An infinitely long conductor PQR is bent to form a right angle as shown in figure. A current I flows through PQR. The magnetic field due to this current at the point M is $H_1$. Now, another infinitely long straight conductor QS is connected at Q, so that current is I/2 in QR as well as in QS, the current in PQ remaining unchanged. The magnetic field at M is now $H_2.$ The ratio $H_1 /H_2$ is given by
- 44563
- 1
- 44595
- 2
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
But magnetic field at M due to QR = 0
$\therefore$ Magnetic field at M due to PQ (or due to current 1 in PQ)$=H_1$
Now $H_2$ = Magnetic field at M due to PQ (current I)
$\, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, $+ magnetic field at M due to QS (current 1/2)
$\, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, $+ magnetic field at M due to QR
$\, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, =H_1+\frac{H_1}{2}+0=\frac{3}{2}H_1$
$\, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \frac{H_1}{H_2}=\frac{2}{3}$
NOTE Magnetic field at any point lying on the current carrying straight conductor is zero.
Top Questions on Moving charges and magnetism
- Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A freely suspended needle of a magnetic compass comes to rest along the geographic
- AP POLYCET - 2024
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- Two charged particles, having same kinetic energy, are allowed to pass through a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of motion If the ratio of radii of their circular paths is $6: 5$ and their respective masses ratio is $9: 4$ Then, the ratio of their charges will be :
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- In a moving coil galvanometer if the number of turns increases by 25%, then change in voltage sensitivity is?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A charge particle of $2 \,\mu C$ accelerated by a potential difference of $100\, V$ enters a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude $4 \,mT$ at right angle to the direction of field The charge particle completes semicircle of radius $3 \,cm$ inside magnetic field The mass of the charge particle is _______ $\times 10^{-18} kg$
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
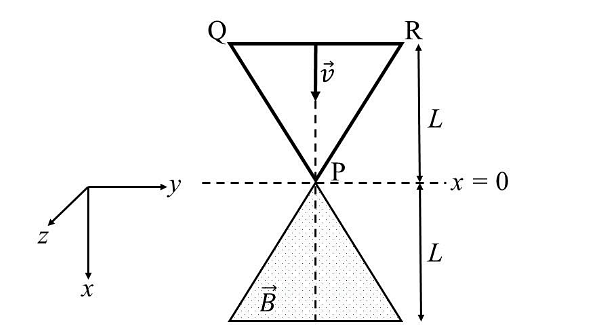
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
- A particle of mass 𝑚 is under the influence of the gravitational field of a body of mass 𝑀 (≫ 𝑚). The particle is moving in a circular orbit of radius \(𝑟_0\) with time period \(𝑇_0\) around the mass 𝑀. Then, the particle is subjected to an additional central force, corresponding to the potential energy 𝑉c(𝑟) = 𝑚𝛼/𝑟 3 , where 𝛼 is a positive constant of suitable dimensions and 𝑟 is the distance from the center of the orbit. If the particle moves in the same circular orbit of radius\( 𝑟_0\) in the combined gravitational potential due to 𝑀 and 𝑉c(𝑟), but with a new time period \(𝑇_1\), then\( (𝑇_1^2 − 𝑇_0^ 2 )/𝑇_1^ 2\) is given by [𝐺 is the gravitational constant.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Centripetal forces
Concepts Used:
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Moving charges generate an electric field and the rate of flow of charge is known as current. This is the basic concept in Electrostatics. Another important concept related to moving electric charges is the magnetic effect of current. Magnetism is caused by the current.
Magnetism:
- The relationship between a Moving Charge and Magnetism is that Magnetism is produced by the movement of charges.
- And Magnetism is a property that is displayed by Magnets and produced by moving charges, which results in objects being attracted or pushed away.
Magnetic Field:
Region in space around a magnet where the Magnet has its Magnetic effect is called the Magnetic field of the Magnet. Let us suppose that there is a point charge q (moving with a velocity v and, located at r at a given time t) in presence of both the electric field E (r) and the magnetic field B (r). The force on an electric charge q due to both of them can be written as,
F = q [ E (r) + v × B (r)] ≡ EElectric +Fmagnetic
This force was based on the extensive experiments of Ampere and others. It is called the Lorentz force.



