Explain why cations are smaller and anions larger in radii than their parent atoms?
Solution and Explanation
A cation has a fewer number of electrons than its parent atom, while its nuclear charge remains the same. As a result, the attraction of electrons to the nucleus is more in a cation than in its parent atom. Therefore, a cation is smaller in size than its parent atom.
On the other hand, an anion has one or more electrons than its parent atom, resulting in an increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in the effective nuclear charge. As a result, the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus is more in anions than in it's the parent atom. Hence, an anion is larger in radius than its parent atom.
Top Questions on Periodic Trends In Properties Of Elements
- The CORRECT order of acidity of the following compounds is
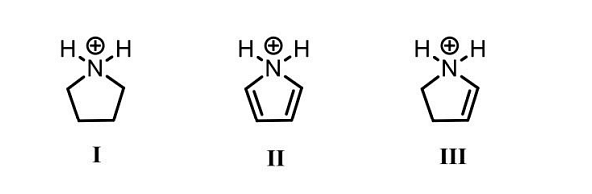
- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Periodic Trends In Properties Of Elements
- The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the shell with n = 2 is______ (in integer). (Given: n = principal quantum number)
- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Periodic Trends In Properties Of Elements
- The CORRECT order of acidity of the following compounds is

- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Periodic Trends In Properties Of Elements
- The CORRECT order of electronegativity is
- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Periodic Trends In Properties Of Elements
- The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the shell with n = 2 is______ (in integer). (Given: n = principal quantum number)
- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Periodic Trends In Properties Of Elements
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- There is mention of three communities in the story: the Marathas, the Mughals, the Anglo-Indians. Which language do you think they used within their communities and while speaking to the other groups?
- CBSE Class XI
- The adventure
- Take one flower of the family Solanaceae and write its semi-technical description. Also draw their floral diagram.
- CBSE Class XI
- The Flower
- Find the derivative of x2 – 2 at x = 10
- CBSE Class XI
- Derivatives
Figures 9.20(a) and (b) refer to the steady flow of a (non-viscous) liquid. Which of the two figures is incorrect ? Why ?

- CBSE Class XI
- Pressure
Figure 8.9 shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young’s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?

- CBSE Class XI
- Stress-strain curve
Concepts Used:
Trends in Periodic Table
The following trend in periodic properties of elements is observed:
Atomic size Trends:
The distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an atom is known as the atomic radius. In a group the atomic size increases due to the addition of shells as we move from one period to another. Across a period the atomic size decreases as the number of shells remain the same while the nuclear charge increases.
Metallic character Trends:
The elements which lose electrons to form cations are known as metals. Metallic character increases as we move down the group because the atomic size increases which lead to easy loss of electrons. On the other hand, it decreases across a period as we move from left to right.
Non-metallic character Trends:
The elements which have a tendency to gain electrons are known as non-metals. The tendency to gain electrons increases on moving across a period due to an increase in the nuclear charge and decrease in the atomic size. Hence, non-metallic character increases across a period.
Ionization potential Trends:
Ionization potential is defined as the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of a gaseous atom and convert it into a positively charged gaseous ion. The periodic properties in terms of ionization potential increase because the atomic size decreases across a period due to increase in the nuclear charge.
Melting Point Trends:
The melting point of an element is basically the energy required to change the state of an element from its solid state to its liquid state. Which essentially implies breaking a few bonds. Thus, higher the stronger the bond between the atoms, higher will be the melting point.



