An elliptical cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge q is placed at the centre of the cavity. The points A and B are on the cavity surface as shown in the figure.then
- electric field near A in the cavity = electric field near B in the cavity
- charge density at A = charge density at B
- potential at A = potential at B
- total electric field flux through the surface of the cavity is $q/ \varepsilon_0$
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
Under electrostatic condition, all points lying on the conductor are at same potential. Therefore, potential at A = potential at B. Hence, option (c) is correct. From Gauss theorem, total flux through the surface of the cavity will be \(\frac{q}{\epsilon_0}\)
NOTE Instead of an elliptical cavity, if it would had been a spherical cavity then options (a) and (b) were also correct.
Approach Solution -2
Option D is correct. The total electric field flux passing through the surface of the cavity equals \(\frac{q}{\epsilon_0}\).
Under electrostatic conditions, all points on the conductor share the same potential. Hence, the potential at point A equals the potential at point B.
According to Gauss's theorem, the total flux passing through the surface of the cavity is \(\frac{q}{\epsilon_0}\).
Top Questions on Electric charges and fields
- Two particles each of mass \(2\) kg are places as shown in \(x→ y\) plane. If the distance of centre of mass from origin is \(\frac{4\sqrt 2}{x}\) find \(x\) :
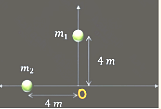
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
- A uniform electric field of $10 N / C$ is created between two parallel charged plates (as shown in figure) An electron enters the field symmetrically between the plates with a kinetic energy $05 eV$ The length of each plate is $10 cm$ The angle $(\theta)$ of deviation of the path of electron as it comes out of the field is ___ (in degree)

- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
- Electric field in a certain region is given by $\overrightarrow{ E }=\left(\frac{ A }{x^2} \hat{i}+\frac{ B }{y^3} \hat{j}\right)$ The $SI$ unit of $A$ and $B$ are :
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
Given below are two statements : One is labelled as Assertion $A$ and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A : Two metallic spheres are charged to the same potential One of them is hollow and another is solid, and both have the same radii Solid sphere will have lower charge than the hollow one
Reason R : Capacitance of metallic spheres depend on the radii of spheres
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belows- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
- A 10 μC charge is divided into two equal parts and kept at 1 cm distance. Find repulsion between charges?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let the function \(f:[1,\infin)→\R\) be defined by
\(f(t) = \begin{cases} (-1)^{n+1}2, & \text{if } t=2n-1,n\in\N, \\ \frac{(2n+1-t)}{2}f(2n-1)+\frac{(t-(2n-1))}{2}f(2n+1) & \text{if } 2n-1<t<2n+1,n\in\N. \end{cases}\)
Define \(g(x)=\int\limits_{1}^{x}f(t)dt,x\in(1,\infin).\) Let α denote the number of solutions of the equation g(x) = 0 in the interval (1, 8] and \(β=\lim\limits_{x→1+}\frac{g(x)}{x-1}\). Then the value of α + β is equal to _____.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Integral Calculus
- A dimensionless quantity is constructed in terms of electronic charge \(e\), permittivity of free space \(\epsilon_0\) , Planck’s constant ℎ, and speed of light c. If the dimensionless quantity is written as \(e^\alpha\epsilon_0^\beta h^\gamma c^\delta\)and n is a non-zero integer, then\((\alpha, \beta,\gamma,\delta)\) is given by
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
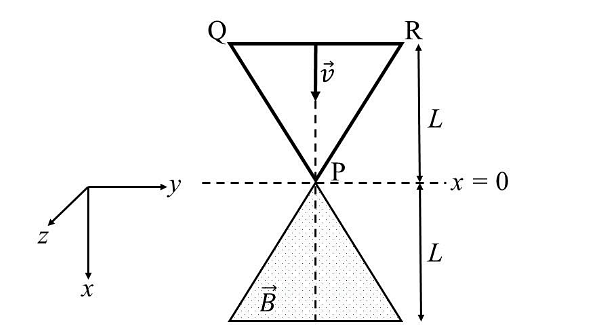
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
Concepts Used:
Electric charges and field
What is Electric Charge
It is the property of subatomic particles that experiences a force when put in an electric and magnetic field.
What is Electric Field
It is a property associated with each point in space when charge is present in any form. The magnitude and direction of the electric field are expressed by E, called electric field strength or electric field intensity.
Electric charges are of two types: Positive and Negative. It is commonly carried by charge carriers protons and electrons.
Properties of Electric Charge
Various properties of charge include the following :-
- Additivity of Electric Charge
- Conservation of Electric Charge
- Quantization of Electric Charge
Types of electric charge
Two kinds of electric charges are there :-
Negative Charge - When an object has a negative charge it means that it has more electrons than protons.
Positive Charge - When an object has a positive charge it means that it has more protons than electrons.
When there is an identical number of positive and negative charges, the negative and positive charges would cancel out each other and the object would become neutral.



