Question:
A solid slab of thickness \( H1 \) is initially at a uniform temperature \( T0 \). At time \( t = 0 \), the temperature of the top surface at \( y = H1 \) is increased to \( T1 \), while the bottom surface at \( y = 0 \) is maintained at \( T0 \) for \( t \geq 0 \). Assume heat transfer occurs only in the \( y \)-direction, and all thermal properties of the slab are constant. The time required for the temperature at \( y = \frac{H1}{2} \) to reach 99% of its final steady value is \( T1 \). If the thickness of the slab is doubled to \( H2 = 2H1 \), and the time required for the temperature at \( y = \frac{H2}{2} \) to reach 99% of its final steady value is \( T2 \), then \( \frac{T2}{T1} \) is .
A solid slab of thickness \( H1 \) is initially at a uniform temperature \( T0 \). At time \( t = 0 \), the temperature of the top surface at \( y = H1 \) is increased to \( T1 \), while the bottom surface at \( y = 0 \) is maintained at \( T0 \) for \( t \geq 0 \). Assume heat transfer occurs only in the \( y \)-direction, and all thermal properties of the slab are constant. The time required for the temperature at \( y = \frac{H1}{2} \) to reach 99% of its final steady value is \( T1 \). If the thickness of the slab is doubled to \( H2 = 2H1 \), and the time required for the temperature at \( y = \frac{H2}{2} \) to reach 99% of its final steady value is \( T2 \), then \( \frac{T2}{T1} \) is .
Updated On: Nov 19, 2024
- 2
- \(\frac14\)
- 4
- \(\frac12\)
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The correct option is (C) :4
Was this answer helpful?
0
1
Top Questions on Heat Transfer
- In given circuit, reading of voltmeter is 1 V, then resistance of
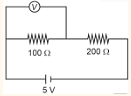
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Heat Transfer
- Ice at temperature –10°C is converted to steam at 100°C, the curve plotted between temperature (T) and time (t) when it is being heated by constant power source is
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Heat Transfer
- The temperatures of two large parallel plates of equal emissivity are 900 K and 300 K. A reflection radiation shield of low emissivity and negligible conductive resistance is placed parallelly between them. The steady-state temperature of the shield, in K, is
- GATE CH - 2024
- Heat Transfer
- Heat Transfer
- The opposite faces of a metal slab of thickness 5 cm and thermal conductivity 400 W m\(^{-1}\) °C\(^{-1}\) are maintained at 500 °C and 200 °C. The area of each face is 0.02 m\(^2\). Assume that the heat transfer is steady and occurs only in the direction perpendicular to the faces. The magnitude of the heat transfer rate, in kW, rounded off to the nearest integer, is ____.
- GATE CH - 2024
- Heat Transfer
- Heat Transfer
- Hot oil at \( 110^\circ \)C heats water from \( 30^\circ \)C to \( 70^\circ \)C in a counter-current double-pipe heat exchanger. The flow rates of water and oil are \( 50 \) kgmin\(^{-1}\) and \( 100 \) kgmin\(^{-1}\), respectively, and their specific heat capacities are \( 4.2 \) kJ kg\(^{-1}\)°C\(^{-1}\) and \( 2.0 \) kJ kg\(^{-1}\)°C\(^{-1}\), respectively. Assume the heat exchanger is at steady state. If the overall heat transfer coefficient is \( 200 \) W m\(^{-2}\)°C\(^{-1}\), the heat transfer area \( A \) in m\(^{2}\) is:
- GATE CH - 2024
- Heat Transfer
- Heat Transfer
View More Questions
Questions Asked in GATE CH exam
- Methane combusts with air in a furnace according to the reaction \( \text{CH}_4 + 2\text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{CO}_2 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \). The heat of reaction \( \Delta H_{\text{rxn}} \) is -880 kJ per mol of CH4 and is assumed constant. The furnace is well-insulated, and no side reactions occur. All components behave as ideal gases with a constant molar heat capacity of 44 J mol\(^{-1}\) °C\(^{-1}\). Air is composed of 20 mol% O2 and 80 mol% N2. The air-fuel mixture enters the furnace at 50°C. The methane conversion \( X \) varies with the air-to-methane mole ratio \( r \) as \( X = 1 - 0.1 e^{-2(r-r_s)} \) with \( 0.9 r_s \leq r \leq 1.1 r_s \), where \( r_s \) is the stoichiometric air-to-methane mole ratio. For \( r = 1.05 r_s \), the exit flue gas temperature in °C, rounded off to 1 decimal place, is _____.
- GATE CH - 2024
- Heat of reaction
- Consider a vapour-liquid mixture of components A and B that obeys Raoult's law. The vapour pressure of A is half that of B. The vapour phase concentrations of A and B are 3 mol m\(^{-3}\) and 6 mol m\(^{-3}\), respectively. At equilibrium, the ratio of the liquid phase concentration of A to that of B is:
- GATE CH - 2024
- Phase equilibria
- A simple distillation column separates a binary mixture of A and B. The relative volatility of A with respect to B is 2. The steady-state composition of A in the vapour leaving the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trays in the rectifying section are 94, 90 and 85 mol%, respectively. For ideal trays and constant molal overflow, the reflux-to-distillate ratio is
- GATE CH - 2024
- Design and operation of equipment for distillation
- Two parallel first-order liquid phase reactions \( A \xrightarrow{k_1} B \) and \( A \xrightarrow{k_2} C \) are carried out in a well-mixed isothermal batch reactor. The initial concentration of A in the reactor is \( 1 \) kmol m\(^{-3}\), while that of B and C is zero. After 2 hours, the concentration of A reduces to half its initial value, and the concentration of B is twice that of C. The rate constants \( k_1 \) and \( k_2 \), in h\(^{-1}\), are, respectively,
- GATE CH - 2024
- Kinetics of homogeneous reactions
- A homogeneous azeotropic distillation process separates an azeotropic AB binary feed using a heavy entrainer, E, as shown in the figure. The loss of E in the two product streams is negligible so that E circulates around the process in a closed- circuit. For a distillation column with fully specified feed(s), given operating pressure, a single distillate stream and a single bottoms stream, the steady-state degrees of freedom equals 2. For the process in the figure with a fully specified AB feed stream and given column operating pressures, the steady-state degrees of freedom equals

- GATE CH - 2024
- Complex number
View More Questions



