If (i) A=\(\begin{bmatrix} \cos\alpha & \sin\alpha\\ -\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha \end{bmatrix}\),then verify that A'A=I
(ii) A= \(\begin{bmatrix} \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha\\ -\cos \alpha & \sin\alpha \end{bmatrix}\),then verify that A'A=I
(ii) A= \(\begin{bmatrix} \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha\\ -\cos \alpha & \sin\alpha \end{bmatrix}\),then verify that A'A=I
Solution and Explanation
(i) \(A=\) \(\begin{bmatrix} \cos\alpha & \sin\alpha\\ -\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
\(\therefore A'=\) \(\begin{bmatrix} \cos\alpha & -\sin\alpha\\ \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
A'A= \(\begin{bmatrix} \cos\alpha & -\sin\alpha\\ \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha \end{bmatrix}\) \(\begin{bmatrix} \cos\alpha & \sin\alpha\\ -\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
= \(\begin{bmatrix} (\cos\alpha) (cos\alpha) + (- \sin\alpha)( -\sin\alpha) & (\cos\alpha)(\sin\alpha)+(-\sin\alpha)(\cos\alpha)\\ (\sin\alpha)(\cos\alpha)+(\cos\alpha)(-\sin\alpha) & (\sin\alpha)(\sin\alpha)+(\cos\alpha)(\cos\alpha) \end{bmatrix}\)
= \(\begin{bmatrix} \cos^2α+\sin^2α & \sinα\cosα-\sinα\cosα\\ \ sinα\cosα-\sinα\cosα & \sin^2α+\cos^2α \end{bmatrix}\)
= \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}= I\)
Hence we verified that: A'A=I
(ii) \(\begin{bmatrix} \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha\\ -\cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
so A'= \(\begin{bmatrix} \sin\alpha & -\cos\alpha\\ \cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
A'A= \(\begin{bmatrix} \sin\alpha & -\cos\alpha\\ \cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)\(\begin{bmatrix} \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha\\ -\cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
= \(\begin{bmatrix} (\sin\alpha)(\sin\alpha)+(-\cos\alpha)(-\cos\alpha) & (\sin\alpha)(\cos\alpha)+(-\cos\alpha)(\sin\alpha)\\ (\cos\alpha)(\sin\alpha)+(\sin\alpha)(-\cos\alpha) & (\cos\alpha)(\cos\alpha)+(\sin\alpha)(\sin\alpha) \end{bmatrix}\)
= \(\begin{bmatrix} \sin^2α\cos^2α & \sinα\cosα-\sin\alpha\cos\alpha & \\ \sinα\cosα-\sinα\cosα & \cos^2α+\sin^2α \end{bmatrix}\)
= \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}= I\)
Hence we verified that: \(A'A=I\)
Top Questions on Matrices
- If the system of linear equations
\( x - 2y + z = -4 \)
\( 2x + \alpha y + 3z = 5 \)
\( 3x - y + \beta z = 3 \)
has infinitely many solutions, then \( 12\alpha + 13\beta \) is equal to - Let \( A \) be a \( 3 \times 3 \) real matrix such that**
\(A \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = 2 \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix}, \quad A \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 1 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = 4 \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix}, \quad A \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix} = 2 \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix}.\)
Then, the system \( (A - 3I) \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} \) has - Consider the 4 × 4 matrix
\(M = \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\)
If ai,j denotes the (i, j)th entry of M-1 , then a4,1 equals __________ (rounded off to two decimal places). - If \( A = \begin{bmatrix} 5 & 1 \\ -2 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \) and \( B^T = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 10 \\ -2 & -1 \end{bmatrix} \), then the matrix \( AB \) is:
- Let \( A \) be a \( 2 \times 2 \) real matrix and \( I \) be the identity matrix of order 2. If the roots of the equation \[ |A - xI| = 0 \] be \( -1 \) and \( 3 \), then the sum of the diagonal elements of the matrix \( A^2 \) is .....
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
What is the Planning Process?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2023
- Planning process steps
Evaluate \(\begin{vmatrix} cos\alpha cos\beta &cos\alpha sin\beta &-sin\alpha \\ -sin\beta&cos\beta &0 \\ sin\alpha cos\beta&sin\alpha\sin\beta &cos\alpha \end{vmatrix}\)
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2021
- Determinants
- Find the vector and the cartesian equations of the lines that pass through the origin and(5,-2,3).
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2021
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Would you agree that promises made to poor children are rarely kept? Why do you think this happens in the incidents narrated in the text?
- CBSE CLASS XII
- Lost Spring
- Why did Sophie wriggle when Geoff told her father that she had met Danny Casey?
- CBSE CLASS XII
- Going Places
Concepts Used:
Transpose of a Matrix
The matrix acquired by interchanging the rows and columns of the parent matrix is called the Transpose matrix. The transpose matrix is also defined as - “A Matrix which is formed by transposing all the rows of a given matrix into columns and vice-versa.”
The transpose matrix of A is represented by A’. It can be better understood by the given example:

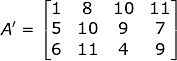
Now, in Matrix A, the number of rows was 4 and the number of columns was 3 but, on taking the transpose of A we acquired A’ having 3 rows and 4 columns. Consequently, the vertical Matrix gets converted into Horizontal Matrix.
Hence, we can say if the matrix before transposing was a vertical matrix, it will be transposed to a horizontal matrix and vice-versa.
Read More: Transpose of a Matrix



