors are commonly used capacitors that are made up of different sets of capacitors.
- In an electrolytic capacitor metallic anode coated with an oxidized layer used as a dielectric.
- A Paper capacitor is also known as a fixed capacitor in which paper is used as the dielectric material.
Read More: Types of Capacitors



